Passive mode-locking laser based on graphite alkene having epitaxial growth on SiC substrate
A technology of epitaxial growth and passive mode-locking, which is applied in the field of laser technology and nonlinear optics, can solve the problems of complicated SESAM manufacturing process, narrow saturable absorption spectrum range, and unobvious saturable absorption effect, and achieve good thermal conductivity and Operability, large pulse energy, highly repeatable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
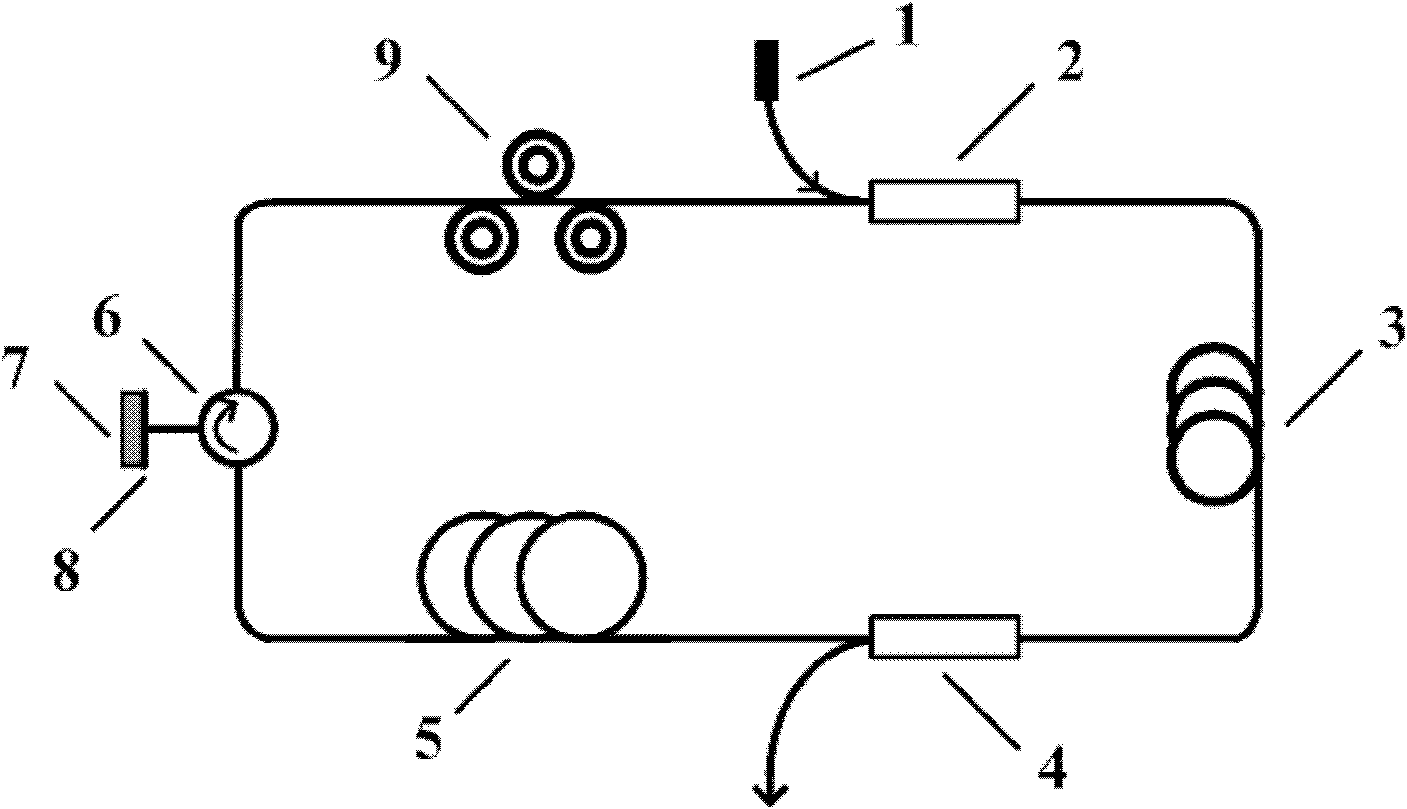
[0031] A graphene passive mode-locked laser structure based on SiC substrate epitaxial growth such as figure 1 shown. The pump source 1 with a central wavelength of 974nm is connected to the pump input end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2; the common end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2 is connected to a 1m long ytterbium-doped single-clad fiber 3; the other end of the ytterbium-doped fiber 3 Connect the laser beam splitter 4 with a splitting ratio of 20:80; the laser beam splitter 4 divides the light into two beams, 20% of the light is output from the output port of the beam splitter 4, and the other 80% of the light reaches the circulator 6 Port 1; since the light can only pass through the three ports of the circulator 6 sequentially in one direction, the light enters from the port 1 of the circulator 6, and the light coming out from the port 2 of the circulator 6 reaches the SiC substrate 7 after passing through the graphene 8, Since the SiC substrate 7 has...
Embodiment 2
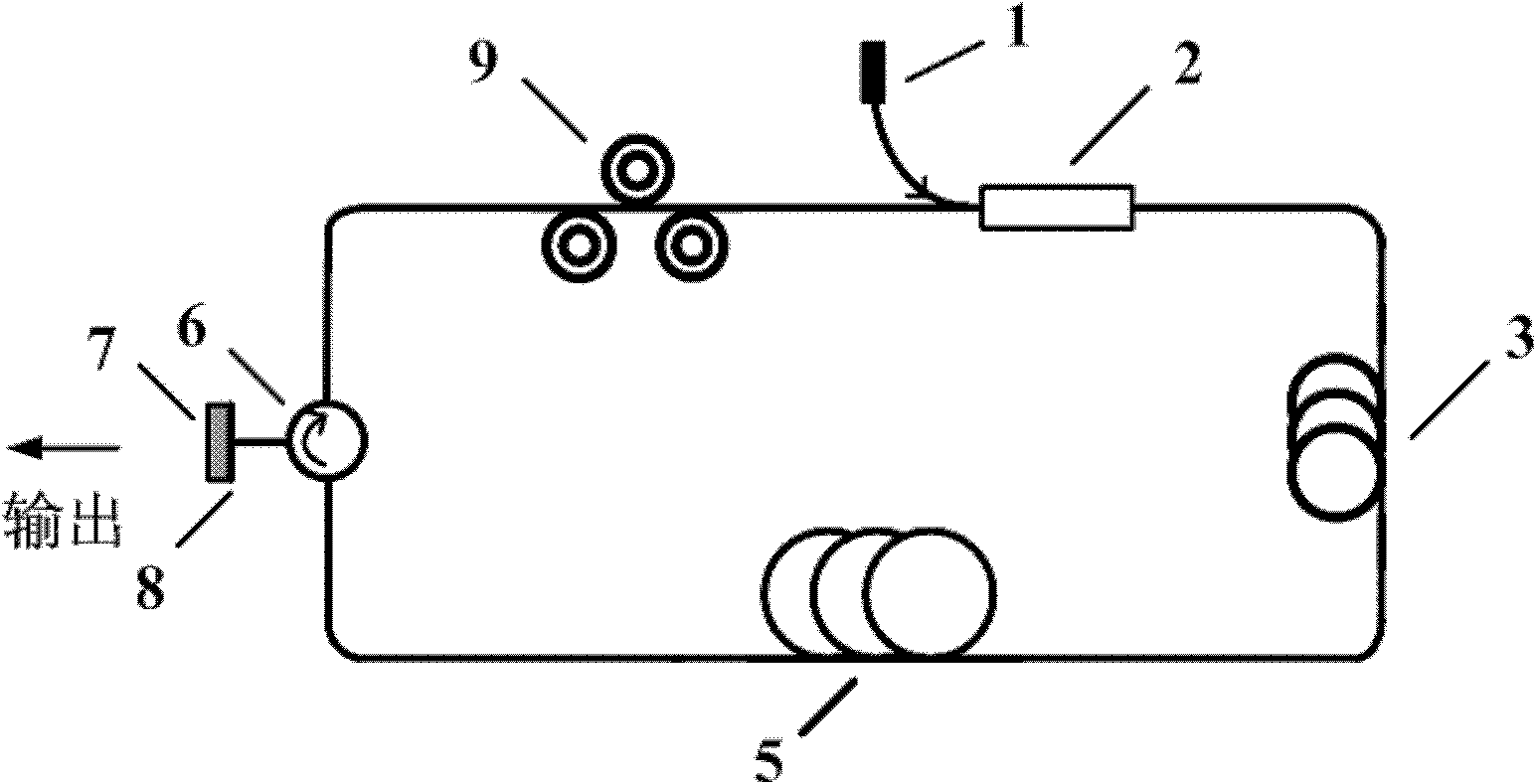
[0033] A graphene passive mode-locked laser structure based on SiC substrate epitaxial growth such as figure 2 shown. The pump source 1 with a central wavelength of 974nm is connected to the pump input end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2; the common end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2 is connected to a 1m long ytterbium-doped single-clad fiber 3; the other end of the ytterbium-doped fiber 3 Connecting the terminal 1 of the circulator 6, since the light can only pass through the three ports of the circulator 6 sequentially in one direction, the light enters through the port 1 of the circulator 6, and the light coming out of the port 2 of the circulator 6 arrives after passing through the graphene 8 SiC substrate 7, because SiC substrate 7 has a certain reflection to laser light, so part of the light is output from SiC substrate 7, and another part of light is reflected by SiC substrate 7 and then passes through port 2 of circulator 6 to reach the end of circu...
Embodiment 3
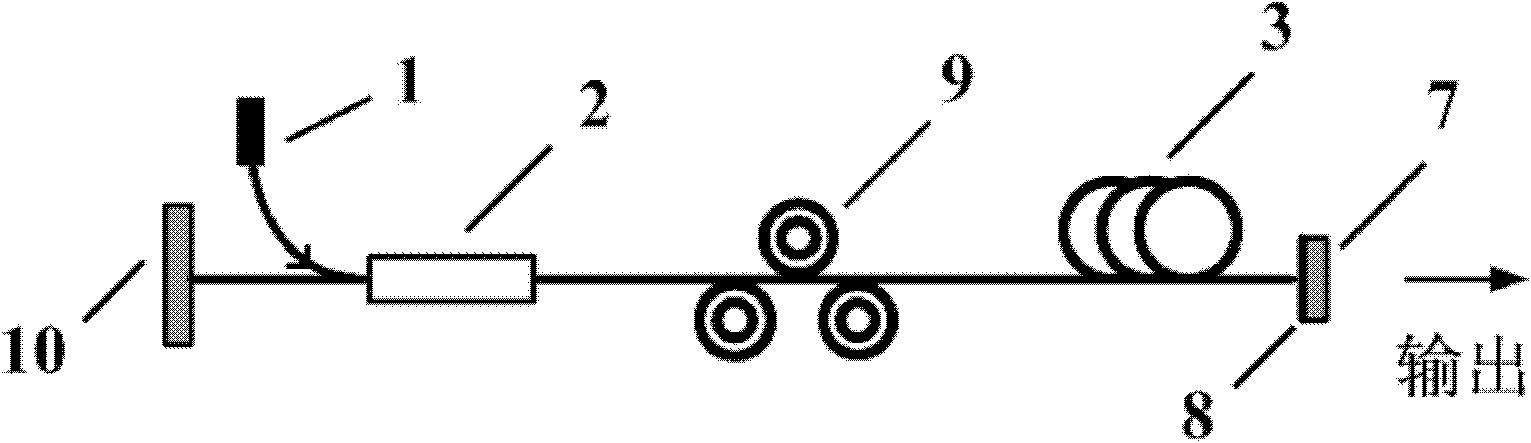
[0035] A graphene passive mode-locked laser structure based on SiC substrate epitaxial growth such as image 3 shown. The pump source 1 with a center wavelength of 974nm is connected to the pump input end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2; the common end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2 is connected to one end of the polarization controller 9; and the other end of the polarization controller 9 is connected to a 3m long The erbium-doped fiber 3; the other end of the erbium-doped fiber 3 is connected to the graphene 8 grown on the SiC substrate 7. The other end of the wavelength division multiplexer 2 is connected to a fiber Bragg grating 10 with a reflectivity of 99%; the SiC substrate 7 has a certain reflection of laser light, so a resonant cavity is formed between the SiC substrate 7 and the fiber Bragg grating 10, and the SiC substrate 7 is used as a laser output mirror to realize mode-locked pulse laser output.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com