Lipoid cation function molecule synthesized from natural cholesterol and amino acid and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of natural amino acids and functional molecules, which is applied in the field of synthesizing lipid-like biological carrier materials, can solve the problems of complex and tedious synthesis steps, poor generality of synthetic preparation methods, etc., achieves high gene transfection efficiency, and is easy to scale at low cost. Preparation and application promotion, the effect of low cytotoxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
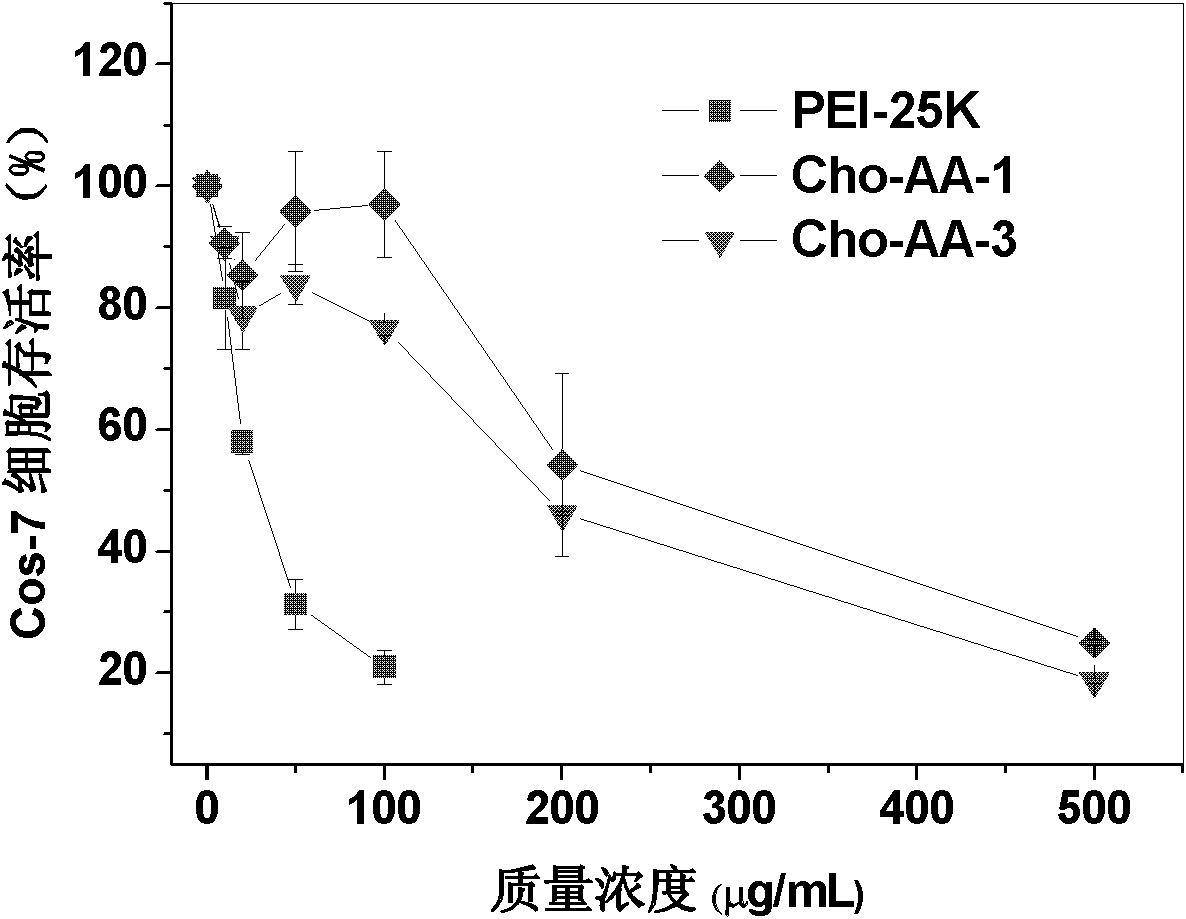
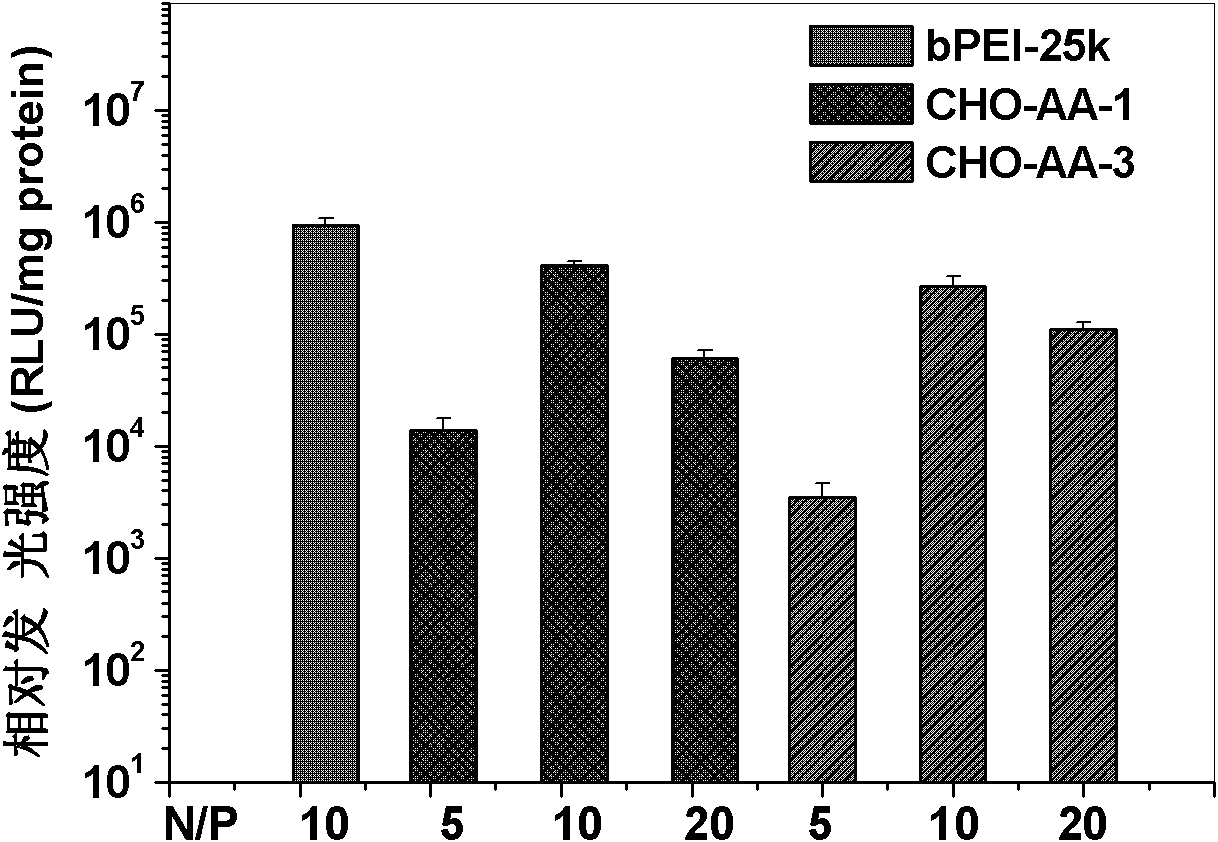
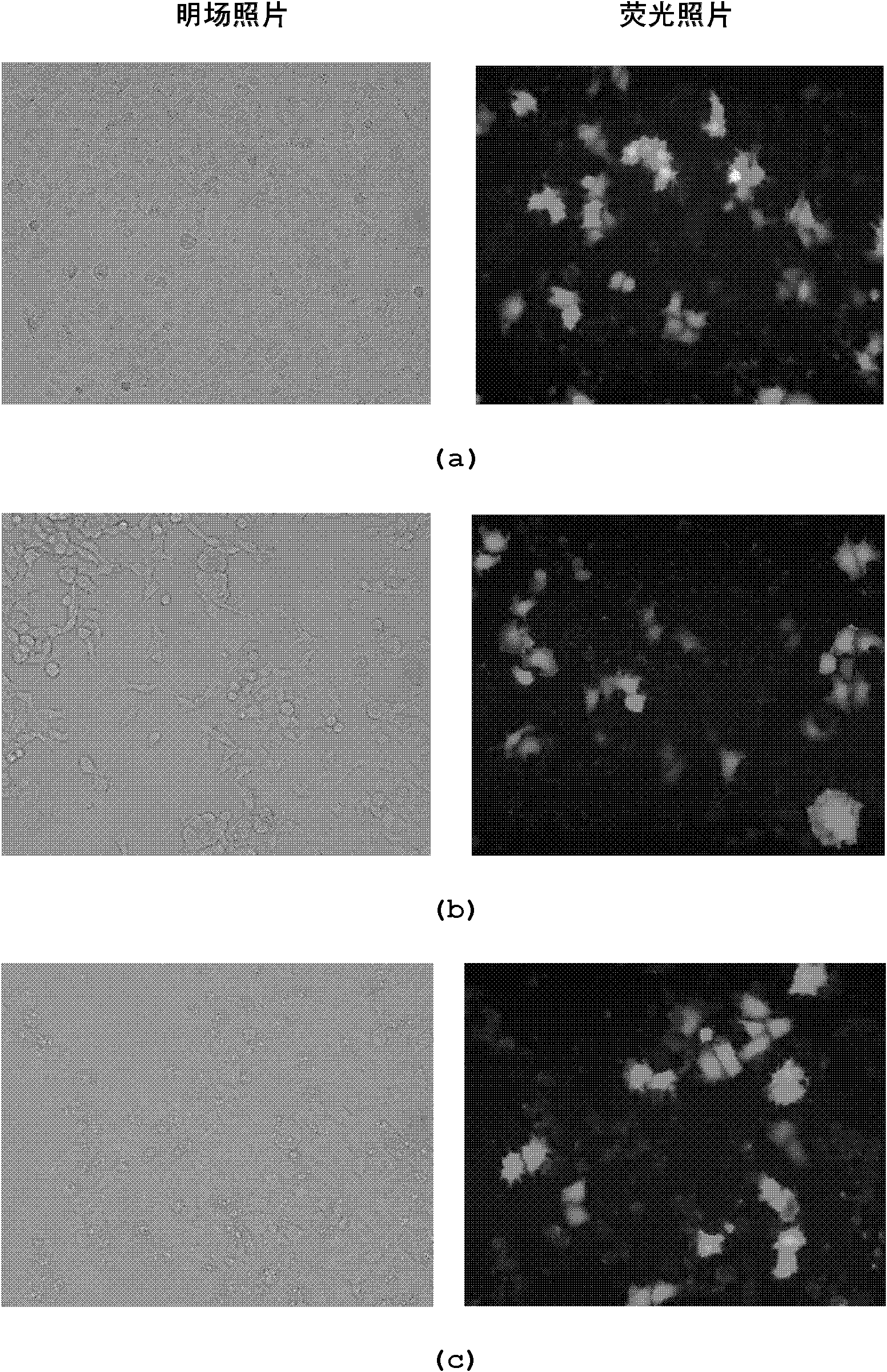
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029]
[0030] Lipid compound CHO-AA-1
[0031] The first step: dissolving hexanediol (12.2g, 0.1mmol) in 30ml of dry dichloromethane, the above solution was slowly added dropwise to cholesterol chloroformate (4.5 ml of triethylamine dissolved in 100ml of dry dichloromethane) g, 0.01 mol) solution, stirred and reacted at 40 °C for 5 h, then distilled off the organic solvent, passed through column chromatography (eluent: ethyl acetate / petroleum ether=1 / 2 v / v), and prepared cholesterol hexylene glycol monolayer The ether carbonate intermediate was synthesized in 80% yield.
[0032] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 300MHz): 5.32 (s, 1H, C=CH, cholesterol), 4.54 (t, 2H, J=6.3 Hz, CH 2 OCO), 4.51(m, 1H, OCOCH), 4.36(t, 2H, J=6.3Hz, CH 2 OCO), 3.79(t, 2H, J=6.3Hz, CH 2 O), 2.30-0.95 (m, 45H, cholesterol) ESI-MS: [M + ]=531.1m / z
[0033] The second step: BOC-lysine (3.5g, 0.01mol) was dissolved in 50ml of dry dichloromethane, and slowly added dropwise to the cholesterol hexanediol monohy...
Embodiment 2
[0037]
[0038] Lipid compound CHO-AA-2
[0039] The first step: dissolving hexanediol (12.2g, 0.1mmol) in 30ml of dry dichloromethane, the above solution was slowly added dropwise to cholesterol chloroformate (4.5 ml of triethylamine dissolved in 100ml of dry dichloromethane) g, 0.01mol) solution, the organic solvent was distilled off after stirring at 40°C for 5h, and then passed through column chromatography (eluent: ethyl acetate / petroleum ether=1 / 2v / v) to prepare cholesterol hexylene glycol monolayer. The ether carbonate intermediate was synthesized in 80% yield.
[0040] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 300MHz): 5.32 (s, 1H, C=CH, cholesterol), 4.54 (t, 2H, J=6.3 Hz, CH 2 OCO), 4.51(m, 1H, OCOCH), 4.36(t, 2H, J=6.3Hz, CH 2 OCO), 3.79(t, 2H, J=6.3Hz, CH 2 O), 2.30-0.95 (m, 45H, cholesterol)
[0041] ESI-MS: [M + ]=531.1m / z
[0042] The second step: BOC-histidine (3.5g, 0.01mol) was dissolved in 50ml of dry organic solvent, and slowly added dropwise to the cholesterol hexanedi...
Embodiment 3
[0046]
[0047] Lipid compound CHO-AA-3
[0048] The first step: dissolving hexanediol (12.2g, 0.1mmol) in 30ml of dry dioxane, the above solution was slowly added dropwise to the cholesterol p-toluenesulfonate ( 5.4g, 0.01mol) solution, stirred and reacted at 80°C for 24h, distilled off the organic solvent, and passed through column chromatography (eluent: ethyl acetate / petroleum ether=1 / 2v / v) to obtain cholesterol hexanediol monoether Intermediate, the synthetic yield is 62%.
[0049] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 300MHz): 5.32 (s, 1H, C=CH, cholesterol), 3.50 (t, 2H, J=6.3 Hz, CH 2 OH), 3.37 (t, 2H, J=5.1 Hz, CHOCH 2 ), 2.30-0.95 (m, 45H, cholesterol)
[0050] ESI-MS: [M + ]=486.4m / z
[0051]The second step: BOC-lysine (3.5g, 0.01mol) was dissolved in 50ml of dry tetrahydrofuran, and slowly added dropwise to the previous step obtained by being dissolved in 20ml of dry tetrahydrofuran under the catalysis of 0.5g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine Cholesterol hexanediol monoether inte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com