Medical moist composite dressing and preparation method thereof
A manufacturing method, wet technology, applied in medical science, non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of frequent replacement of medical wet dressings, achieve the effect of facilitating the growth of crawling, reducing the number of replacements, and accelerating healing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
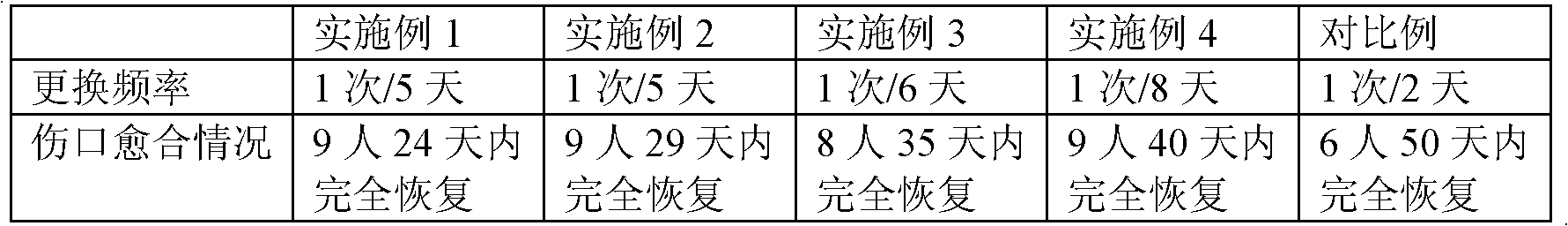
Embodiment 1
[0029] First, the polyglycol lactide slices are dried under vacuum (vacuum degree 750-760mmHg) for 12 hours at a drying temperature of 120°C, and the moisture content of the slices after drying is less than 80 ppm. The dried polyglycolide chips are extruded by a screw on a spinning and drafting integrated machine, drafted in two stages, and wound to obtain polyglycolide filaments. The screw temperature is respectively: Zone 1 220 ℃, Zone 2 230℃, zone 3 230℃, zone 4 240℃; spinning melt pump (0.3cc) speed is 16r / min; the temperature and speed of the first drafting roll are 50℃, 120m / min; second drafting The temperature and speed of the roller are respectively 70°C and 380m / min; the temperature and speed of the third drafting roller are 120°C and 600m / min respectively; the winding speed is 580m / min. The obtained fiber had a breaking strength of 5.8 cN / dtex, a breaking elongation of 22.0%, and a strength retention rate of 30 to 50% in 2 weeks. After the obtained polyglycolide fila...
Embodiment 2
[0032] According to the same method as described in Example 1, a polyglycolide staple fiber with a monofilament fineness of 2.5dtex and a length of 55mm was obtained. The polyglycolide staple fiber and the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose staple fiber (monofilament fineness 1.5dtex, fiber length 51mm, breaking strength 1.5~3.5cN / dtex) pre-mixed according to the weight ratio of 30:70, and then go through opening, mixing, carding, laying, pre-needling, lower main needle, upper main needle, heat treatment (110℃), forming and processing into needle punched non-woven fabric. For the acupuncture process, select 40# puncture needle, puncture 3 times, the depth of acupuncture is 6mm, 3~4mm, 3~4mm respectively. Among them, the density of the medical composite dressing is controlled to 160g / m by adjusting the thickness of the mesh 2 , The water absorption rate reaches more than 10 times, and the bidirectional breaking elongation rate> 30%. Adjust the pH of the medical composite dressing t...
Embodiment 3
[0034] According to the same method as described in Example 1, a polyglycolide staple fiber with a monofilament fineness of 3.5dtex and a length of 76mm was obtained. The polyglycolide staple fiber and the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose staple fiber (monofilament fineness 1.5dtex, fiber length 45mm, breaking strength 1.5~3.5cN / dtex) pre-mixed according to the weight ratio of 40:60, and then go through opening, mixing, carding, laying, pre-needling, lower main needle, upper main needle, heat treatment (140℃), formed, processed into needle punched non-woven fabric, and then sterilized by gamma rays. For the acupuncture process, select 40# puncture needle, puncture 3 times, the depth of acupuncture is 6mm, 3~4mm, 3~4mm respectively. Among them, the density of the medical composite dressing is controlled to 130g / m by adjusting the thickness of the mesh 2 , The water absorption rate reaches more than 10 times, and the bidirectional breaking elongation rate> 30%. Adjust the pH of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com