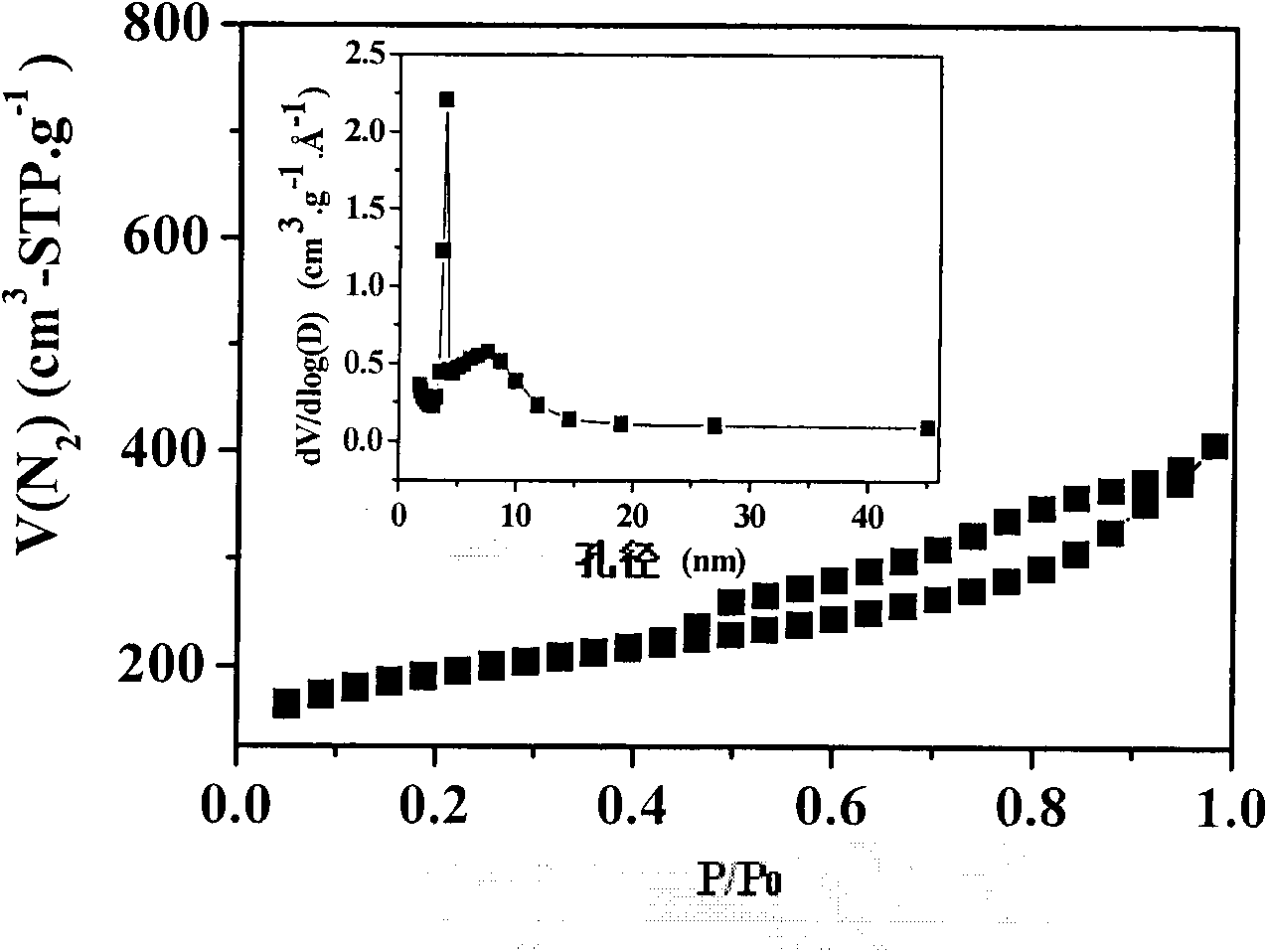
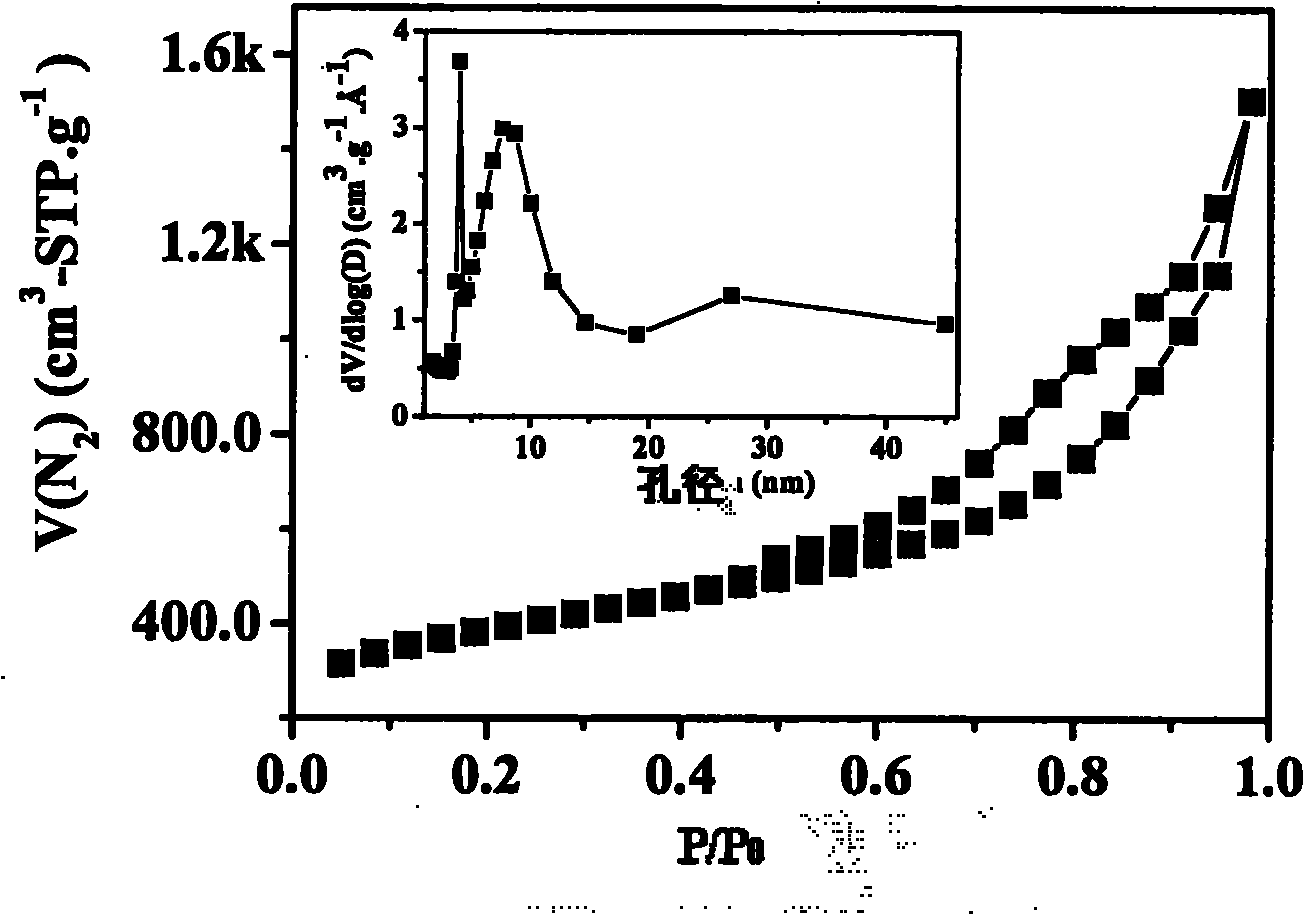
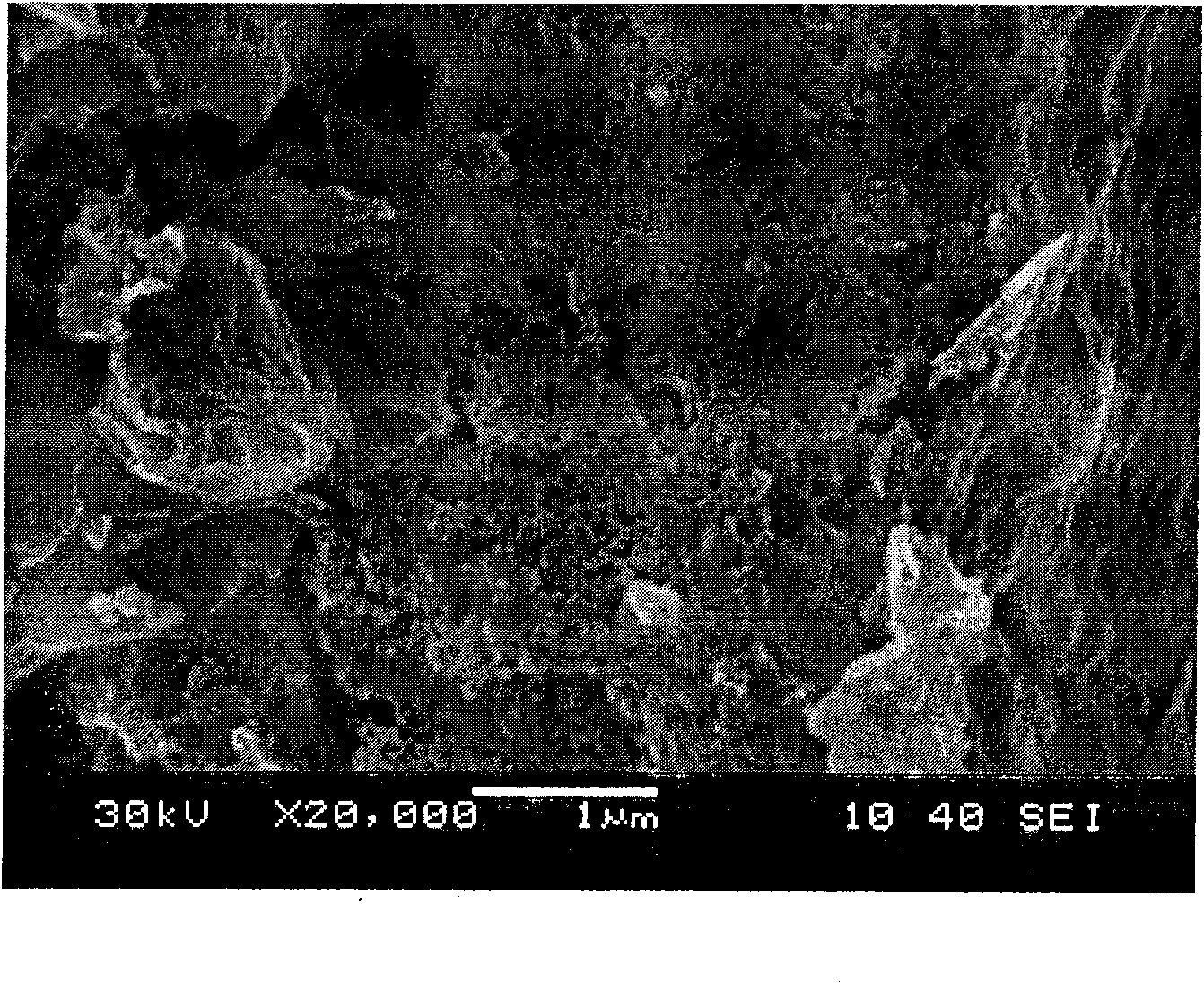
Method for preparing high-surface-area nitrogenous mesoporous carbon material
A high surface area, porous carbon technology, applied in the field of preparation of high surface area nitrogen-containing mesoporous carbon materials, can solve the problems that it is difficult to meet high surface area and high nitrogen content at the same time, the template agent cannot be reused, and the nitrogen content of carbon materials is low. , to achieve good application prospects, high mesopore rate, and large total pore volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Weigh 23.5g of melamine, 45g of urea and 153g of 37% formaldehyde solution (weight ratio is 100:183:650), add 100g of water (196.5g of water in the mixture at this time); adjust the pH value to 9 with sodium carbonate, stir to dissolve Completely, add 35g of potassium chloride (148 parts by weight), stir to dissolve, and adjust the pH to 3.5 with hydrochloric acid; transfer the mixed solution to a 55°C oil bath or water bath for heating, and at this time, the raw materials undergo a polymerization reaction, and after about 0.5 hours To obtain a white resinous mixture, raise the temperature to 80°C and keep it for 4 hours, then transfer it to an oven at 140°C for curing for 24 hours to obtain a white solid; transfer the white solid to a carbonization furnace, and raise the temperature to 850°C in flowing helium , carbonized at constant temperature for 0.5 hours, and cooled to room temperature; the carbonized solid product was taken out, boiled with dilute hydrochloric aci...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Weigh 32g of melamine, 0g of urea and 114g of 37% formaldehyde solution (weight ratio is 100:0:356.), add 200g of water (272g of water in the mixture at this time); adjust the pH value to 8 with sodium hydroxide, stir to dissolve Completely, add 445g of zinc chloride (1390 parts by weight), stir to dissolve, and then adjust the pH to 3.5 with hydrochloric acid; transfer the mixed solution to a 40°C oil bath or water bath for heating, and at this time, the raw materials undergo a polymerization reaction, about 0.1 hours Afterwards, a white resinous mixture was obtained, which was heated to 60° C. and maintained for 6 hours, and then transferred to a 180° C. oven for solidification for 12 hours to obtain a tan solid; the tan solid was transferred to a carbonization furnace, and the temperature was raised to Carbonize at 500°C for 12 hours at a constant temperature, cool to room temperature; take out the carbonized solid product, boil it with dilute hydrochloric acid and di...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Take by weighing 47.5g of melamine, 15g of urea and 120g of 37% formaldehyde solution (weight ratio is 100:32:255), add 100g of water (175g of water in the mixture at this moment); adjust the pH value to 10.5 with ammonia water, stir and dissolve completely, Add 213g of calcium chloride (453 parts by weight), stir and dissolve, then adjust the pH to 5 with hydrochloric acid; transfer the mixed solution to an 80°C oil bath or water bath for heating, at this time, the raw materials undergo a polymerization reaction, and after about 0.5 hours, The white resinous mixture was heated to 90°C and kept for 0.1 hour, then transferred to a 220°C oven for solidification for 4 hours to obtain a white solid; the white solid was transferred to a carbonization furnace, and the temperature was raised to 800°C in flowing argon, Carbonize at constant temperature for 2 hours, cool to room temperature; take out the carbonized solid product, boil it with dilute hydrochloric acid and distille...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com