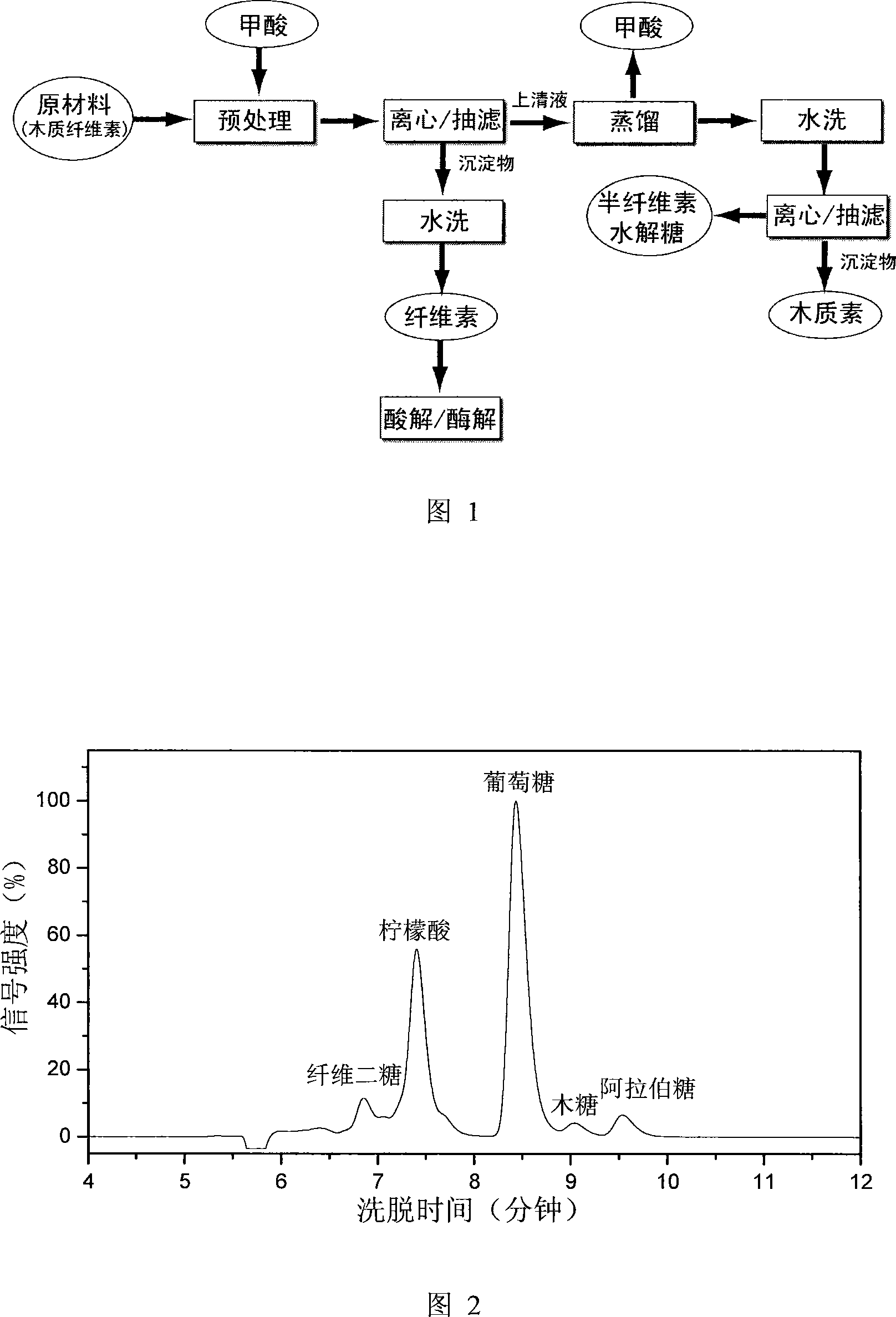
Method for separating lignocellulose-containing biomass with methanoic acid
A technology of lignocellulose and lignin, which is applied in the field of separating lignocellulose-containing biomass into lignin, separating lignocellulose-containing biomass, hemicellulose and cellulose components, and can solve the problem of increased operational difficulty etc. to save energy, achieve solvent recovery, and achieve high concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
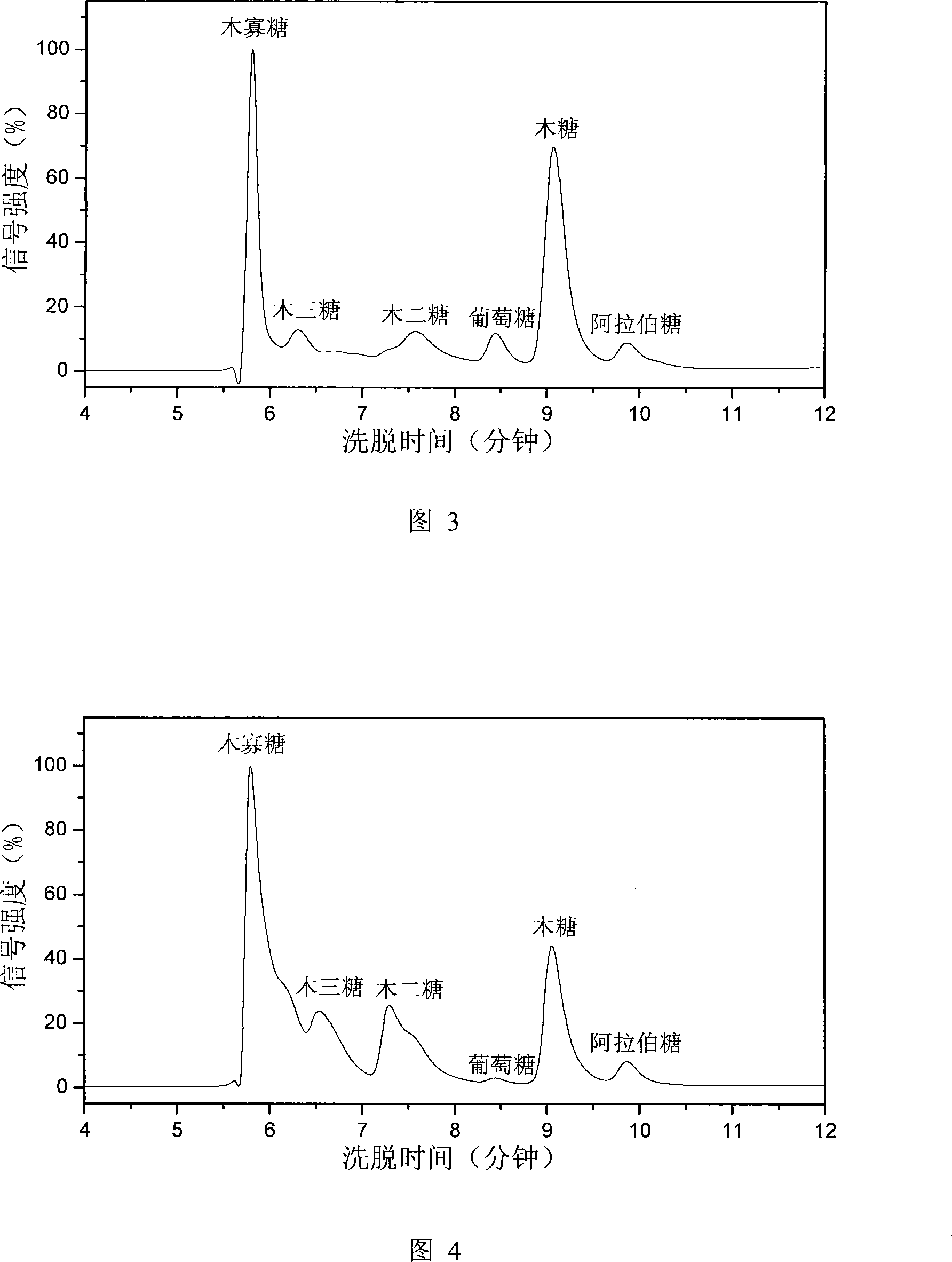
[0030] The corn stalks are crushed, and the material of the stalks with a particle size of 20-80 meshes is composed of 35.6% cellulose, 21.6% hemicellulose and 18.1% lignin. Weigh 1000g of 20-80 mesh straw, add 10L formic acid (88%) and 100mL hydrochloric acid (37%) into the pretreatment bottle, start the constant temperature water bath, keep the reaction temperature constant at 65°C, the oscillation speed at 150rpm, and treat at normal pressure 3h, the sample bottle was taken out, placed in a low-temperature water bath, and the reaction slurry was subjected to solid-liquid separation (vortex centrifugation or suction filtration), wherein, the solid components were washed with water and then dried to obtain a total of 431g of materials, including 75.1% cellulose, The retention rate reaches 91%. Under the action of cellulase (30FPU / g glycoside), the material is hydrolyzed for 24h in pH4.8 citric acid buffer solution at 50°C, and its hydrolyzate is measured by HPLC (as shown in F...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The corn cob is crushed, wherein the core material with a particle diameter of 20-80 meshes is composed of 35.9% cellulose, 35.2% hemicellulose and 18.1% lignin. Weigh 100g of 20-80 mesh straw, add 1L of formic acid (88%) and 5mL of hydrochloric acid (37%) into the pretreatment bottle, start the constant temperature water bath, keep the reaction temperature constant at 55°C, the oscillation speed at 150rpm, and treat at normal pressure 3h, the sample bottle was taken out, placed in a low-temperature water bath, and the reaction slurry was subjected to solid-liquid separation (vortex centrifugation or suction filtration), wherein, the solid component was washed with water and then dried to obtain a total of 45.8g of material, which contained cellulose 68.5 %, the retention rate reaches 87%. Under the action of cellulase (30FPU / g glycoside), the material is hydrolyzed in pH4.8 citric acid buffer solution at 50°C for 24 hours, and the cellulose conversion rate can reach 72%...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com