Metal particle-amorphous diamond composite anode for fuel cell and preparation method thereof
A technology of amorphous diamond and metal particles, which is applied in the direction of battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems that hinder the use of amorphous diamond films, poor conductivity of amorphous diamond films, and low catalytic activity of films, and achieve long-term catalytic ability Stable, good chemical stability, excellent anti-adsorption ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The platinum metal particle-phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond composite anode of this embodiment can be obtained through the following steps:
[0036] (1) Put the high-purity carbon target and the substrate after ultrasonic cleaning into the vacuum chamber of the filtered cathodic vacuum arc system, and use argon ions to etch the substrate surface for 10 minutes to remove the oxide layer on the substrate surface;
[0037] (2) Pass into working gas in vacuum chamber, and this working gas contains phosphine 10sccm, argon 10sccm;
[0038] (3) Use the graphite cathode to excite the discharge of the high-purity carbon target to generate carbon plasma. The carbon plasma bombards the phosphine gas in the vacuum chamber under the action of the -200V pulsed negative bias accelerating electric field to ionize it, and the generated carbon, phosphorus, and hydrogen The mixed plasma is deposited together on the substrate to form phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond film;
[0039] (4...
Embodiment 2
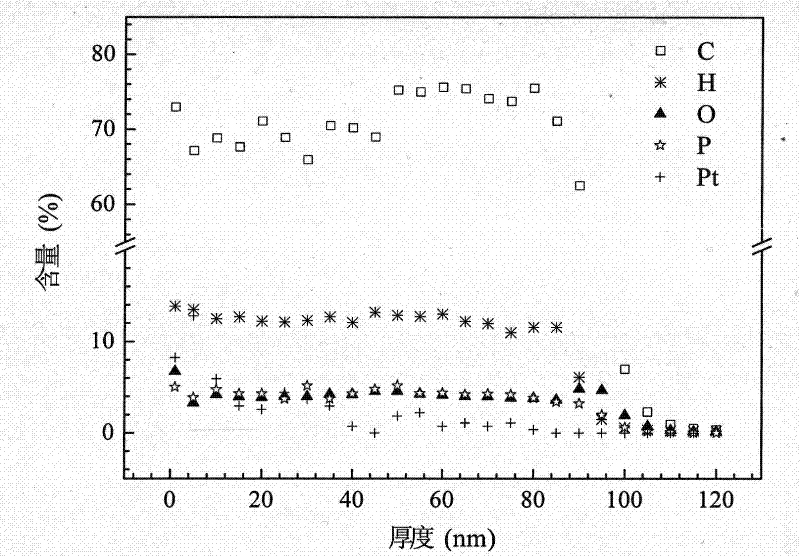
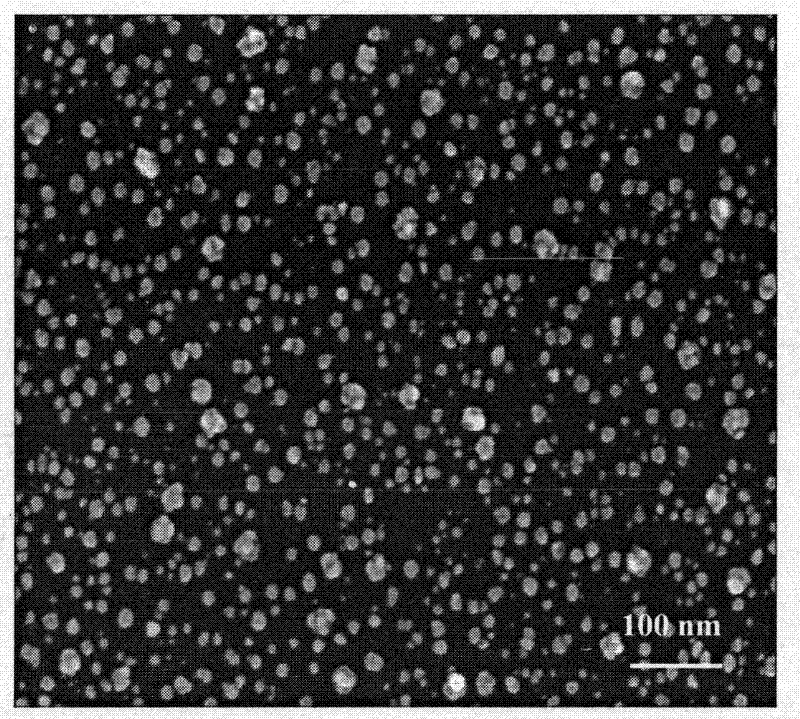
[0043] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that, during the preparation process of the platinum metal particles-phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond composite anode, the working gas fed into the vacuum chamber is 30 sccm, including 20 sccm of phosphine and 10 sccm of argon. Through the secondary ion mass spectrometry test, the platinum nanoparticle-phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond composite anode of the present embodiment is composed of 63.3% carbon, 5.8% phosphorus, 8.8% oxygen, 13.6% hydrogen and 8.5% by mass percentage. % platinum composition. Increasing the flow rate of phosphine in the working gas can increase the phosphorus content in the phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond film, and further improve the conductivity of the film. The deposition amount of platinum nanoparticles on the surface of phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond film also increased correspondingly. The diameter of platinum nanoparticles varied in the range of 6.5-39.4nm, mainly distributed...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The difference between this example and example 1 is that during the preparation process of the platinum metal particles-phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond composite anode, the working gas is 10 sccm of phosphine and 0 sccm of argon gas into the vacuum chamber; The deposition potential of electroplated platinum metal particles on the phosphorus amorphous diamond film is -0.6V, and the deposition time is 20s. According to the secondary ion mass spectrometry test, the composite anode of this embodiment is made of 58.7% carbon, 6.3% phosphorus, 9.3% oxygen, 14.0% hydrogen and 11.7% platinum in terms of mass percentage. The diameter of platinum nanoparticles varies in the range of 5.8-38.9nm, mainly distributed in the range of 8-15nm, and the particle density is 1.3×10 12 piece / cm 2 . This shows that the more negative the deposition potential, the more favorable the deposition of platinum nanoparticles on the surface of phosphorus-doped amorphous diamond film, and the gre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com