Superfine high-dispersion super-paramagnetism ferrate nano particles and preparation method thereof
A nanoparticle and superparamagnetic technology, which is applied in the field of ultrafine and highly dispersed superparamagnetic ferrite nanoparticles and its preparation, can solve the problems of high synthesis temperature and high cost of raw materials, and achieve low reaction temperature, simple operation, small size Narrow distribution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Below further illustrate the present invention by embodiment:
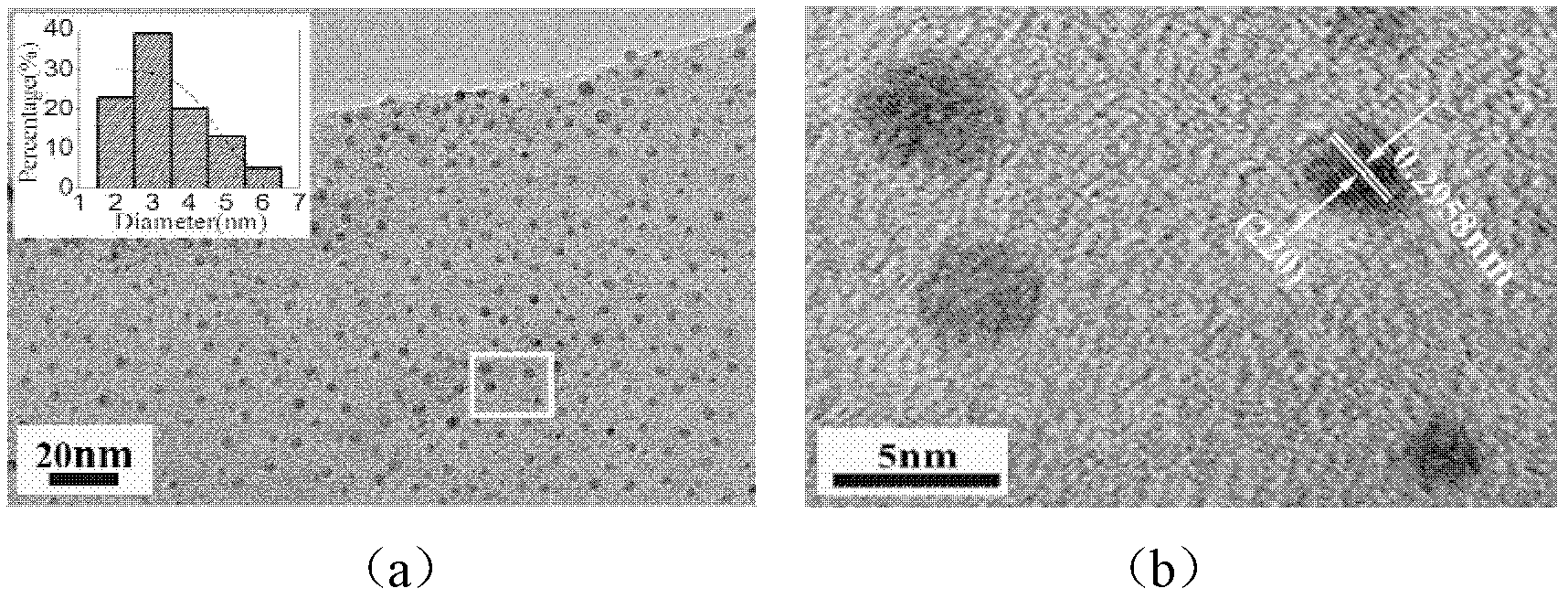
[0033] First, the anhydrous FeCl 3 (1.13g) and MgCl 2 (0.075g) was dissolved in absolute ethanol (70ml) to be configured as an ethanol solution of ferric chloride and magnesium chloride, and under magnetic stirring, 2mL of oleic acid was added to the ethanol solution. Then the 10mL NaOH ethanol solution that will configure is joined in the ethanol solution of ferric chloride and magnesium chloride (the addition of sodium hydroxide=the valence state of metal ion×the addition of metal chloride, two kinds of metal ions Mg 2+ with Fe 3+ Total after calculation respectively), fully mixed for 1 h under the action of magnetic stirring, and then introduced into a polytetrafluoroethylene reactor for solvothermal reaction. The temperature of the solvothermal reaction is 150 ° C, and the solvothermal time is 2 h. After the mixed solution was cooled to room temperature (25°C), it was centrifuged and ultrasonically w...
Embodiment 2
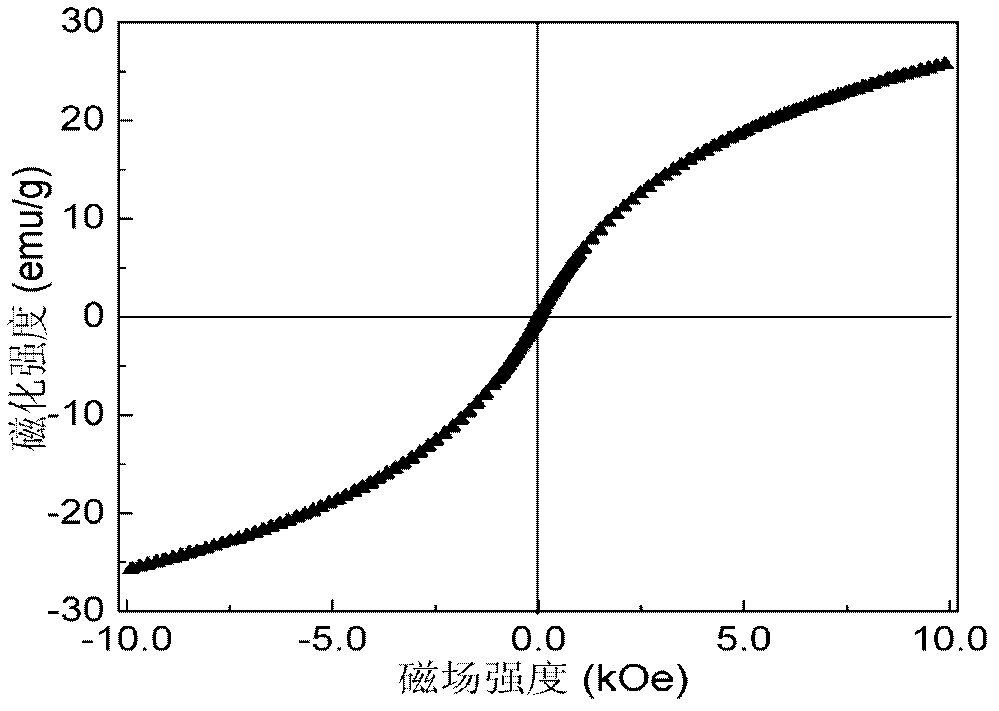
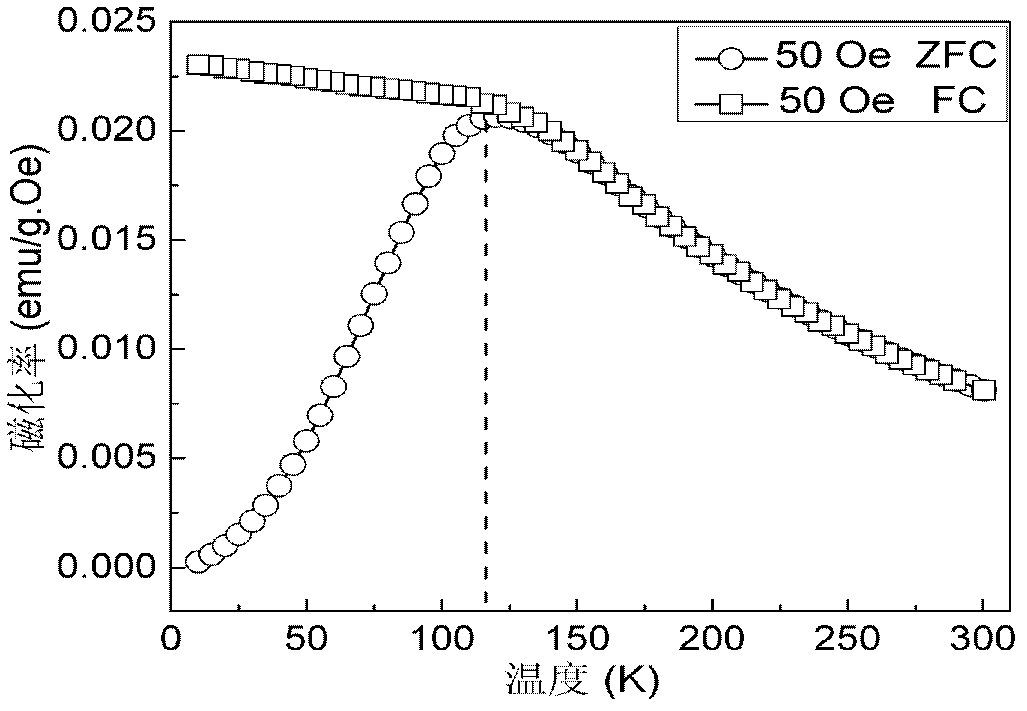
[0039] The difference from Example 1 is that the method provided by the present invention is used to prepare ultrafine and highly dispersed superparamagnetic zinc ferrite nanoparticles, and the product particles are characterized by transmission electron microscopy. The product particles are completely crystallized, spherical, highly dispersed, and the average particle size is about 5.9nm, cubic spinel Zn with uniform size distribution 0.45 Fe 2.37 o 4 Nanoparticles have a saturation magnetization of 29.3emu / g under an applied magnetic field at a temperature of 300K and a magnetic induction of 1T, and are suitable for biomedical applications including cell labeling, hyperthermia, and magnetic resonance imaging.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The difference from Example 1 is that the method provided by the present invention is used to prepare ultrafine and highly dispersed superparamagnetic manganese ferrite nanoparticles, and the product particles characterized by transmission electron microscopy are completely crystallized, spherical, highly dispersed, and the average particle size is about 3.5nm, cubic spinel structure Mn with uniform size distribution 0.11 Fe 2.52 o 4 Nanoparticles have a saturation magnetization of 57emu / g under an applied magnetic field at a temperature of 300K and a magnetic induction of 1T, and are suitable for biomedical applications including cell labeling, hyperthermia, and magnetic resonance imaging.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com