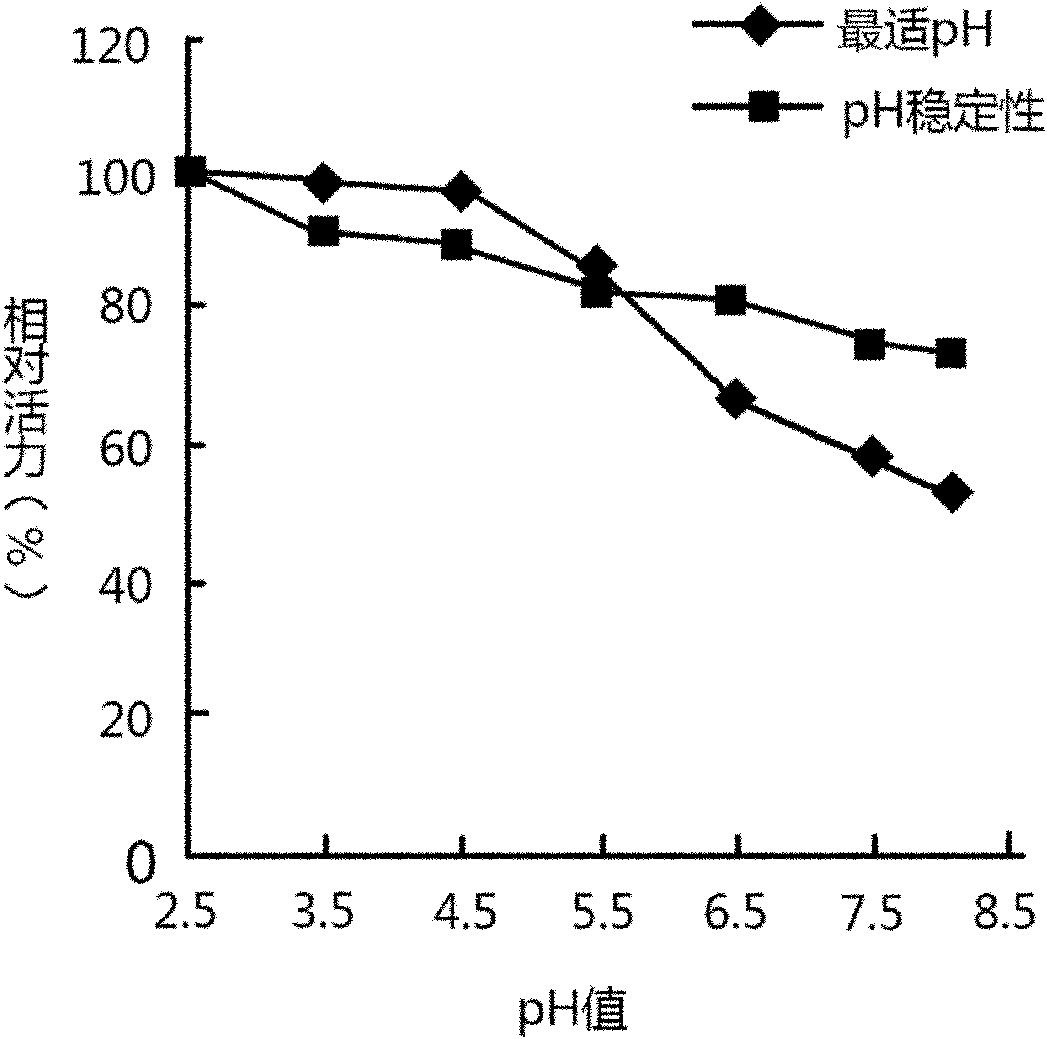
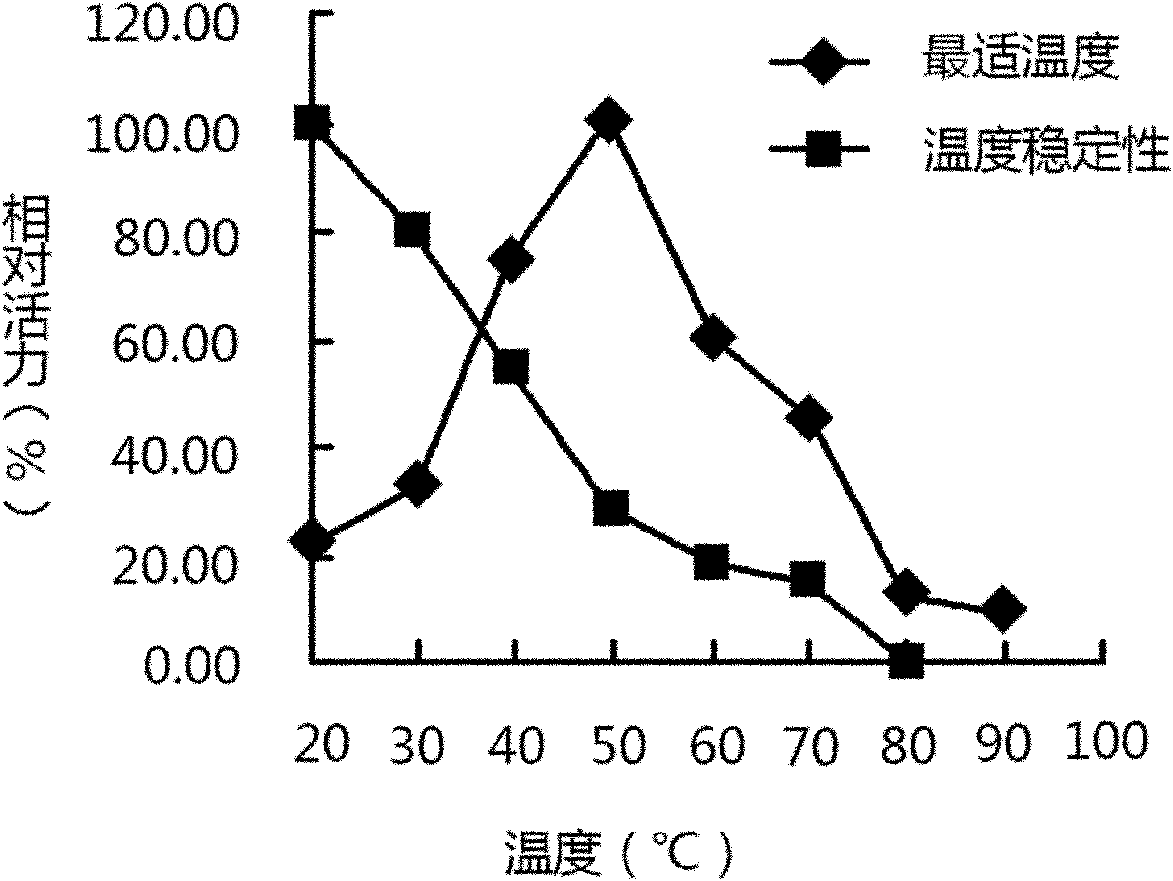
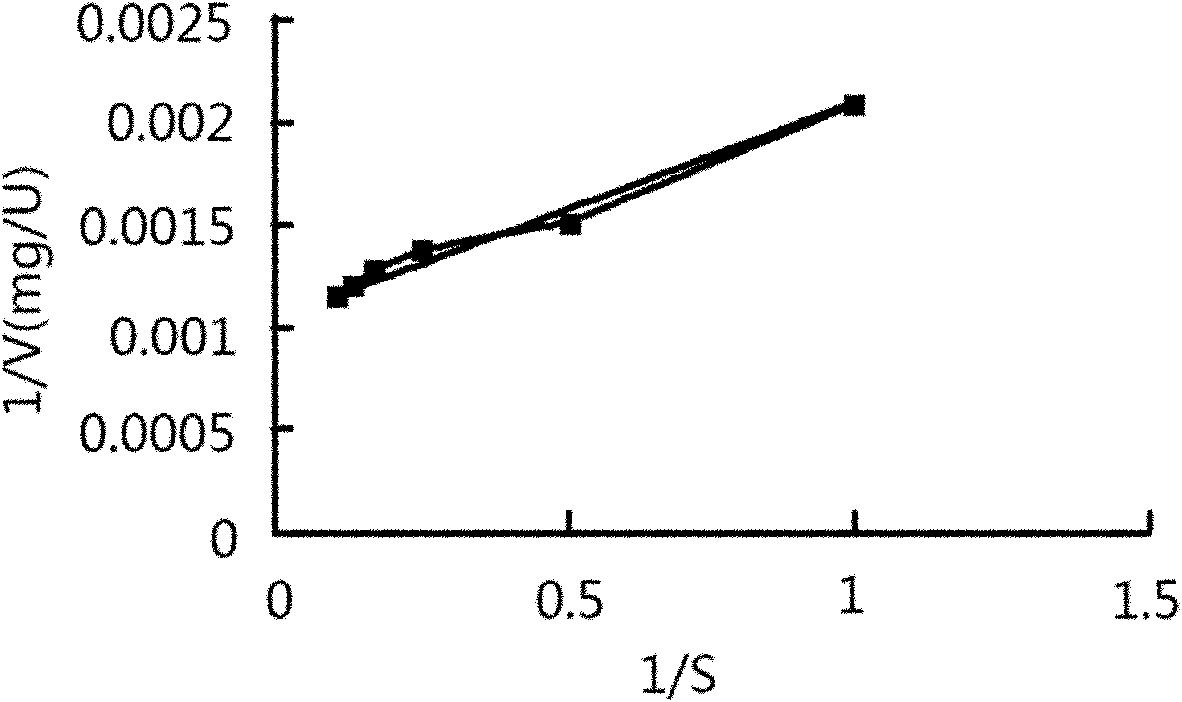
Bacterial strain for producing beta-mannanase and production process of bacterial strain
A technology of mannanase and bacterial strains, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of high cost, low activity of mannanase, and low yield, and achieve good pH value and temperature stability, good stability, and high enzyme activity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 Bacterial Strain Isolation and Purification
[0021] 1. Medium
[0022] Enrichment medium (g / L): konjac powder 20, KH 2 PO 4 0.5, pH natural;
[0023] Separation medium (g / L): konjac powder 5.0, yeast extract 2.0, peptone 10, KH 2 PO 4 0.1, MgSO 4 ·6H 2 O 0.12, agar 20.0, pH natural;
[0024] Fermentation medium (g / L): konjac powder 20.0, yeast extract 5.0, NaNO 3 5.0, MgSO 4 ·6H 2 O0.2,K 2 HPO 4 5.0, pH natural;
[0025] 2. Isolation of strains
[0026] Collect the soil samples from the konjac planting ground, dilute them with sterile water and let them stand, take an appropriate amount of supernatant and inoculate them into the enrichment medium, cultivate them on a shaker at 37°C for 36 hours, and take 1.0mL of the culture solution with the most obvious viscosity drop in the shaker flask , after gradient dilution according to the conventional method, spread on the separation medium plate, and then put it in a constant temperature incubator for...
Embodiment 2
[0027] The preliminary identification of embodiment 2 bacterial strains
[0028] According to the "Common Bacteria System Identification Handbook" and "Microbiology Experiment Handbook", the preliminary identification of its morphological characteristics, culture characteristics, physiological and biochemical assays, etc. was carried out.
[0029] The strain is a Gram-positive bacillus with a capsule. It can grow in the temperature range of 20-60°C, the optimum growth temperature is 37-50°C, the growth pH is 5-11, and the optimum growth pH is 7-8. Ability to hydrolyze starch, able to withstand 7% NaCl growth, nitrate reduction, catalase determination, V.P experiment, citrate and propionate utilization, nitrite reduction, gelatin liquefaction, methyl red experiment, casein hydrolysis results It was positive, and the results of hydrogen sulfide test and indole test were negative. The strain was identified and named as Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) Bacillus subtilis-hzb...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3 Fermentative production of β-mannanase
[0031] Inoculate the bacterial strain into the seed medium and cultivate it for 24 hours to obtain the seed liquid, put the seed liquid into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 30ml of fermentation medium, and place it in a rotary constant temperature and speed regulating shaker cabinet for aerobic fermentation , rotate at 200r / min, ferment at 37°C for 24 hours, centrifuge the fermentation broth at 1000r / min for 10 minutes, take the supernatant, which is the crude enzyme solution of β-mannanase, and store at 4°C.
[0032] Seed medium (g / L): sodium chloride 10, peptone 10, yeast extract 5, agar 20.
[0033] Fermentation medium (g / L): konjac powder 20.0, yeast extract 5.0, K 2HPO 4 5.0g, MgCl 2 .·6H 2 O 0.2, NaNO 3 5.0, pH5.5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com