Nano chitosan derivative and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of nano-chitosan and derivatives, applied in the field of biomedical nano-materials, can solve the problems of enrichment and purification of phosphorylated polypeptides, and achieve good biocompatibility, strong adsorption capacity, and cheap materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
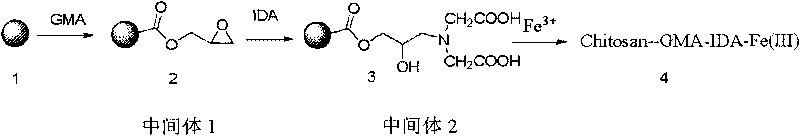
[0027] Embodiment 1: the preparation of chitosan-GMA epoxy medium (chitosan-GMA)
[0028] In a 100mL three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer and a condenser, 0.5g of chitosan (Qingdao Haihui Biological Co., Ltd.) was dissolved in 30mL of an aqueous solution containing dilute acetic acid (2wt%), and 0.5mL of formazan was added. Glycidyl acrylate, stir, then add 0.035 g of ammonium persulfate and 0.035 g of sodium thiosulfate, heat up to 50 ° C, react for 2 hours, stop the reaction, after cooling down to room temperature, centrifuge to remove the supernatant, and then wash with water , to obtain a solid.
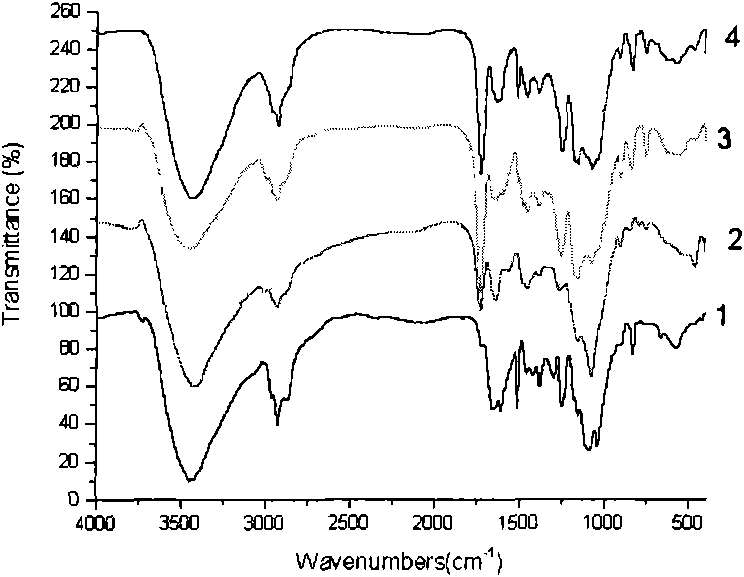
[0029] Structure: image 3 A is the chitosan-GMA epoxy dielectric negative staining transmission electron microscope image, as can be seen from the figure, this material is spherical, and the size is 20-100nm; its infrared spectrum ( figure 2 .2) The characteristic peaks are: 3410.2, 2927.2, 1730.7, 1639.8, 1452.3, 1259.8, 1157.9, 1076.9, 905.7, 846.0, 752...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: the preparation of chitosan-GMA-IDA carboxylic acid medium (chitosan-GMA-IDA)
[0031] In the 100mL three-necked flask equipped with stirrer, thermometer and condenser tube, the composite medium prepared in Example 1 is charged, and 0.5 gram of sodium iminodiacetate, 0.25 gram of sodium chloride and 20 mL of sodium carbonate of 2N are added The solution was heated up to 60° C., reacted for 5 hours, stopped the reaction, cooled to room temperature, filtered, washed with water until neutral, and a solid was obtained.
[0032] Structure: image 3 The negative staining transmission electron microscope figure of B chitosan-GMA-IDA carboxylic acid medium, as can be seen from the figure, this material is spherical, and size is 20-100nm; Its infrared spectrum ( figure 2 .3) The characteristic peaks are: 3437.9, 2929.8, 1929.5, 1640.1, 1607.3, 1452.1, 1387.3, 1253.4, 1154.4, 1072.1, 908.5, 842.1, 754.6; elemental analysis results are C 46.89%, H 7.19%, N 2.46%. ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: prepare the chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe(III) (chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe(III)) of fixed transition metal ion
[0034] Put the chitosan-GMA-IDA prepared in Example 2 into a beaker, add 20 mL of 100 mM ferric chloride solution, stir, react at room temperature for 2 hours, filter, wash with water, dry, and grind to obtain a solid powder.
[0035] Structure: image 3 C is a transmission electron microscope figure of chitosan-GMA-IDA-Fe(III), as can be seen from the figure, the particle size of this nanomaterial is 20-100nm, and the surface is combined with metal iron ions; The iron content measured by the spectrometer was 15.52 mg / g (average value of three times). Its infrared spectrum ( figure 2 .4) The characteristic peaks are: 3424.0, 2927.2, 1728.8, 1635.0, 1510.4, 1454.5, 1384.7, 1249.7, 1158.1, 1073.1, 908.9, 834.4, 753.0. Elemental analysis: C 43.87%, H 6.93%, N 2.33%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com