Clean metallurgical method for low-temperature molten salt of lead
A low-temperature molten salt, clean technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, can solve the problems of air, land and water pollution, difficult to deal with, flue gas pollution, etc., to promote technological progress, improve vertical yield, and promote energy saving and reduction. row effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
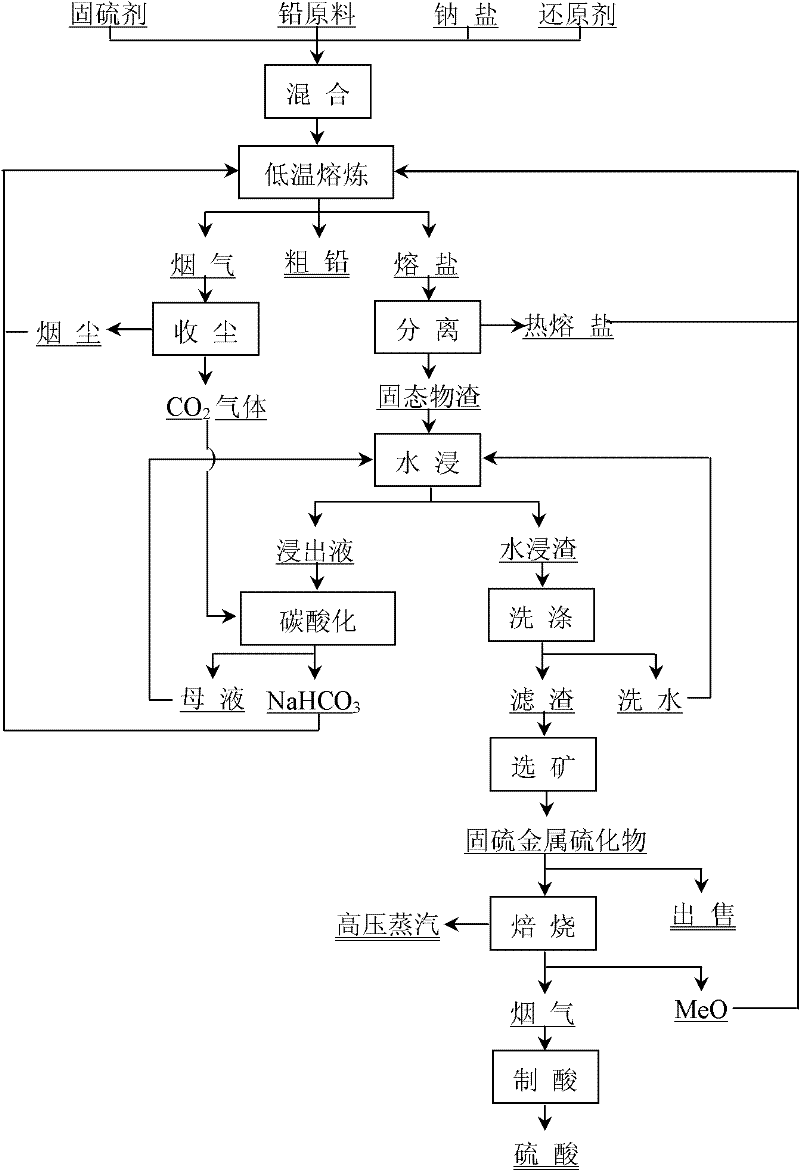
[0037] The chemical composition of lead sulfide concentrate is (%): Pb70.12, Fe6.08, S15.04, Zn2.84, Cu0.40, SiO 2 0.79. , the chemical composition of pulverized coal is (%): C 82.33, S 3.01, SiO 2 6.66, CaO 0.83, Al 2 o 3 4.81. Weigh 100g of lead sulfide concentrate, 10.0g of pulverized coal, 200g of industrial grade sodium carbonate and 35.07g of sub-zinc oxide containing Zn78.33% and mix them evenly, put them into a graphite crucible, and then melt in a resistance furnace at 900°C for 2h. 67.34g of crude lead containing Pb 98.40% was produced, and the direct recovery rate of lead reached 94.5%; hot state molten salt clarified and separated the solid to obtain 162.5g of molten sodium carbonate and 111.7g of solid slag of a small part of sodium carbonate bonded, Leach with 300mL tap water at room temperature for 3h to obtain dry leaching residue 71.3%, containing Zn 42.51%, S21.01%, sulfur fixation rate 99.61%; filtrate volume is 340mL, containing Na 2 CO 3 180g / L, a...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Using waste storage battery cement as raw material, the composition is: Pb74.15%, S7.85%, coke powder as reducing agent, containing C82%, ash10%. Weigh 100g of cement, 15g of coke powder and 31.79g of copper oxide soot containing Cu49.03% respectively, add 162.5g of molten sodium carbonate returned in Example 1, mix evenly, put into a graphite crucible, and cover the NaHCO returned in Example 1 3 65g. Melting 1.5h at 870 DEG C in the electric resistance furnace then, the crude lead 72.13g that output contains Pb 97.66%, the direct recovery rate of lead reaches 95.00%; Obtain molten sodium carbonate 146g and molten sodium carbonate after clarification and separation of solid matter in hot state molten salt 71.2 g of solid slag bonded with a small portion of sodium carbonate was leached with 300 mL of tap water at room temperature for 2 hours to obtain 54.2 g of dry leached residue, containing 28.76% Cu, 14.48% S, and a sulfur fixation rate of 99.99%; Filtrate volume is...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Using lead-copper concentrate as raw material, its composition (%) is: Pb40.85, Cu18.17, Zn8.87, S20.16%, SiO 2 3.27, Fe5.66, the pulverized coal of Example 1 is used as reducing agent, and the copper oxide soot of Example 2 is used as sulfur-fixing agent. Weigh 500g of lead-copper concentrate, 40g of pulverized coal, and 127.76g of copper oxide soot containing Cu49.03%, add 852g of sodium carbonate, mix evenly, put them into a graphite crucible, and then cover with NaHCO 3 325g. Melting 1.0h at 860 DEG C in the electric resistance furnace then, the crude lead 194.96g that output contains Pb 98.06%, the direct recovery rate of lead reaches 93.60%; 591.56g of solid slag bonded with a small portion of sodium carbonate was leached with 1500mL of tap water at room temperature for 2.5h, and washed with water to obtain 284.5g of dry leached slag, containing Cu53.95%, Zn15.59%, S34.80 %, the sulfur fixation rate is 98.12%; the filtrate volume is 1760mL, containing Na 2 CO ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com