Method for recovering cobalt and lithium from waste lithium cobaltite and preparing lithium cobaltite
A waste lithium cobaltate and lithium cobaltate technology, which is applied in the fields of materials, resource recycling and metallurgy, can solve the problems of high energy consumption and high recycling cost, and achieve the effects of low energy consumption, low consumption of auxiliary materials and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
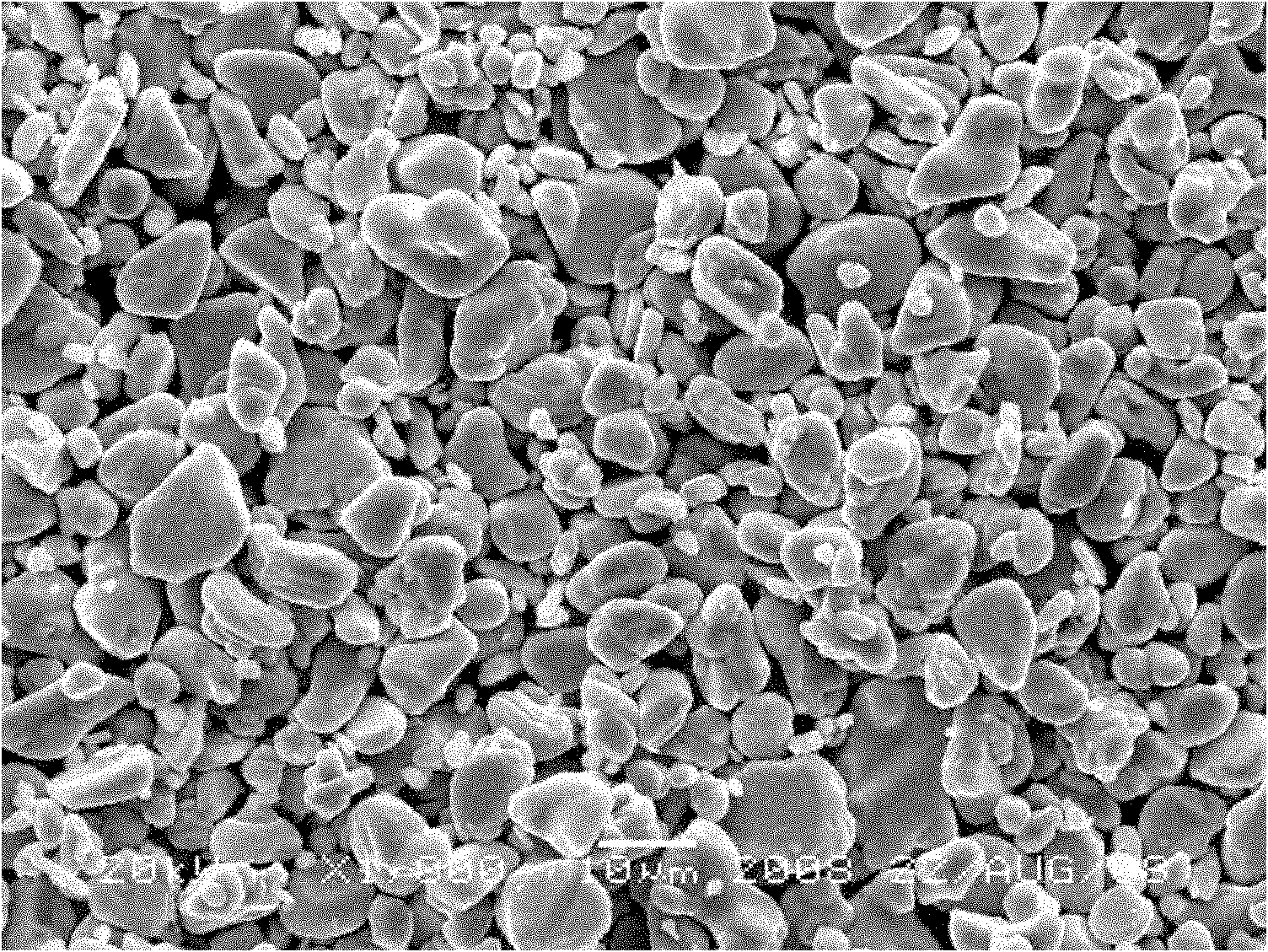
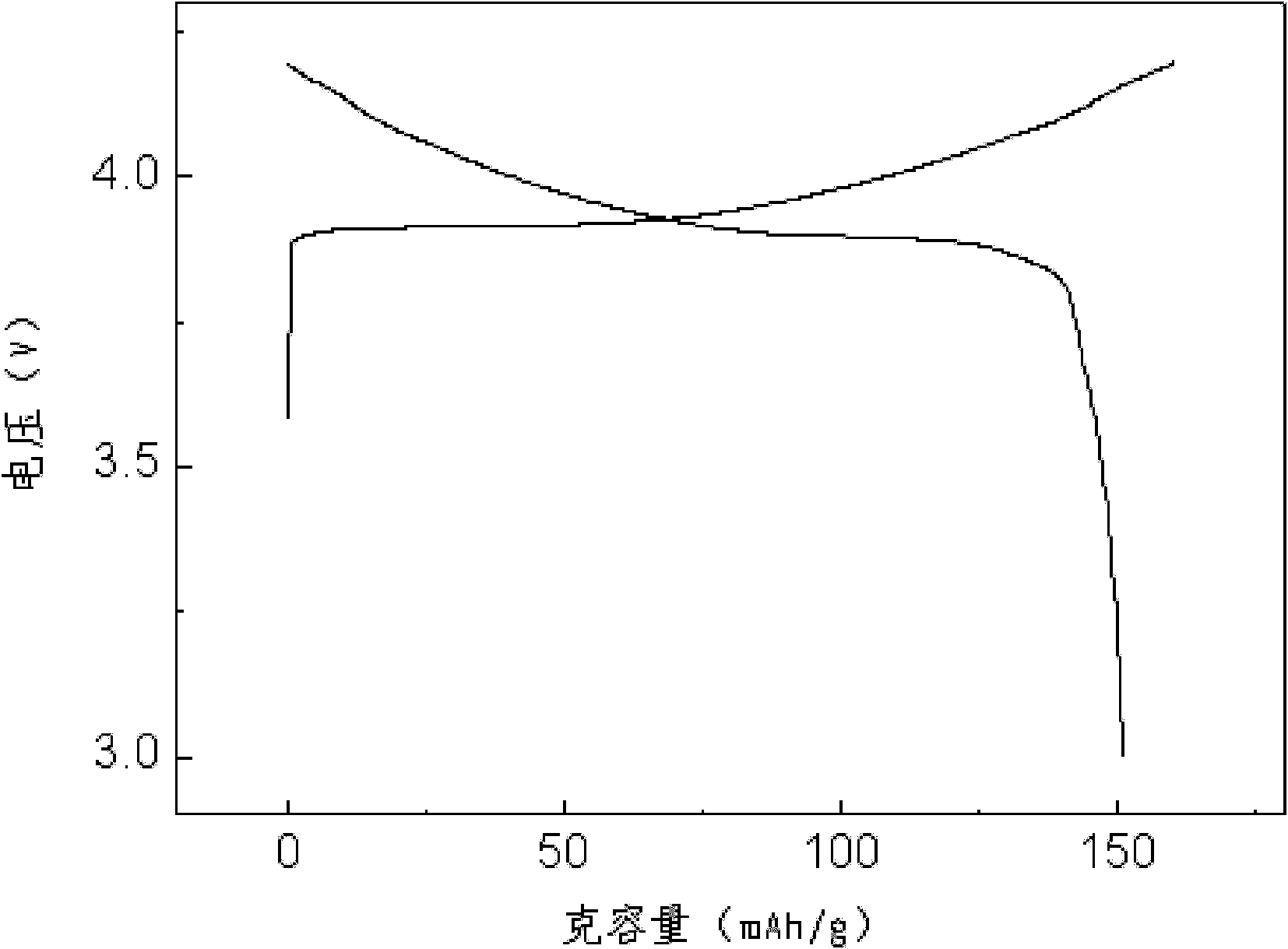
Examples
Embodiment 1
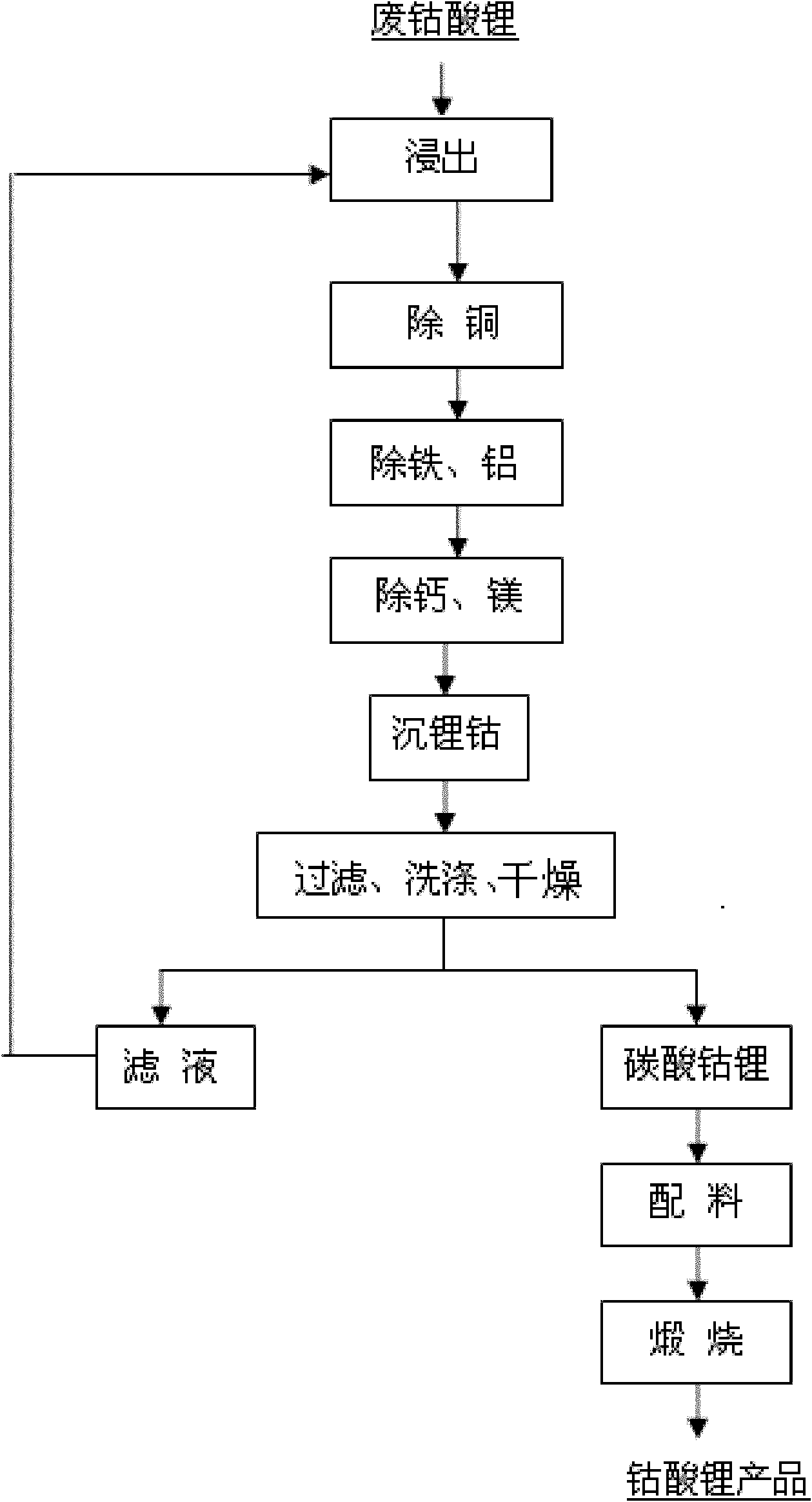
[0024] Take 2kg of spent lithium cobaltate, add 10L of water, add 1.7L of 98% sulfuric acid, slowly add 1.2L of 30% hydrogen peroxide, keep the temperature at about 65°C, keep stirring, react for 1.5h, and filter to obtain about 12L of filtrate. The copper in the solution was measured to be 10 mg / L, and 1.8 g of iron powder was added, stirred continuously, reacted for half an hour, and filtered to obtain about 12 L of filtrate. Add sodium carbonate to adjust the pH value of the solution after copper removal to 5.0 to remove iron and aluminum, keep stirring during the reaction and keep the system temperature at 70°C, and filter after the pH value reaches 5.0. After removing iron and aluminum, the calcium and magnesium in the solution were measured to be 5 mg / L and 65 mg / L, respectively, and 5 g of sodium fluoride was added. During the reaction, the temperature of the system was kept at 80 ° C with continuous stirring, and after half an hour of reaction, it was filtered. The sol...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Take 2kg of waste lithium cobaltate, add 10L of the filtrate after the precipitation of cobalt lithium in Example 1, add 2.1L of 36% hydrochloric acid and 1L of 98% sulfuric acid, slowly add 150g of iron powder, keep the temperature at about 65°C, and continue stirring. After reacting for 1.5h, filter to obtain about 10L of filtrate. Add sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value of the solution after copper removal to 4.8 to remove iron and aluminum, keep stirring during the reaction and keep the system temperature at 85°C, and filter after the pH value reaches 4.8. Calcium and magnesium in the solution after iron and aluminum removal were measured to be 5mg / L and 65mg / L, respectively, and 5g of sodium fluoride was added. During the reaction, the temperature of the system was kept at 80°C with continuous stirring, and after half an hour of reaction, the solution was filtered to obtain the solution after removal of impurities. About 10L, its composition is shown in Table 2...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Take 2kg of waste lithium cobaltate, add 10L of the filtrate after cobalt lithium precipitation in Example 2, add 1.7L of 98% sulfuric acid, slowly add 300g of sodium metabisulfite, keep the temperature at about 65°C, keep stirring, react for 1.5h, filter, Get about 10L of filtrate. The copper in the solution was measured to be 12 mg / L, and 2.0 g of iron powder was added, stirred continuously, reacted for half an hour, and filtered to obtain about 10 L of filtrate. Add ammonium carbonate to adjust the pH value of the solution after copper removal to 5.0 to remove iron and aluminum. During the reaction, keep stirring and keep the system temperature at 90°C. Filter after the pH value reaches 5.0. Calcium and magnesium in the solution after iron and aluminum removal were measured to be 10mg / L and 70mg / L respectively, and 7g of sodium fluoride was added, stirring was continued during the reaction and the temperature of the system was kept at 85°C, the reaction was filtered ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com