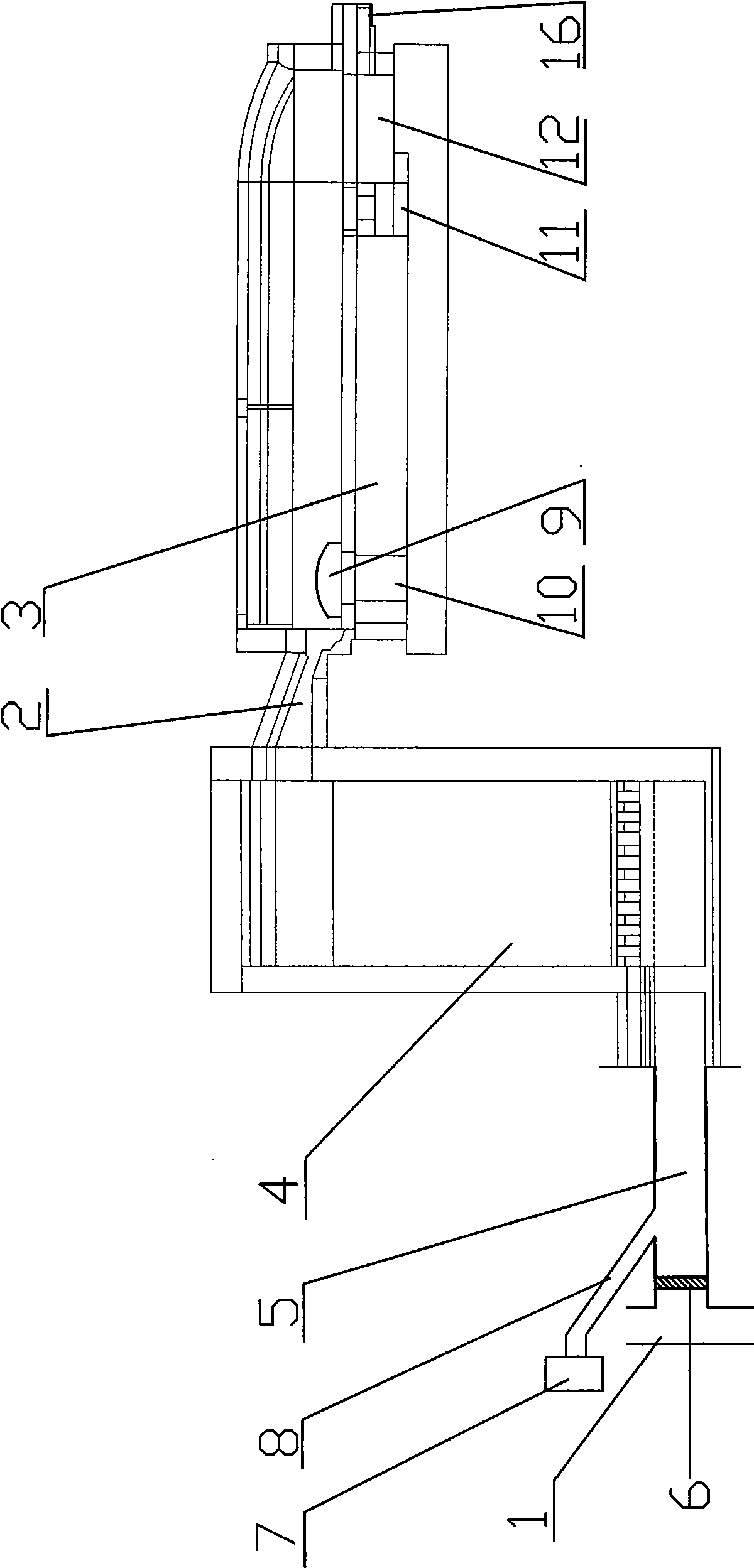
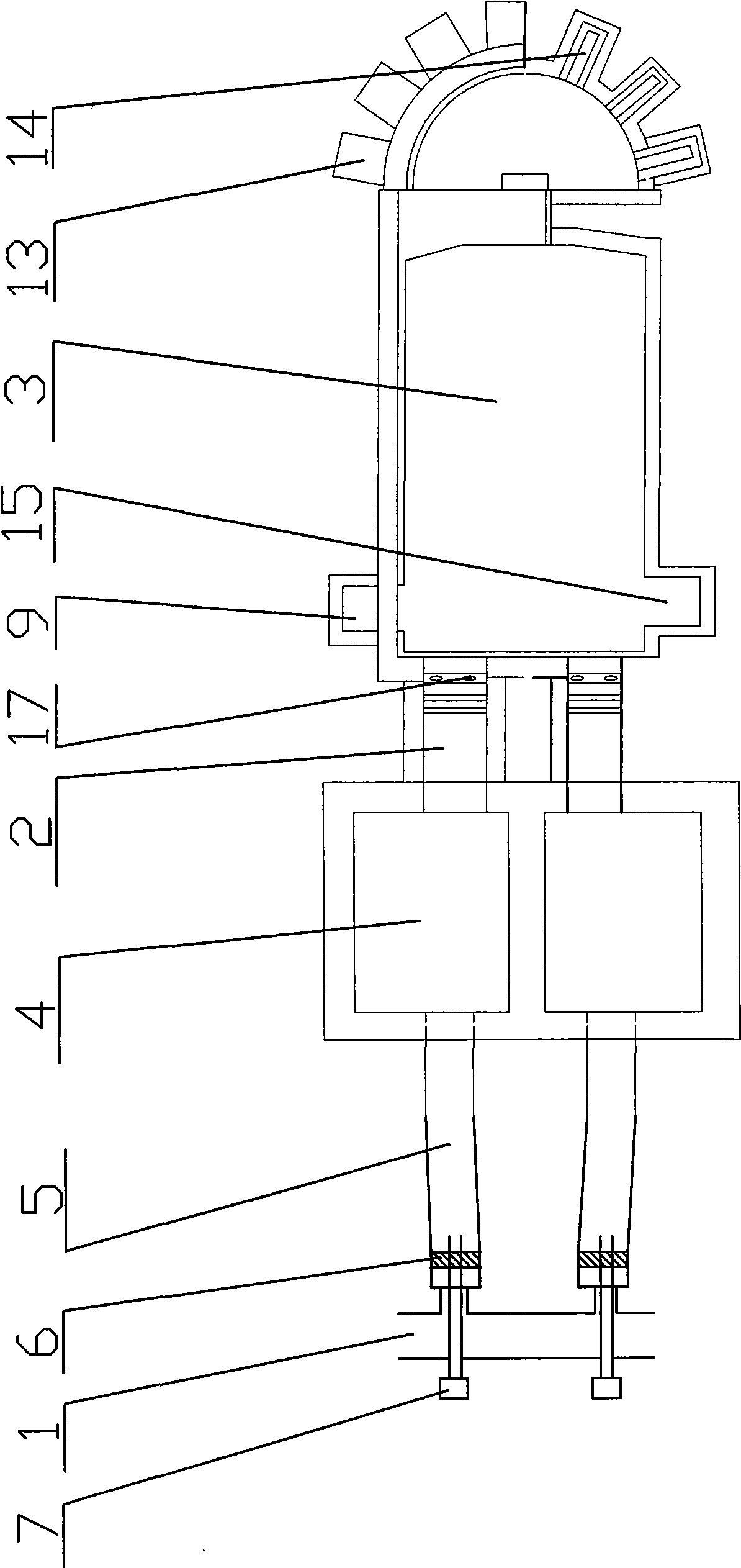
Production formula for alkali-resistant glass marble, production method and production kiln thereof
A technology for producing recipes and glass balls, applied in glass production, glass forming, glass furnace equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the service life of the furnace, low temperature of the stock, and temperature difference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] A production formula for alkali-resistant glass balls, the raw materials of which include quartz sand, zircon sand, fluorite, potassium nitrate, soda ash, rutile, calcite and slaked lime clinker, based on the standard weight (100kg) of the finished glass ball. On the premise of calculating the loss on ignition, the weight ratio of each component is: 35% of quartz sand, 33% of zircon sand, 3% of fluorite, 2% of potassium nitrate, 30% of soda ash, 4.5% of rutile, and 10 of calcite. The loss on ignition (Loss on ignition, abbreviated as LOI), also known as loss on ignition, refers to the crystal water discharged from the blank during the firing process, and the CO produced by the decomposition of carbonate 2 , SO decomposed from sulfate 2 , And the loss of organic impurities after being eliminated. Relatively speaking, if the ignition loss is large and the flux content is too much, the higher the shrinkage rate of the sintered product will be. The alkali-resistant quartz sand ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] A production formula for alkali-resistant glass balls, the raw materials of which include quartz sand, zircon sand, fluorite, potassium nitrate, soda ash, rutile, calcite, and slaked lime clinker, based on the standard weight (100kg) of the finished glass ball. On the premise of calculating the loss on ignition, the weight ratio of each component is: 39% of quartz sand, 34% of zircon sand, 4% of fluorite, 4% of potassium nitrate, 45% of soda ash, 4.5% of rutile, and 15% of calcite. . The loss on ignition (Loss on ignition, abbreviated as LOI), also known as loss on ignition, refers to the crystal water discharged from the blank during the firing process, and the CO produced by the decomposition of carbonate 2 , SO decomposed from sulfate 2 , And the loss of organic impurities after being eliminated. Relatively speaking, if the ignition loss is large and the flux content is too much, the higher the shrinkage rate of the sintered product will be. The alkali-resistant quartz s...
Embodiment 3
[0070] A production formula for alkali-resistant glass balls. The raw materials include quartz sand, zircon sand, fluorite, potassium nitrate, soda ash, rutile, calcite, and slaked lime clinker. Under the premise of calculating the loss on ignition, the weight ratio of each component is: 37% quartz sand, 36% zircon sand, 3.6% fluorite, 3% potassium nitrate, 40% soda ash, 4.5% rutile, and 13% calcite; The loss on ignition (Loss on ignition, abbreviated as LOI), also known as loss on ignition, refers to the crystal water discharged from the blank during the firing process, and the CO produced by the decomposition of carbonate 2 , SO decomposed from sulfate 2 , And the loss of organic impurities after being eliminated. Relatively speaking, if the ignition loss is large and the flux content is too much, the higher the shrinkage rate of the sintered product will be. The alkali-resistant quartz sand is SiO 2 Quartz sand raw material with a content of 98%; the zircon sand is ZrO 2 The ra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Uniformity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com