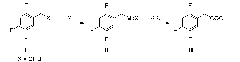
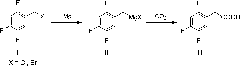Method for preparing 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid
A technology of trifluorophenylacetic acid and trifluorophenylacetic acid salt, which is used in pharmaceutical chemical intermediates and related chemical fields, can solve the problems of harsh reaction conditions, difficult to control impurities, long process routes, etc., and achieves short synthesis routes and mild conditions. , Environmentally friendly effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Step 1: Preparation of 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride
[0038] In a 250mL three-necked flask, 120mL of tetrahydrofuran and magnesium chips (7.2g, 0.45mol) were successively added at room temperature under nitrogen protection, and 1,2-dibromoethane (0.56g, 0.003mol) was slowly added dropwise under stirring and waited for temperature Raised to 30°C, slowly added 2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl chloride (9g, 0.05mol) dropwise, and then continued to slowly drop 2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl chloride (45g, 0.25mol) after the temperature rose to 60°C mol) to keep the solution slightly boiling, reflux reaction for 5-6 hours after the dropwise addition, until the magnesium chips basically disappear, and 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride is obtained.
[0039] Step 2: Preparation of 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid
[0040] Under the protection of nitrogen, add solid dry ice 10g×3 in batches to the reaction liquid containing 61g of 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride obtained i...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Step 1: Preparation of 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium bromide
[0043] In a 250mL three-necked flask, 140mL of tetrahydrofuran and magnesium powder (7.2g, 0.45mol) were sequentially added at room temperature under nitrogen protection, and 2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl bromide (5g, 0.02mol) was slowly added dropwise under stirring. After the temperature rises to 65°C, continue to slowly add 2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl bromide (70g, 0.31mol) dropwise to keep the solution slightly boiling. After the dropwise addition, reflux for 2-3 hours. After the magnesium powder basically disappears, the preparation In 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium bromide.
[0044] Step 2: Preparation of 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid
[0045]Under the protection of nitrogen, add solid dry ice 10g×3 in batches to the reaction liquid containing 61g of 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride obtained in Example 1, add once every 3 hours, and control the reaction temperature at 0°C -15°C. After the dry ice is co...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Step 1: Preparation of 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride
[0048] In a 250mL three-necked flask, 120mL of methyl tert-butyl ether and magnesium chips (7.2g, 0.45mol) were successively added at room temperature under nitrogen protection, and 1,2-dibromoethane (0.56g, 0.003m0l) when the temperature rises to 30°C, slowly add 2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl chloride (9g, 0.05mol) dropwise, and then slowly add 2,4,5-trifluorobenzyl chloride after the temperature rises to 60°C Chlorine (45g, 0.25mol) kept the solution slightly boiling. After the dropwise addition, the solution was refluxed for 5-6 hours. After the magnesium dust basically disappeared, 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride was obtained.
[0049] Step 2: Preparation of 2,4,5-trifluorophenylacetic acid
[0050] Under the protection of nitrogen, add solid dry ice 10g×3 in batches to the reaction liquid containing 61g of 2,4,5-trifluorobenzylmagnesium chloride obtained in Example 1, add once every 3 hours, and cont...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com