Compound mycelium capable of degrading sulpho-glucoside and applications thereof
A technology of glucoside and compound bacteria, applied in the field of applied microorganisms, can solve the problems of not considering the influence of content, low efficiency of glucoside degradation, single enzyme system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Embodiment 1: the screening of bacterial strain
[0014] 1 medium
[0015] Basal medium: use rapeseed meal cake at a ratio of 1:6 (g / ml) to add water at about 90°C, heat in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes, filter after cooling, and take the filtrate as the basal medium.
[0016] Culture medium for isolating bacteria: add 0.05% beef extract, 0.15% peptone, 0.5% NaCl, 2% agar, 0.15% natamycin to the basal medium, pH7.0-7.2.
[0017] Isolation fungal medium: basal medium plus K 2 HPO 4 0.1%, KCl 0.5%, MgSO 4 0.05%, FeSO 4 0.001%, agar 2%, chloramphenicol 0.1%, PH natural.
[0018] Strain re-screening medium: remove protein from basal medium, add 2% agar after filtration, pH is natural.
[0019] Solid-state fermentation medium: 15g of crushed rapeseed meal.
[0020] 2 Screening of dominant degrading strains
[0021] 2.1 Isolation, purification and screening of strains
[0022] Take 1g of soil to prepare soil dilution and dilution gradient, make two parallels...
Embodiment 2
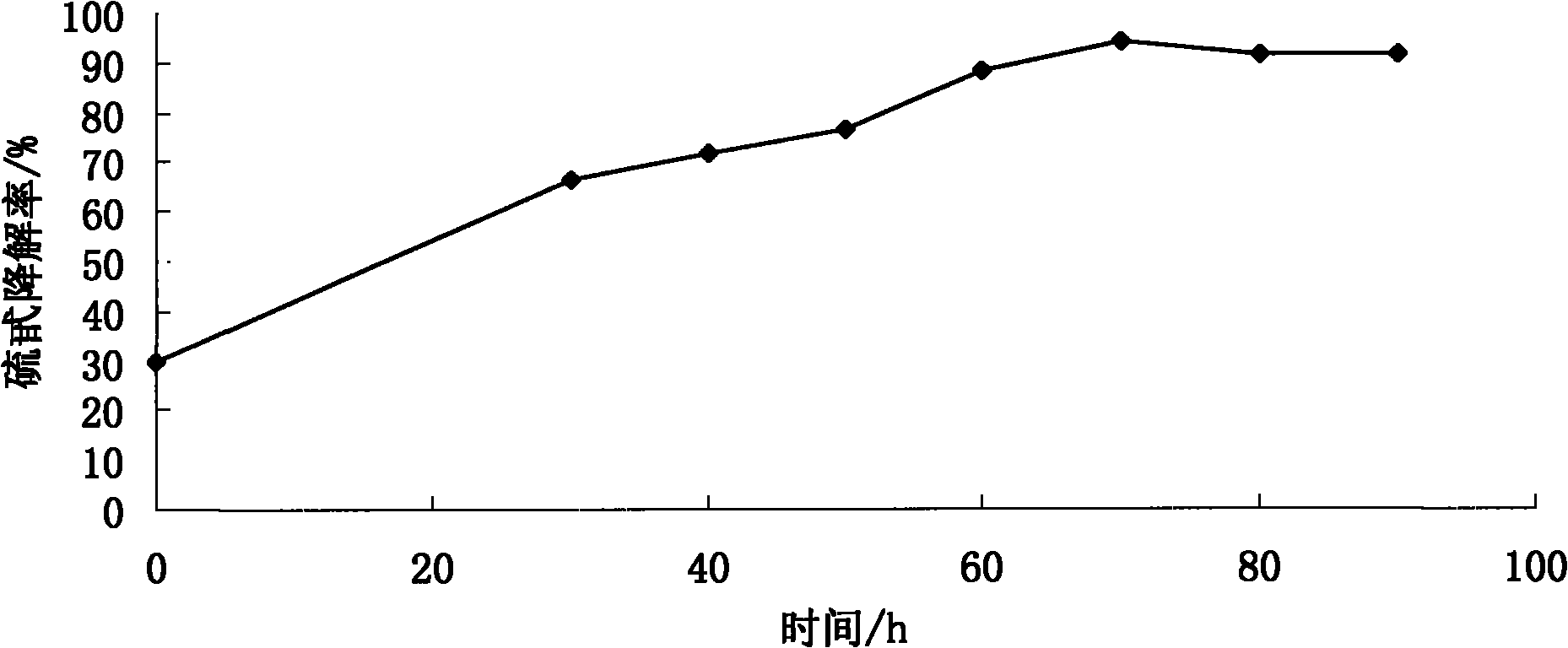
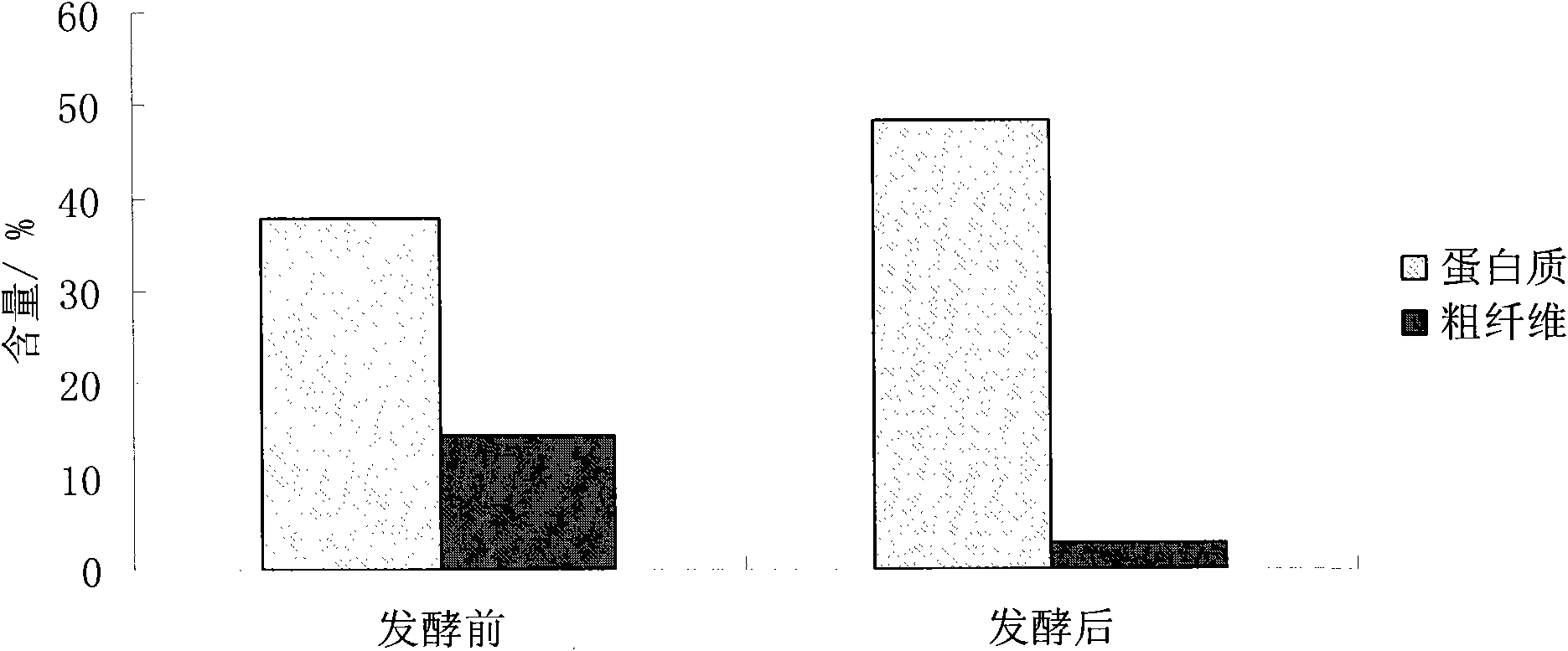
[0032] Effect of the proportioning ratio of embodiment 2 strains on glucosinolate degradation rate and protein content
[0033] Preparation of yeast seed liquid: After the yeast is activated on the inclined surface of the YEPD solid test tube for 3 days, pick a ring into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask filled with 50ml of YEPD liquid medium, and culture it at 120r / min at 28°C for about 16h on a shaker to prepare the yeast seed liquid.
[0034] Preparation of the spore suspension: the mold was activated on the PDA slant medium for about 5 days, and then transferred to another test tube slant. After the spores matured, the spore suspension prepared on the slant was washed with 5 ml of sterile water.
[0035] Add 3% (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 Use as inorganic nitrogen source and 1% glucose, and choose fermentation temperature 30 ℃, material water ratio 1: 1.3, take different volumes of spore suspension and yeast seed liquid to compound, the inoculation amount and compounding situation of mold an...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Identification of embodiment 3 strains
[0042] 1.1 Morphological observation of strains
[0043] Connect the bacterial strains to the solid medium, and cultivate them under suitable conditions for a period of time to observe the plate colony morphology of the bacterial species.
[0044] 1.2 Molecular biological identification of strains
[0045] The bacteria isolated in this experiment were sent to Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. for identification.
[0046] 1.3 Results
[0047] 1.3.1 Morphological identification of plates
[0048] After strain C4 was placed on the PDA plate for 5 days, the colony layer was thin, small and round. The spore heads are dense, the surface is subdivided, khaki to yellowish brown, the apical capsule of the conidia is hemispherical, and the stalks are double-layered. See attached figure 1 . After the C8 strain was cultured on the PDA plate for 48 hours, the diameter of the colony could reach about 6cm, the colony shape was s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com