Antibacterial lipopeptide of endophytic Bacillus subtilis and separation and purification method
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and antibacterial lipopeptide, applied in the field of extracellular antibacterial lipopeptide and its separation and purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The acquisition of embodiment 1 antimicrobial lipopeptide crude extract
[0021] The endophytic Bacillus subtilis Jaas ed1 was transferred to the NB culture solution (the NB culture solution is beef extract 0.3%, yeast extract 0.1%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 1.0%, pH 6.8-7.0), in Shake culture at 30°C and 120r / min for 48h, 4°C, 10000r / min, centrifuge for 10min, remove the bacteria, collect the supernatant, then add ammonium sulfate solids in batches while stirring with a magnetic bar, statically at 4°C After standing overnight, centrifuge at 10000r / min for 18min, and dissolve the precipitate obtained in 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0). According to the above method, carry out ammonium sulfate segmental salting-out on the supernatant, and collect the precipitates with ammonium sulfate saturation at 0-30%, 30-40%, 40-50%, 50-60%, and 60-70% respectively , dissolved in 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0). The antibacterial activity of the above ammonium sulfate precipita...
Embodiment 2
[0022] The separation and purification of embodiment 2 antimicrobial lipopeptides
[0023]The antimicrobial lipopeptide crude extract is loaded on the Sephedex G-25 molecular sieve chromatography column, eluted with 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (pH7.0), the flow rate is 1ml / min, and detected at OD 280nm of ultraviolet light, there is I , II two absorption peaks, collect each peak component, and detect the bacteriostasis activity to Verticillium dahliae of eggplant, wherein peak I has bacteriostasis activity. Concentrate the peak I collection solution obtained by molecular sieve chromatography, load the sample on Cellulose DEAE-52 anion exchange column, and use 0.05mol / L containing 0mol / L, 0.1mol / L, 0.4mol / L, 1.0mol / L NaCl respectively Gradient elution with L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) at a flow rate of 1ml / min, detected at UV light OD 280nm, and eluted in 0.1mol / L, 0.4mol / L, 1.0mol / L NaCl phosphate buffer respectively Absorption peaks appeared at each concentration, and the peak...
Embodiment 3
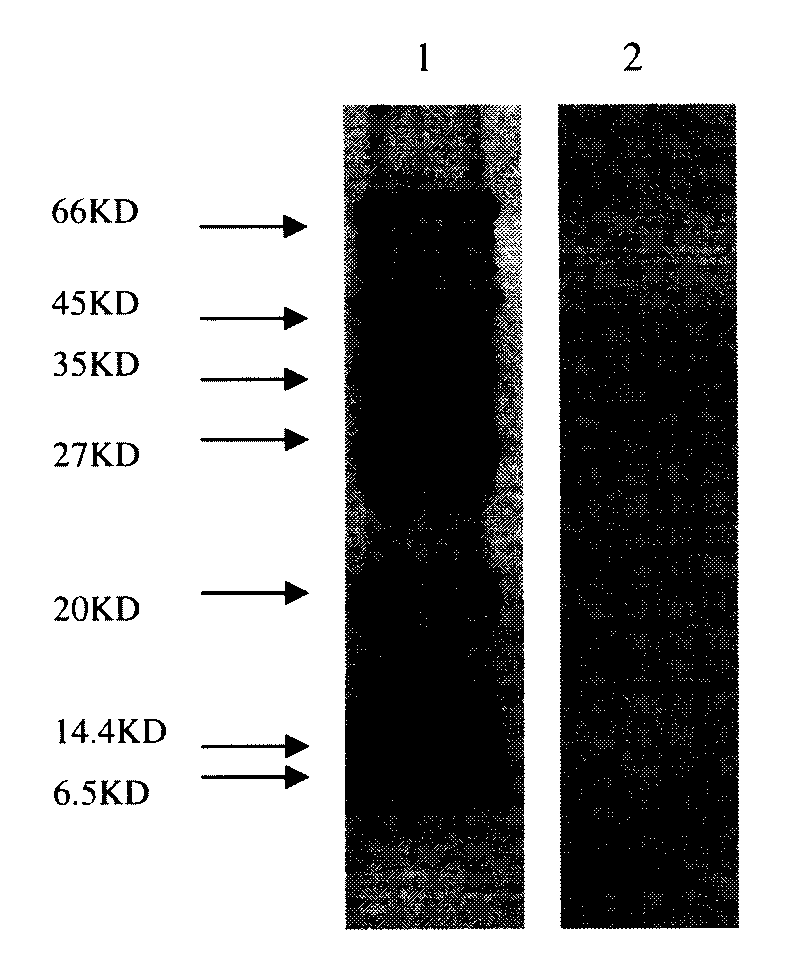
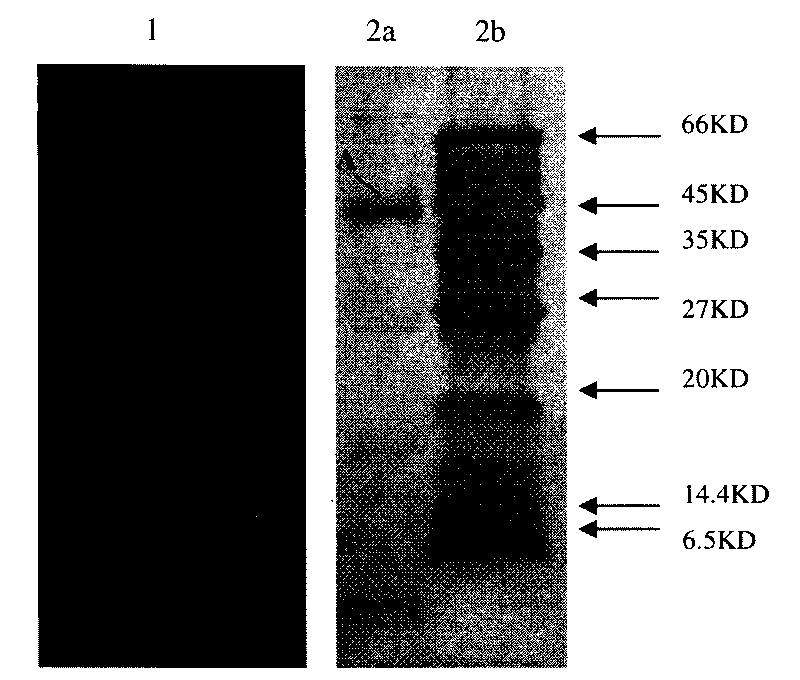
[0024] Embodiment 3 Utilizes biological self-imaging technique to search for antimicrobial lipopeptide target band
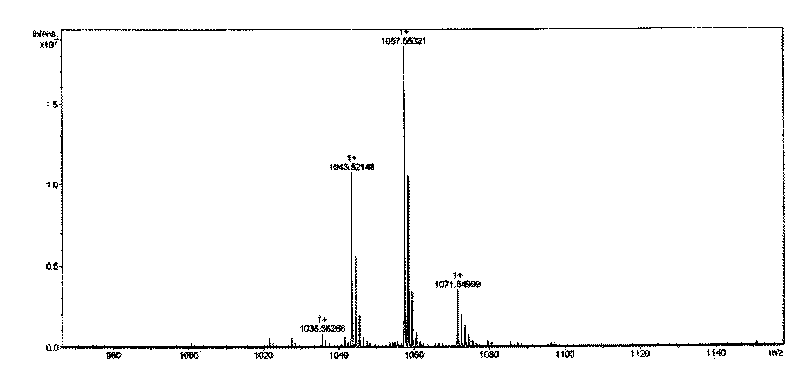
[0025] The antibacterial activity of the antibacterial activity peak substance collection solution after the antibacterial lipopeptide crude extract was chromatographed by Sephedex G-25 molecular sieve chromatography column and Cellulose DEAE-52 anion exchange column was detected in situ by Tricine-SDS-PAGE gel, That is to use biological autoradiography to find the target band of antibacterial lipopeptide. In Tricine-SDS-PAGE, the separation gel concentration is 16.5%, the interlayer gel concentration is 10%, and the stacking gel concentration is 4%. The antibacterial lipopeptide crude extract is subjected to Sephedex G-25 molecular sieve chromatography column and CelluloseDEAE-52 anion exchange column After the bacteriostatic activity peak substance collection solution after chromatography was concentrated, the sample was loaded in parallel on two sample wells ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com