Plane-configured organic infrared or ultraviolet photovoltaic semiconductor detector
An organic ultraviolet light, planar configuration technology, applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of not meeting the requirements of practical infrared detectors, limiting the application of infrared detectors, and the response band is not ideal, achieving low power consumption, reducing device costs, Easy to form array effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
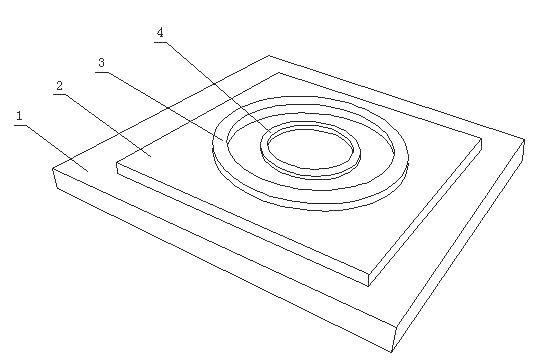
[0044] as attached image 3 As shown, a quartz plate is used as the substrate 1, and a 1 μm thick organic ultraviolet semiconductor anthracene 2 is deposited on the quartz substrate by thermal evaporation, and a high work function Au outer ring is deposited on the anthracene film by thermal evaporation with the help of a mask. Electrode 4, in which the width of the ring is 500 nm, and the thickness of the Au film is 300 nm. Similarly, a low work function yttrium inner ring electrode 3 is deposited on the anthracene film by thermal evaporation using a mask plate and precise alignment technology, wherein the width of the ring is 500 nm, and the thickness of the yttrium film is 300 nm.
[0045]
Embodiment 2
[0047] as attached Figure 4 As shown, a quartz plate is used as the substrate 1, and a 500nm high work function metal Au film is deposited on the quartz substrate by magnetron sputtering, and then the Au film is subjected to glue rejection, pre-baking, exposure, development, and film hardening. , etching, and glue removal to form the gold interdigitated right electrode 4, and then use a lift-off photolithography process to prepare a low work function metal yttrium interdigitated left electrode 3 with a thickness of 500 nm, dissolve the phenanthrene with cyclohexane, and absorb the phenanthrene with a dropper Cyclohexane solution, drop it on the interdigital electrode, and make the film thickness of phenanthrene reach 500nm after the solvent evaporates.
[0048]
Embodiment 3
[0050] as attached Figure 5 As shown, a glass sheet is used as a substrate 1, and a 1 μm-thick organic infrared semiconductor iodine-doped phthalocyanine erbium 2 is deposited on the glass substrate by thermal evaporation. Deposit high work function Au right strip electrode 4 on the erbium film, wherein the width of the Au strip is 500nm, the length of the Au strip is 2.5μm, and the thickness of the Au film is 300nm; Methods A low work function yttrium left strip electrode 3 was deposited on the iodine-doped erbium phthalocyanine film. The width of the yttrium strip was 500 nm, the length of the yttrium strip was 2.5 μm, and the thickness of the yttrium film was 300 nm.
[0051]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com