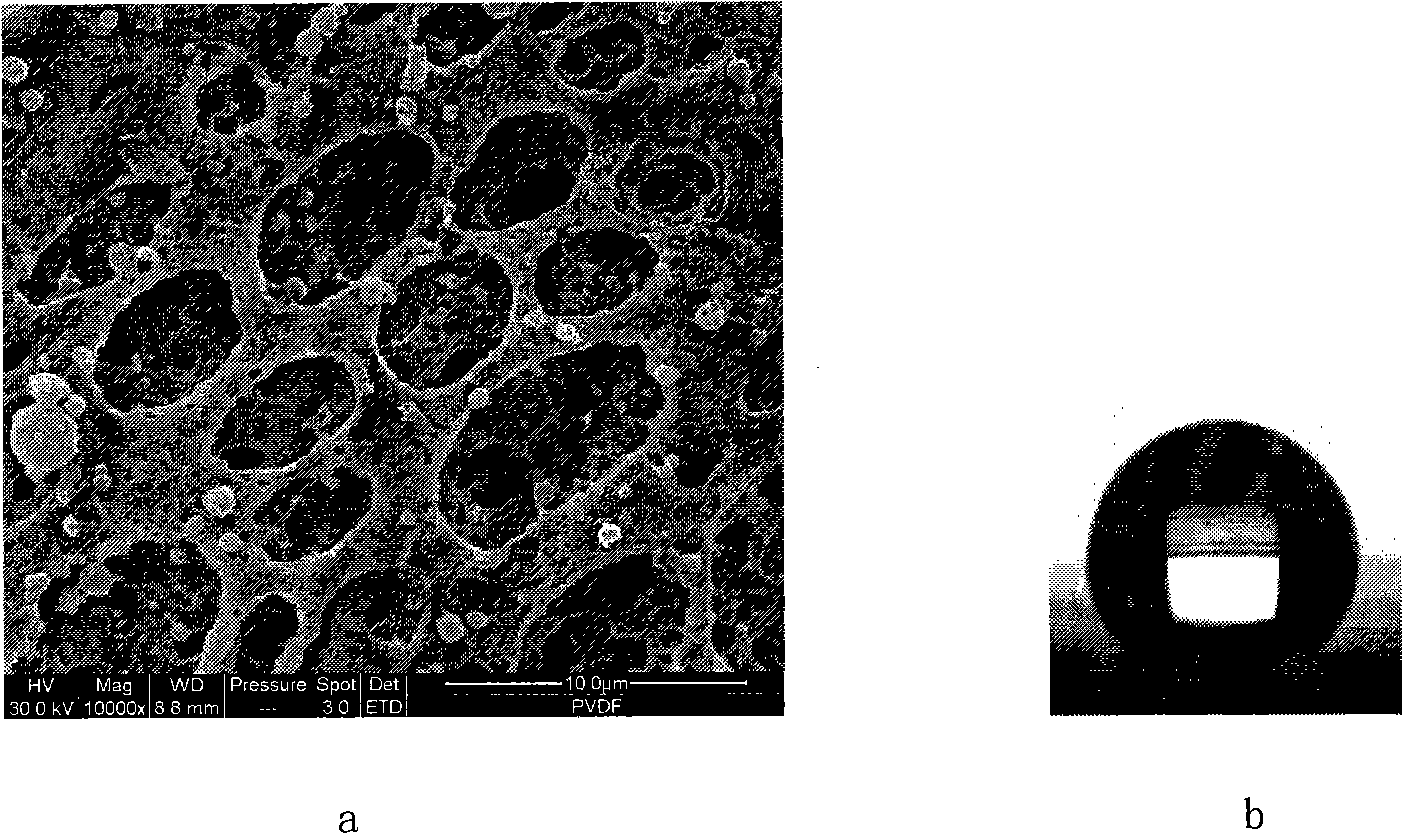
Preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride dewatering microporous film
A polyvinylidene fluoride and microporous membrane technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of strong hydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride microporous membranes, can solve the problems of non-penetrating membrane pores, accelerated film formation speed, high retention rate, etc. Effects of film formation speed, improved hydrophobicity, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hydrophobic Microporous Membrane Prepared by Gel in Alkali Vapor and Then in Acid
[0027] 1) The total amount of casting solution is 100g. First, mix PVDF (10wt%), DMAC (70wt%), LiCl (4wt%), tetraethoxysilane TEOS (16wt%) and stir for 6 hours with a magnetic stirrer , to obtain a clarified casting solution, and then place it in a 50°C oven for 48 hours to fully mature and defoam;
[0028] 2) Scrape the casting solution obtained in step 1) on a glass plate into a 0.15 mm thick liquid film with a scraper, then immediately place the glass plate in an atmosphere of NaOH alkali vapor with a pH of 12 and a relative humidity of 85%. , keep the liquid film in the alkali vapor atmosphere for 4 minutes to obtain the nascent film;
[0029] 3) Then immerse the nascent membrane in a hydrochloric acid gel bath (20°C, pH = 1). After the membrane is completely peeled off from the glass plate, continue to soak in the gel bath for 30 minutes, and then transfer t...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hydrophobic Microporous Membrane Prepared by Gel in Alkali Vapor and Then in Acid
[0033] 1) The total amount of casting solution is 100g. First, mix PVDF (10wt%), DMAC (64wt%), LiCl (4wt%) and TEOS (22wt%) and stir for 6 hours with a magnetic stirrer to obtain a clarified casting solution. Membrane solution, and then put it in an oven at 50°C for 48 hours to fully mature and defoam;
[0034] 2) Scrape the casting solution obtained in step 1) on a glass plate into a 0.15mm thick liquid film with a scraper, then immediately place the glass plate in an atmosphere of NaOH alkali vapor with a pH of 13 and a relative humidity of 85%. , keep the liquid film in the alkali vapor atmosphere for 4 minutes to obtain the nascent film;
[0035] 3) Then immerse the nascent membrane in a hydrochloric acid gel bath (20°C, pH=3). After the membrane is completely peeled off from the glass plate, continue to soak in the gel bath for 30 minutes, and then transfer ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hydrophobic Microporous Membrane Prepared by Gel in Water Vapor and Then in Acid
[0039] 1) The total amount of casting solution is 100g. First, mix PVDF (10wt%), DMAC (73wt%), LiCl (5wt%) and TEOS (12wt%), and stir for 7 hours with a magnetic stirrer to obtain a clarified casting solution. Membrane solution, and then put it in an oven at 50°C for 48 hours to fully mature and defoam;
[0040] 2) After scraping the casting solution obtained in step 1) into a liquid film with a thickness of 0.15 mm on a glass plate, immediately place the glass plate in a water vapor atmosphere (relative humidity 80%) to allow the liquid film to Keep it in the water vapor atmosphere for 3 minutes to get the nascent eco-film;
[0041] 3) Then immerse the nascent membrane in a hydrochloric acid gel bath (18°C, pH=0.5). After the membrane is completely peeled off from the glass plate, continue to soak in the gel bath for 30 minutes, and then transfer to deionized wat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com