Rice wine yeast metabolic engineering bacterium low in urea yield and construction method thereof
A rice wine yeast, metabolic engineering technology, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, to achieve the effects of reducing urea secretion, low urea production level, and low EC content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1, TPI1 p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t Gene cassette construction
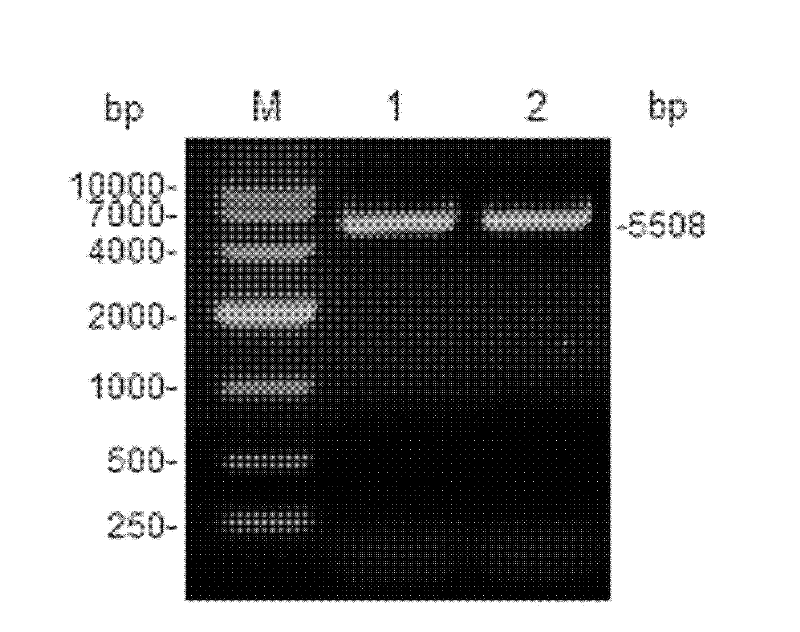
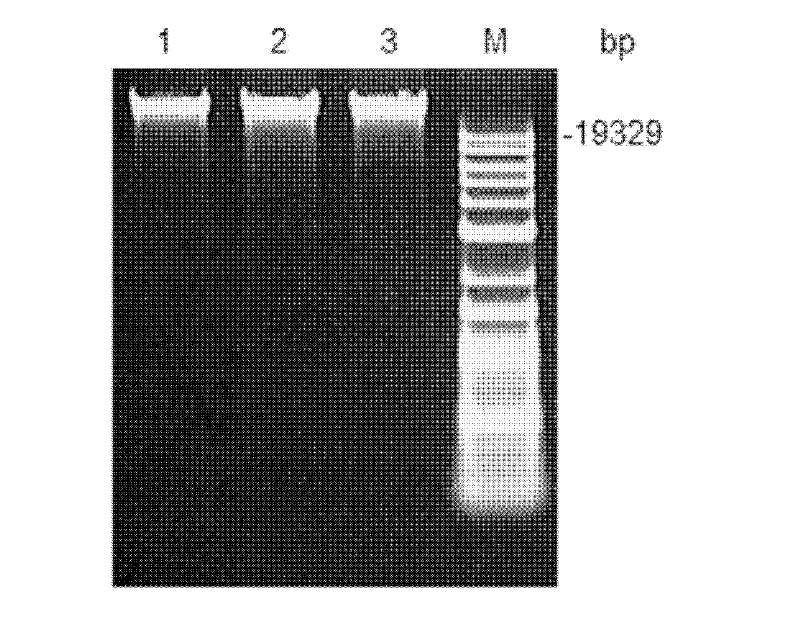
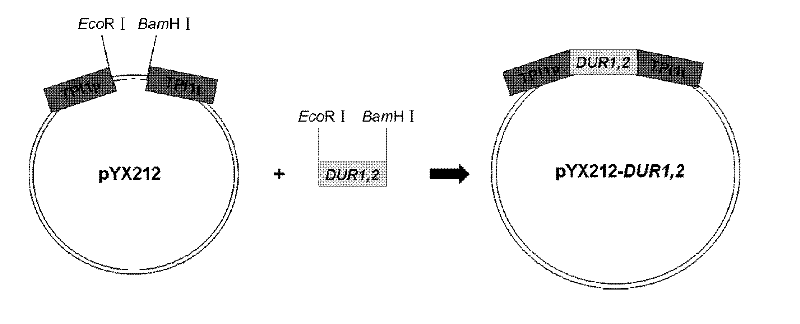
[0021] Yeast genome extraction kit was used to extract the total DNA of rice wine yeast genome ( figure 1 ). Utilize the Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.cerevisiae) standard strain genome sequence database (http: / / www.yeastgenome.org / ) information published on the Internet, design appropriate primers and restriction sites (P1: ACTGAG GAATTC ATGACAGTTAGTTCCGATACAACTGCTG, EcoR I; P2: TCAGGA GGATCC TCATGCCAATGTCTCTATGACGGCCACT, BamH I), with the extracted genomic DNA as template, PCR amplification obtains DUR1, 2 gene coding frame sequence ( figure 2 ), after double-digesting the gene and Escherichia coli-Saccharomyces cerevisiae shuttle plasmid pYX212 (Invitrogen), the recombinant plasmid pYX212-DUR1,2 was constructed by DNA ligation reaction, so that the expression of DUR1,2 was placed in the constitutive high-expression promoter TPI1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae p TPI1 t under control ( image 3 and ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2, trp1-TPI1 p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t - Construction of the trp1 gene cassette
[0023] Design primers (P3: TCAGGA CCATGG CATTTAATAGAACAGCATCGT,Nco I;P4:ACTGAG AAGCTT CTTCTGAATCAAACAAG, Hind III), cloned a 1104bp TRP1 gene fragment including the coding frame and part of the upstream and downstream sequences from the rice wine yeast genome, and subcloned it into the vector YRp7 through DNA restriction and ligation reactions to construct the recombinant plasmid YRp7-trp1. Design primers for TPI1 by PCR p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t The restriction site EcoR V was added to both ends of the gene cassette. Simultaneous digestion of YRp7-TRP1 and TPI1 with EcoR V p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t , through DNA ligation, the recombinant plasmid YRp7-(trp1-TPI1 p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t -trp1)( Figure 5 ). By designing head-to-tail primers and performing PCR with the recombinant plasmid as a template, trp1-TPI1 with 562bp and 542bp trp1 homology arms at both ends can be amplified in one step p -DUR1,2...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Embodiment 3, integrated with TPI1 p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t Obtaining engineering strains of gene cassettes
[0025] Linear trp1-TPI1 was transformed by lithium acetate conversion p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t -The trp1 gene cassette fragment and the circular plasmid pUT332 (containing the phleomycin resistance gene) are exogenous DNA, and the two are co-transformed with competent rice wine yeast, and then the transformants are screened with a selection medium plate (YPD+100 μg / mL phleomycin), and the colonies PCR identified TPI1 p -DUR1,2-TPI1 t The gene cassette was successfully integrated into the engineering strain of the TRP1 gene locus, and the correctness of the integrated sequence was confirmed by DNA sequencing ( Figure 6 ). Use non-selective medium (YPD) to continuously subculture yeast engineering strains for 10 generations, and use the phenomenon that the intracellular plasmids of wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae are unstable and easy to lose (the loss probability of in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com