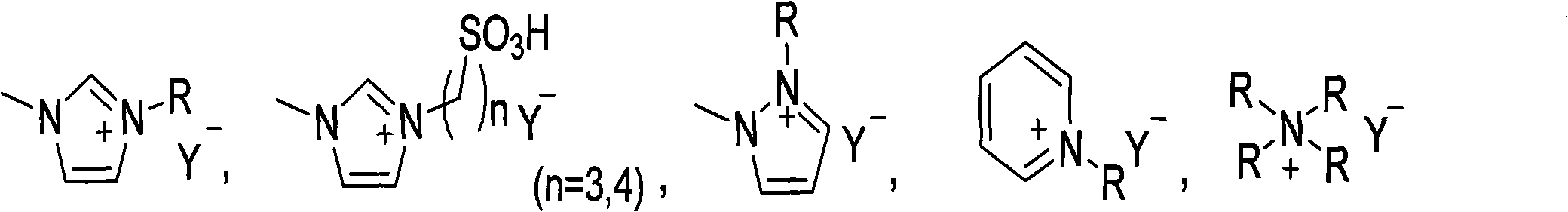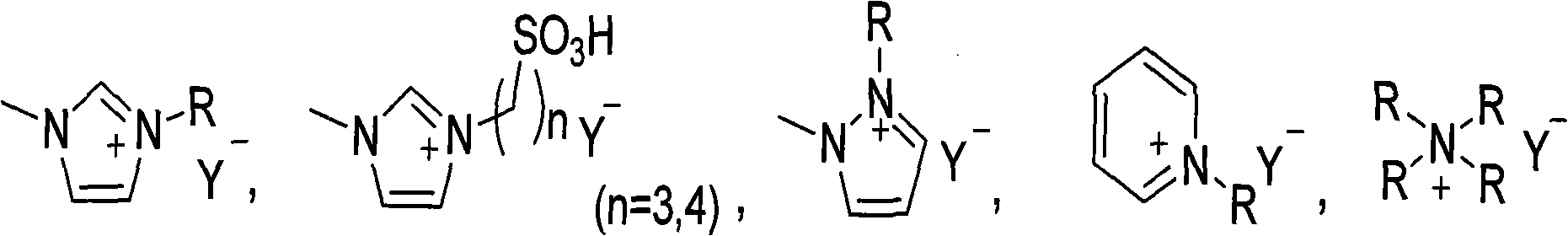Nucleoside preparation technology by using solvent-free melting method and catalyst used thereby
A catalyst, melting method, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, organic compound/hydride/coordination complex catalysts, preparation of sugar derivatives, etc. problems such as the need for base changes, to achieve the effects of stable reaction, improved yield and low carbonization degree
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
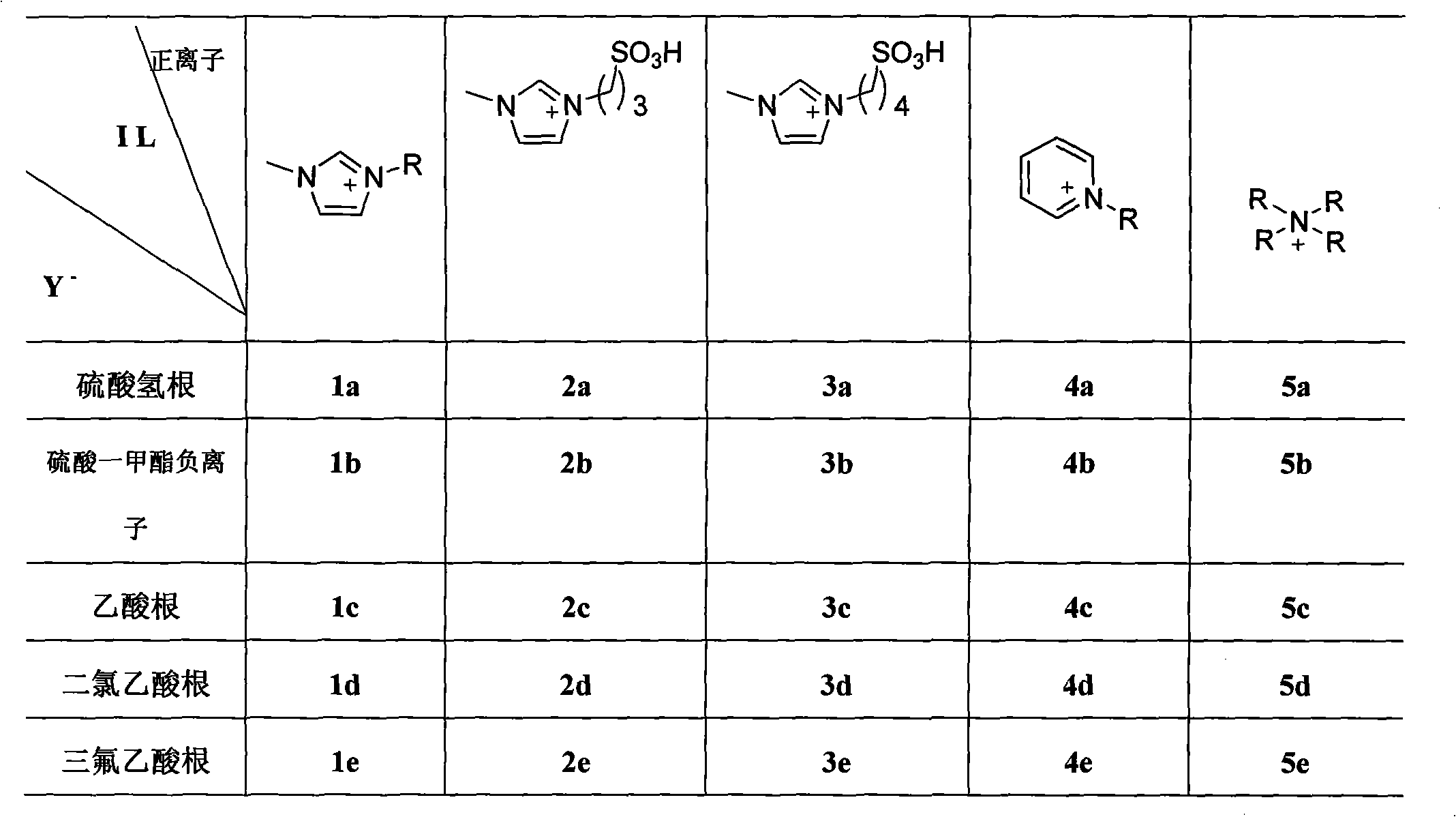
[0019] Example 1. A catalyst used in the preparation of nucleosides by a solvent-free melting method. The catalyst is an acidic or partially acidic ionic liquid as a catalyst. The ionic liquid catalyst is a quaternary ammonium salt type ionic liquid that is liquid at normal temperature. Molecular structure selected from:
[0020]
[0021] Among them, the positive ions are selected from the following five types of quaternary ammonium ions: imidazolium quaternary ammonium cations, imidazolylpropane / butanesulfonic acid quaternary ammonium cations, pyrazole quaternary ammonium cations, pyridinium quaternary ammonium cations, tetraalkyl ammonium cations, Quaternary ammonium positive ions, they are all quaternary ammonium ions substituted by alkyl R, R is a normal alkyl group of C2-C9; negative ion Y - It is a negative one-valent inorganic acid or organic acid radical, selected from: hydrogen sulfate, monomethyl sulfate anion, monoethyl sulfate anion, acetate, chloroacetate, dic...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2. In the catalyst described in Example 1: in the ionic liquid catalyst, R is a C3-C6 normal alkyl group.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Example 3. A process for preparing nucleosides using the solvent-free melting method of the catalyst described in embodiment 1 or 2, the steps of which are as follows: purines or pyrimidines and other heterocycles protected by equimolar amounts of carbohydrate derivatives and silylating Under the catalysis condition of the ionic liquid catalyst, the compound is heated to a molten state to obtain the corresponding nucleoside, and the heating temperature is controlled at 85-120°C; the sugar derivative is an acyl-protected sugar compound .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com