Method for determining copper ions by selenium film modified electrode
A technology for modifying electrodes and copper ions, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity of anodic dissolution method, affecting analytical performance, application limitations, etc., to improve reproducibility and accuracy, improve sensitivity, detect low limit effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] This embodiment adopts Potentiostat / Galvanostat BAS-100A chronopotential analyzer and electrochemical three-electrode test system, uses pyrolytic graphite (EPPG) as the electrode substrate, reduces the selenium film formed by co-enrichment as the working electrode, and platinum wire as the counter electrode , Ag / AgCl is the reference electrode, and the copper ion content in the sample is tested by anodic stripping differential chronopotential method. Reduction co-enrichment and anodic stripping conditions are respectively: the enrichment potential is -200mV, the enrichment time is 180s, and the resting time is 20s; during the test, the anodic stripping current is +2.0μA, and the scan rate is 20mV s -1 , the frequency is 20Hz.
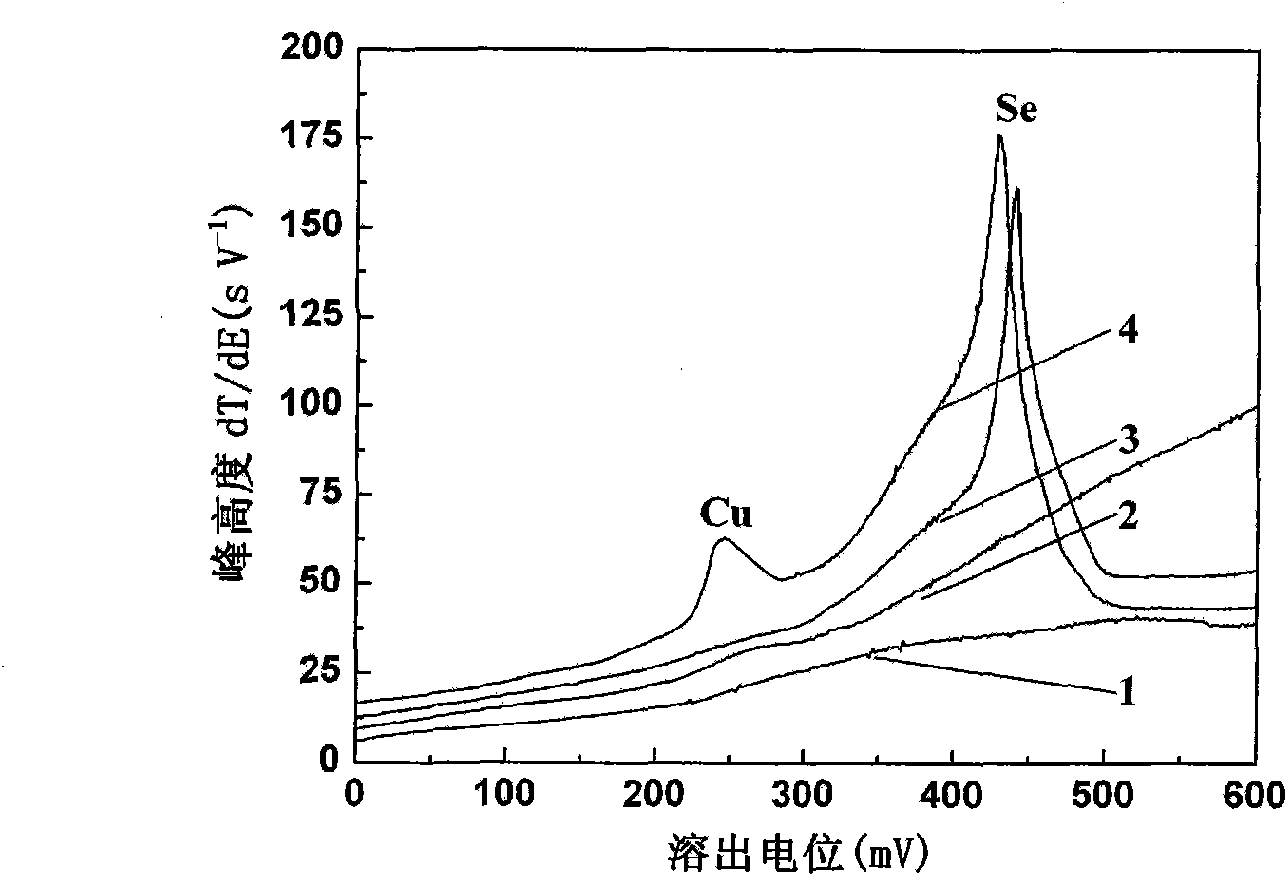
[0022] See attached figure 1 , curve 1 in the figure is for 0.01molL by the above method -1 HCl+5.0gL -1 The results obtained from the KCl solution test; Curve 2 is the addition of 20.0 μgL to the solution described in Curve 1 -1 After Cu(II)...
Embodiment 2
[0026] This embodiment adopts Potentiostat / Galvanostat BAS-100A chronopotential analyzer and electrochemical three-electrode test system, uses pyrolytic graphite (EPPG) as the electrode substrate, reduces the selenium film formed by co-enrichment as the working electrode, and platinum wire as the counter electrode , Ag / AgCl as the reference electrode, using anodic stripping differential chronopotentiometry to measure different concentrations of copper ions in simulated water samples; at the same time, 1.0 μg L -1Cu(II) for the anti-interference detection of different ions. Reduction co-enrichment and anodic stripping conditions are respectively: the enrichment potential is -300mV, the enrichment time is 180s, and the resting time is 20s; during the test, the anodic stripping current is +2.0μA, and the scan rate is 20mV s -1 , the frequency is 20Hz.
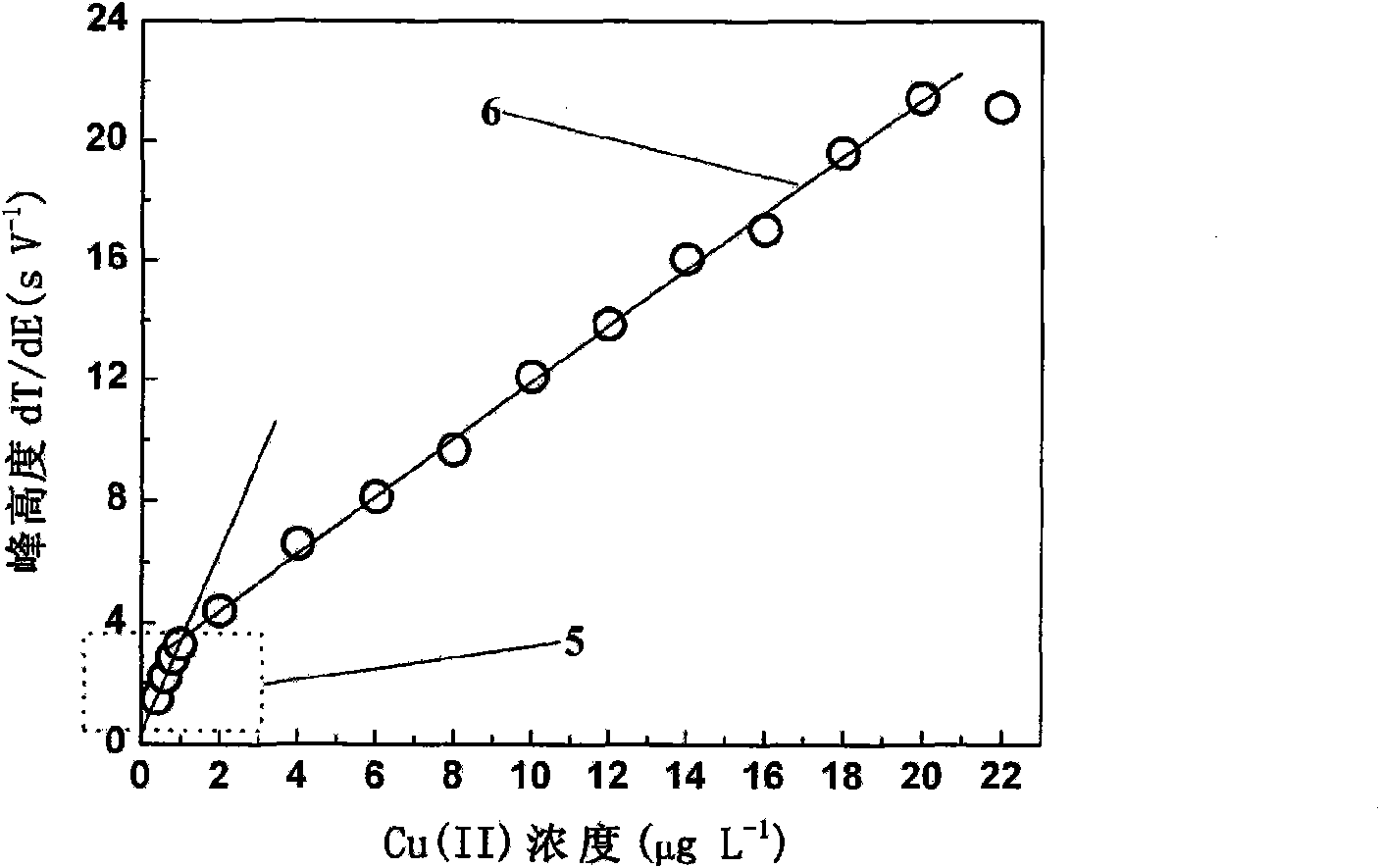
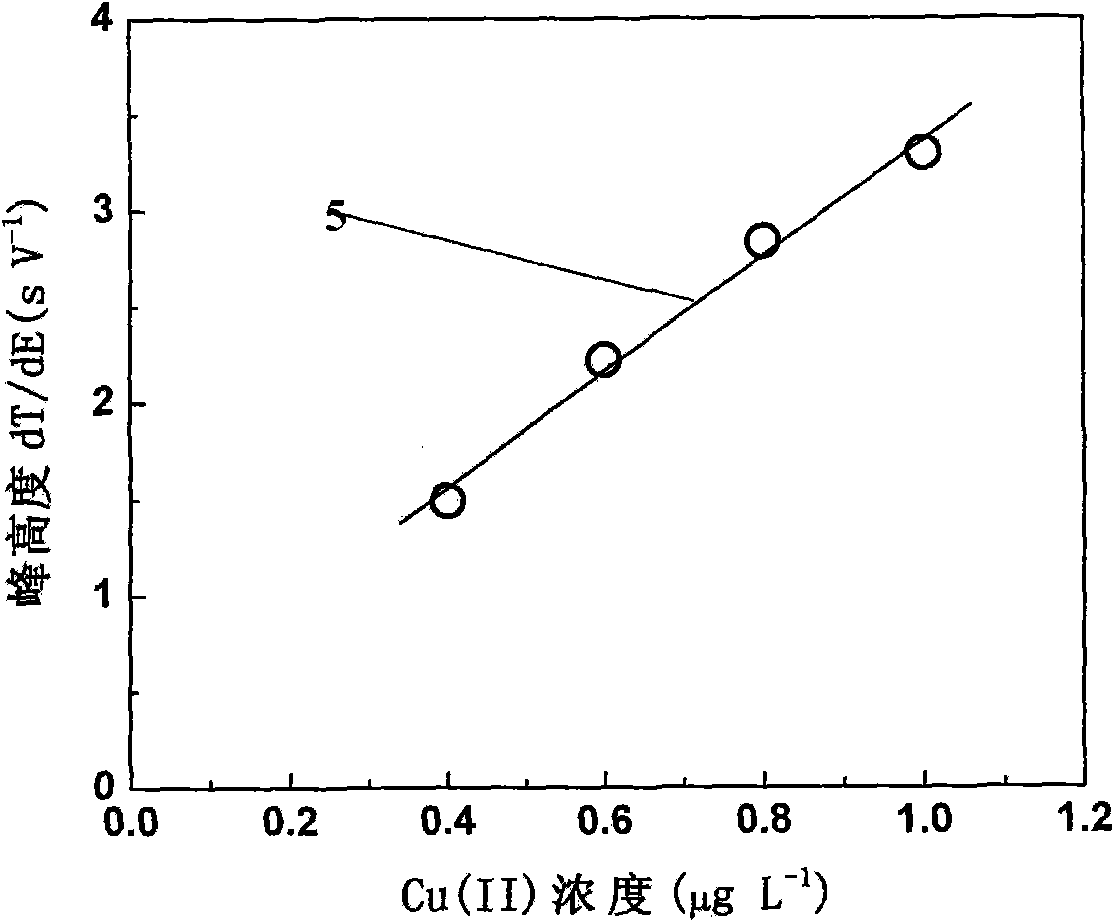
[0027] See attached figure 2 And attached image 3 , for containing 0.01mol L -1 HCl, 10.0gL -1 KCl, 1.0 mg L -1 Cu(II) o...
Embodiment 3
[0032] This embodiment adopts Potentiostat / Galvanostat BAS-100A chronopotential analyzer and electrochemical three-electrode test system, uses pyrolytic graphite (EPPG) as the electrode substrate, reduces the selenium film formed by co-enrichment as the working electrode, and platinum wire as the counter electrode , Ag / AgCl as the reference electrode, using the anodic stripping differential chronopotential method to determine the copper ion content of simulated water samples, spiked seawater and tap water samples. Reduction co-enrichment and anodic stripping conditions are respectively: the enrichment potential is -300mV, the enrichment time is 180s, and the resting time is 20s; during the test, the anodic stripping current is +2.0μA, and the scan rate is 20mV s -1 , the frequency is 20Hz.
[0033] Simulation sample: adopt the test method of embodiment 1 or 2, be 0.40 μ g L to known Cu (II) concentration -1 The simulated sample 1, the known Cu(II) concentration is 3.0μg L -1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com