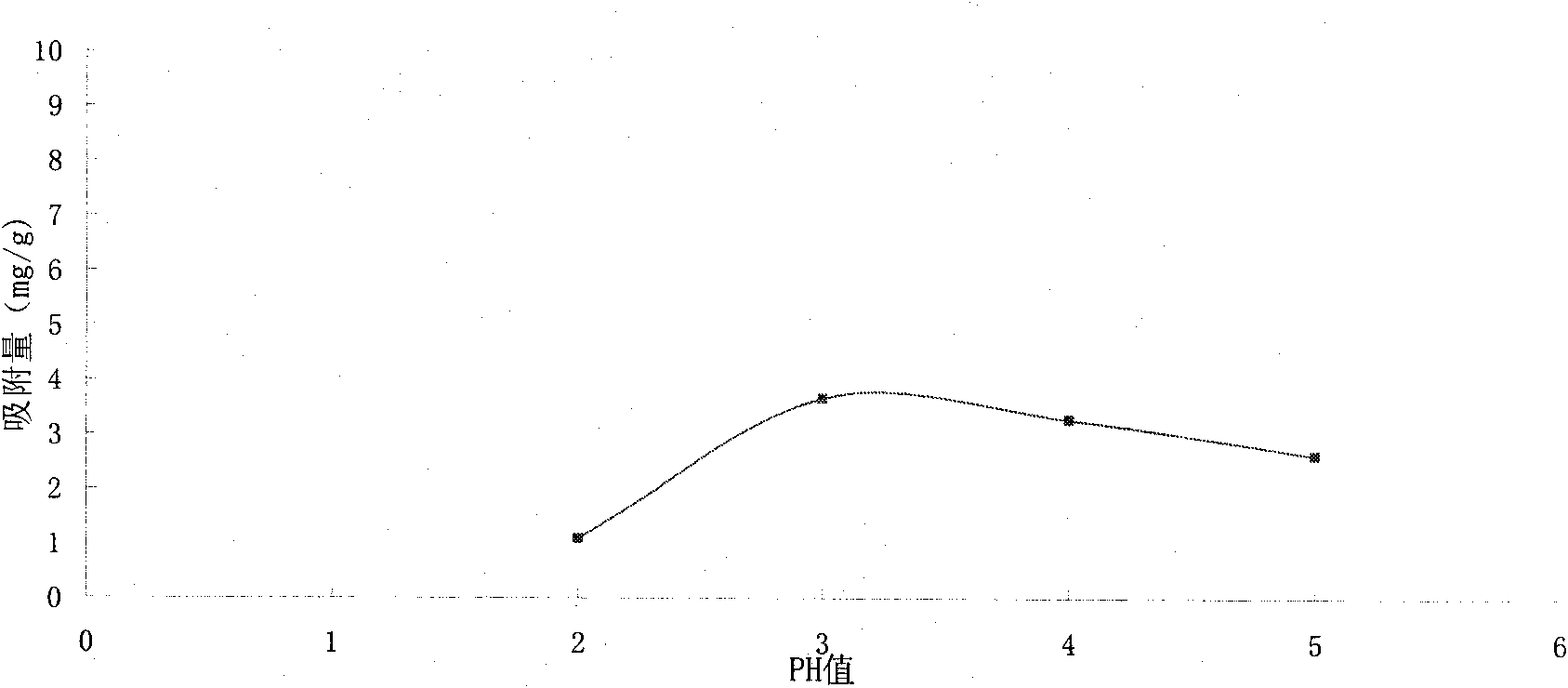
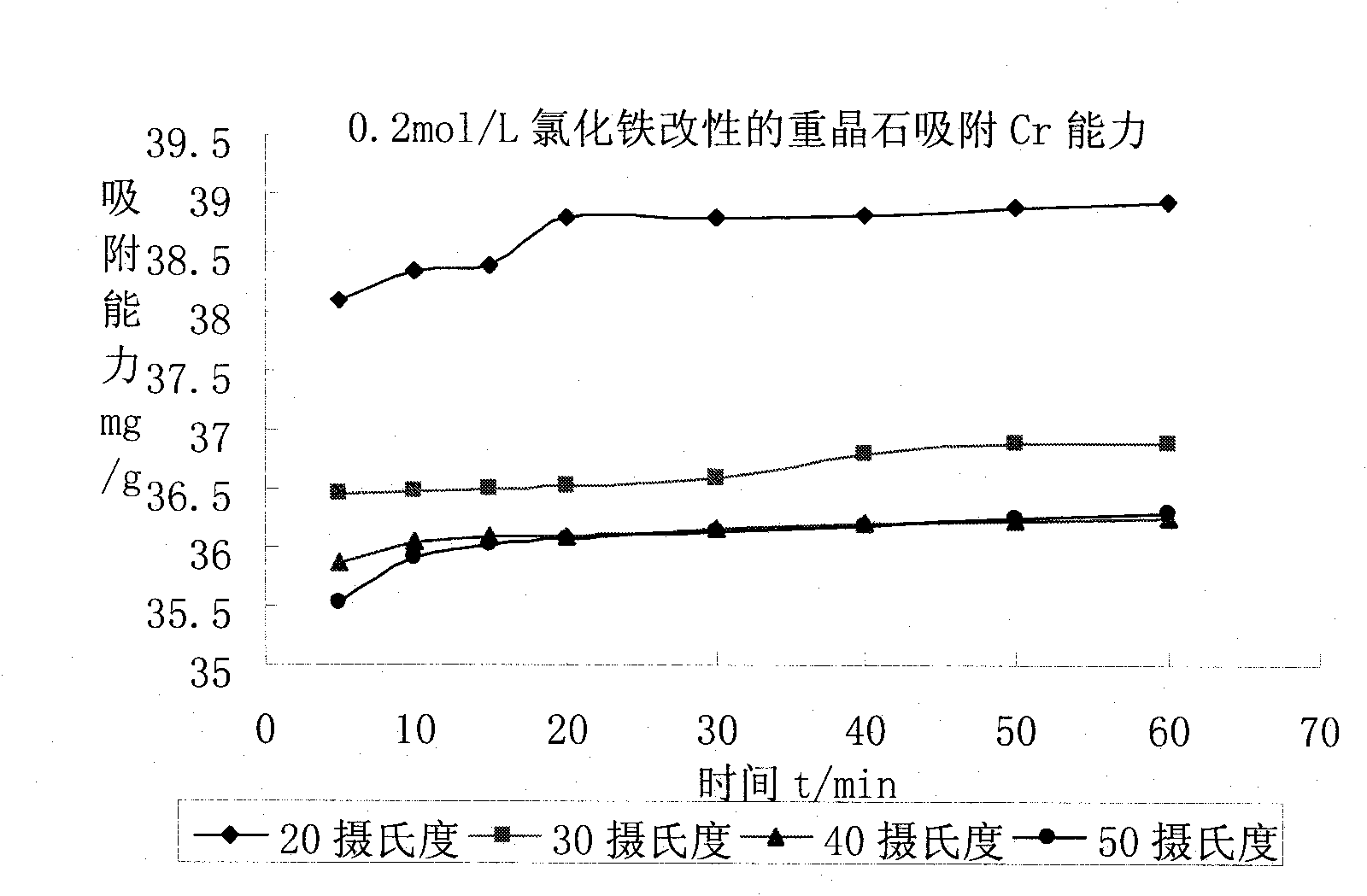
Method for treating chromium-containing wastewater by using barite adsorbent
A barite and adsorbent technology, which is applied in the field of barite adsorbent to treat chromium-containing wastewater, can solve the problems of no popularization, high power consumption, and little actual effect, and achieve easy popularization and application, simple preparation process, and easy operation convenient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] Preparation of the adsorbent:
[0026] The preparation method of barite adsorbent is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0027] 1. Put the barite mineral material in an electric blast drying oven and roast at 100-110°C for 3-4 hours, cool to room temperature, grind and sieve through 80-100 mesh to obtain barite powder;
[0028] 2. Mix the above-mentioned barite powder with 0.10-0.20mol / L ferric chloride solution according to the weight ratio of barite powder: ferric chloride solution = 2-3:100, oscillate at a constant temperature of 300 times / min for 20-24 hours and pump Filter, and wash the filter cake with distilled water 2 to 3 times;
[0029] 3. Dry the above-mentioned washed and filtered filter cake in a blast drying oven at a temperature of 140-150°C for 1-2 hours;
[0030] 4. Crush and grind the dried filter cake above, and sieve it with 80-100 meshes to get the barite adsorbent. figure 1 .
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: Screening of different adsorbents
[0032] Take 0.2g different adsorbents such as barite, natural zeolite, sepiolite, bentonite, kaolin, diatomaceous earth, vermiculite powder, and 100ml concentration of potassium chromate solution of 50mg / L (simulating chromium in electroplating wastewater ion concentration) mixed, shaken in a water bath constant temperature oscillator at 20°C for 1 hour, after the reaction, the solution was centrifuged, and the supernatant was put into a small test tube, and analyzed and detected by a Shimadzu AA-6200 atomic spectrophotometer.
[0033] Table 2 Screening of the best adsorbent
[0034] Adsorbent removal rate (%)
[0035] Barite 99.00
[0036] Natural zeolite 83.59
[0037] Meerschaum 85.93
[0038] Bentonite 81.45
[0039] Kaolin 76.06
[0040] Diatomaceous earth 65.91
[0041] Vermiculite powder 71.46
[0042] Experimental results: barite is used to adsorb and treat heavy metal chromium in wastewater, which is bet...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2 Different initial concentration is to the influence test of adsorption:
[0044] Take 0.5g of barite adsorbent and mix it with 100ml of potassium chromate solution (simulating the concentration of chromium ion in electroplating wastewater) with a concentration of 30, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 500mg / L respectively, and mix them at 20°C at room temperature , PH value of 3 to 4 conditions in a water bath constant temperature oscillator for 1 hour, after the reaction, the solution is centrifuged, the supernatant is taken into a small test tube, and analyzed by Shimadzu AA-6200 atomic spectrophotometer to detect Cr6+ ions concentration.
[0045] Table 3 Adsorption experiments at different initial concentrations (adsorption of Cr6+)
[0046] Cr6+ initial concentration Cr6+ removal rate
[0047] (mg / L)
[0048] 30 100.00%
[0049] 50 99.02%
[0050] 100 99.02%
[0051] 150 98.29%
[0052] 200 98.25%
[0053] 250 98.13%
[0054] 300 97.63%
[0055] 500...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com