Catalyst for producing low-carbon olefins through catalytic cracking by fixed bed
A catalytic cracking and catalyst technology, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, hydrocarbon cracking to hydrocarbon production, molecular sieve catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of catalyst deactivation, easy carbon deposition, etc., and achieve the effect of improving weight yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
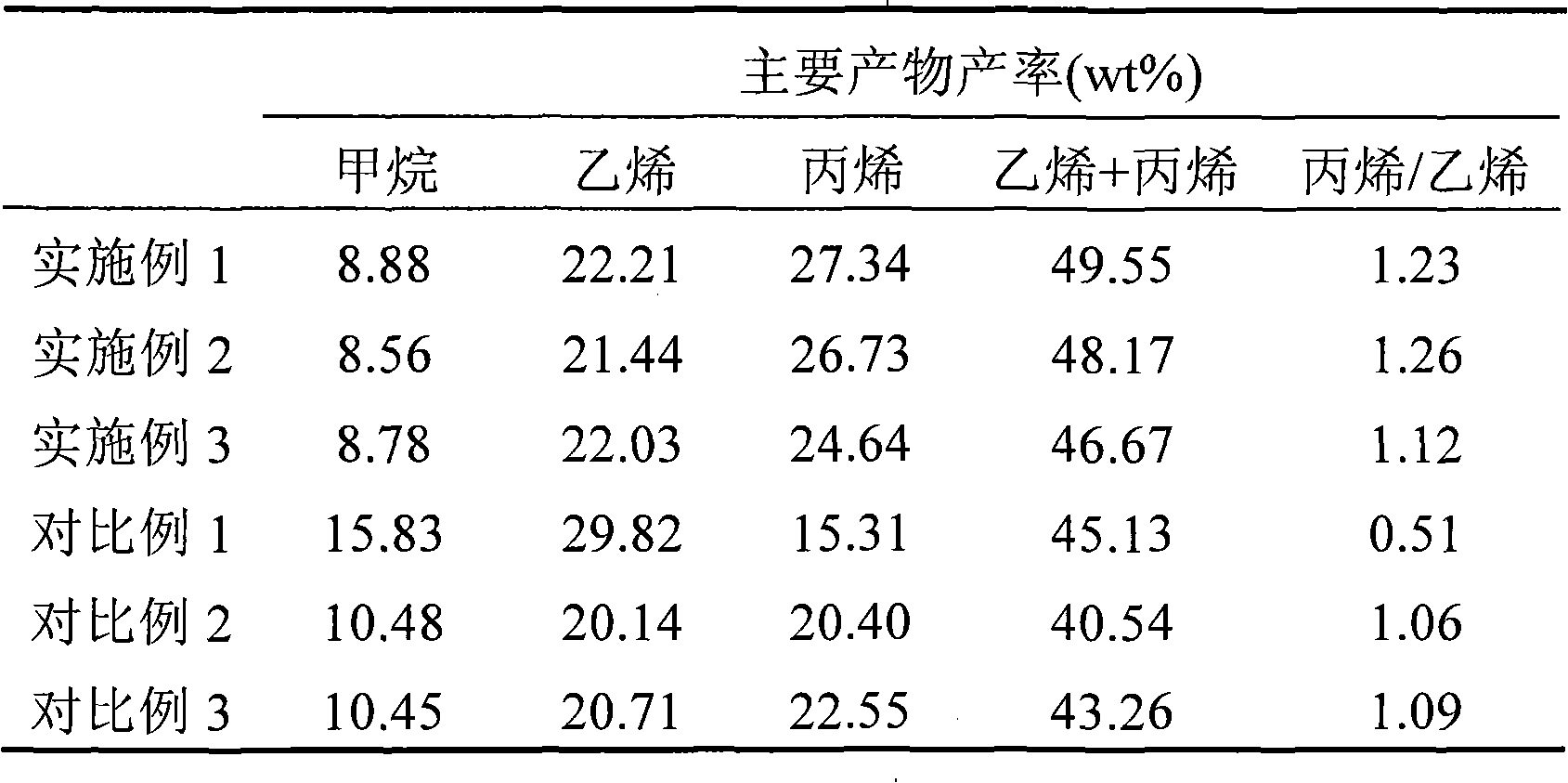
[0036]Catalyst preparation: 30g of HSZM-5 molecular sieve (mole ratio of silicon to aluminum = 360) was uniformly mixed with 10g of alumina, kneaded, and extruded to shape. Dry at 100°C for 10 hours, and bake at 560°C for 4 hours. The molded product was immersed in an aqueous solution containing diammonium hydrogen phosphate, cobalt nitrate, and magnesium nitrate for 2 hours, filtered, dried, and calcined for 4 hours at a temperature higher than the decomposition temperature of the above-mentioned salts. Based on the weight percentage of the catalyst, the finally obtained catalyst contains 70.73% molecular sieve, 25.00% binder, 3.94% magnesium oxide, 0.10% cobalt oxide and 0.23% phosphorus oxide.
[0037] The prepared catalysts were evaluated in a small tubular fixed bed reactor. The evaluation condition is: the weight space velocity of naphtha is 1h -1 , the reaction temperature is 650° C., the pressure is normal pressure, and the water-to-oil feed weight ratio is 1. The r...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Catalyst preparation: catalyst shaping is the same as embodiment 1. Immerse the molded product in an aqueous solution containing diammonium hydrogen phosphate, cobalt nitrate, magnesium nitrate and calcium nitrate for 2 hours, filter, dry, and bake at a temperature higher than the decomposition temperature of the above salt for 4 hours. Based on the weight percent content of the catalyst, the finally obtained catalyst contains 73.41% molecular sieve, 22.30% binder, 1.57% magnesium oxide, 2.37% calcium oxide, 0.10% cobalt oxide and 0.25% phosphorus oxide .
[0040] Catalyst evaluation conditions are the same as in Example 1. The reaction results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Catalyst preparation: catalyst molding method is the same as embodiment 1. Immerse the molded product in an aqueous solution containing diammonium hydrogen phosphate, cobalt nitrate, magnesium nitrate and calcium nitrate for 2 hours, filter, dry, and bake at a temperature higher than the decomposition temperature of the above salt for 4 hours. Based on the weight percent content of the catalyst, the finally obtained catalyst contains 73.41% molecular sieve, 22.45% binder, 1.52% magnesium oxide, 2.35% calcium oxide, 0.05% cobalt oxide and 0.22% phosphorus oxide .
[0043] Catalyst evaluation conditions are the same as in Example 1. The reaction results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com