Method for modifying functional plants polysaccharide
A modification method, plant polysaccharide technology, applied in the field of functional plant polysaccharide modification, can solve the problems of low toxicity and low transfection efficiency, and achieve high recovery rate and high gene transfection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1) Polysaccharide extraction and purification
[0033] Take 500 grams of any of biologically active medicinal plants, such as shiitake mushrooms, scutellaria baicalensis, ganoderma lucidum, rice kernels, cactus, versicolor versicolor, and wolfberry, add 3 times the amount of water and boil for 3 hours, and add the obtained solution to 95% ethanol solution after concentration , stirring while adding, so that the final ethanol concentration was 65%, after centrifugation, the resulting precipitate was freeze-dried to obtain 22.5 grams of crude polysaccharide.
[0034] Take 10 grams of crude polysaccharide, dissolve it in 200 ml of aqueous solution, put it into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 15,000 and dialyze for 48 hours after dissolving, take out the solution in the bag, add 2 grams of activated carbon for decolorization, filter, and continue to use the filtrate with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 15,000 After dialysis for 48 hours, the solution in ...
Embodiment 2
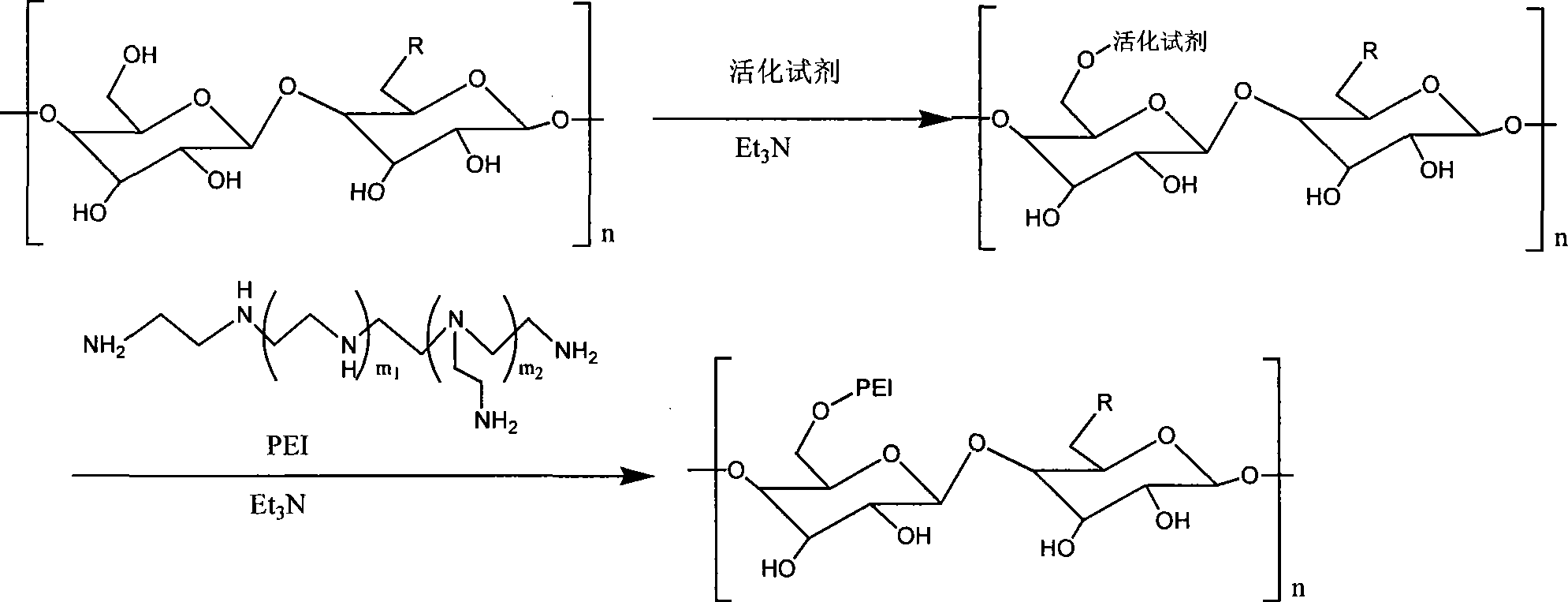
[0042] Take 0.5 g of the purified Scutellaria baicalensis polysaccharide in Example 1 and dissolve it in 15 ml of phosphate buffer. Take 0.2 g of N,N'-disuccinimidyl sulfate, dissolve it in 10 ml of dichloromethane, and slowly add it to the polysaccharide solution under the protection of nitrogen and avoiding light, and stir while adding. After the internal addition is completed, react in the dark for 90 minutes after the addition.
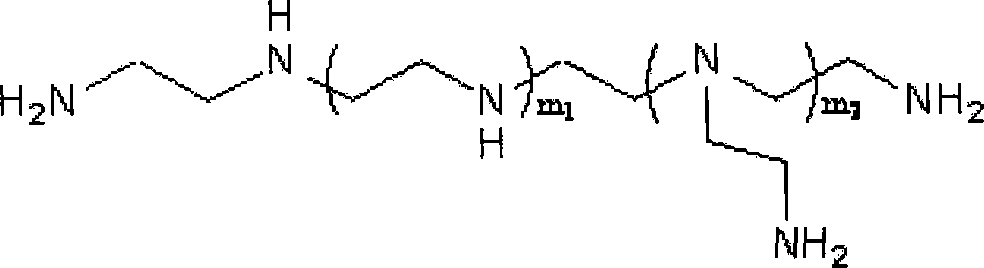
[0043] Take 0.6 g of polyethyleneimine with a molecular weight of 1200, dissolve it in 15 ml of phosphate buffer solution, add 0.2 ml of triethylamine as a catalyst, add it into the activated polysaccharide solution under the protection of light and nitrogen, and stir while adding, Complete the addition within 150 minutes, and react in the dark for 150 minutes after the addition.
[0044] The completed solution was put into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut off of 15,000, dialyzed for 48 hours, and the solution in the bag was freeze-drie...
Embodiment 3
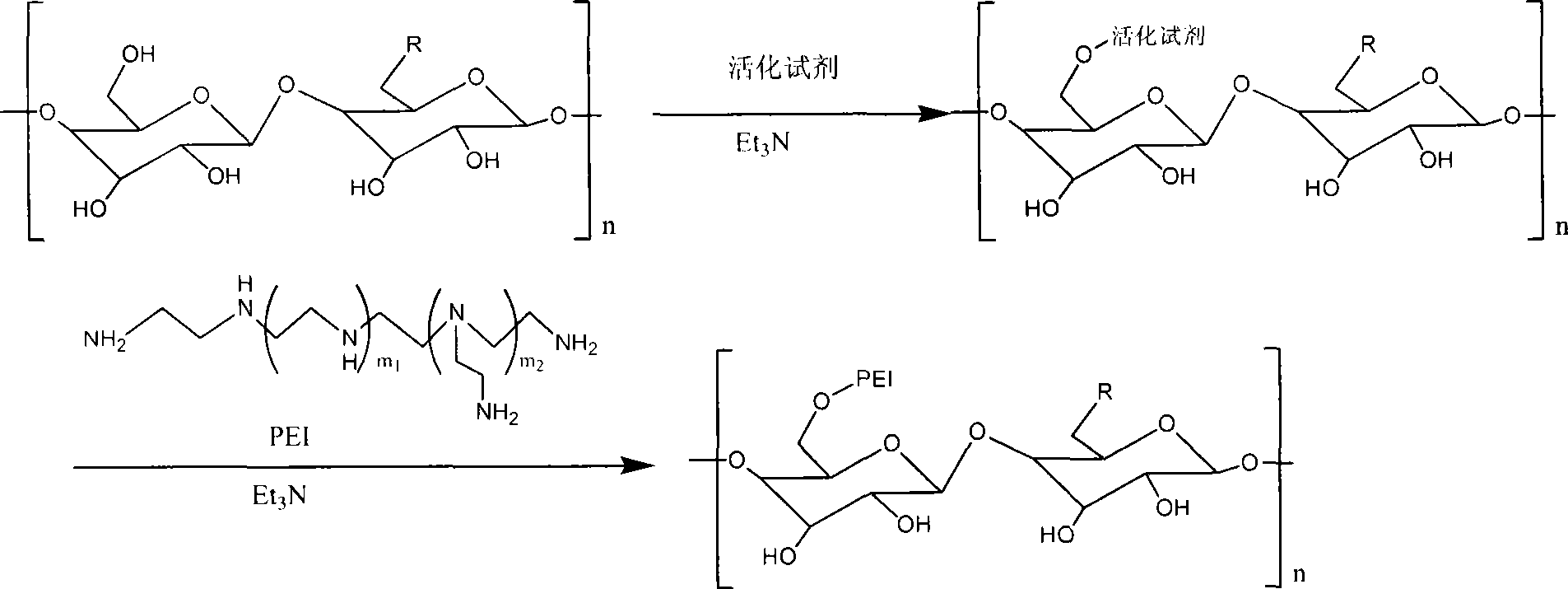
[0047] Take 0.1 g of Polysaccharide polysaccharide purified in Example 1 and dissolve it in 5 ml of phosphate buffer. Take 0.3 g of benzotriazole carbonate, dissolve it in 10 ml of dichloromethane, and slowly add it to the polysaccharide solution under nitrogen protection and dark conditions, do not add while stirring, add it within 100 minutes, after the addition is complete React for 80 minutes.
[0048] Take 0.4 g of polyethyleneimine with a molecular weight of 2000, dissolve it in 10 ml of phosphate buffer solution, add 0.3 ml of triethylamine as a catalyst, add it into the activated polysaccharide solution under the protection of light and nitrogen, and stir while adding, Complete the addition within 130 minutes, and react in the dark for 130 minutes after the addition.
[0049] The solution that completed the reaction was put into a 15000 dialysis bag, dialyzed for 48 hours, and the solution in the bag was freeze-dried.
[0050] Through gel chromatographic analysis, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com