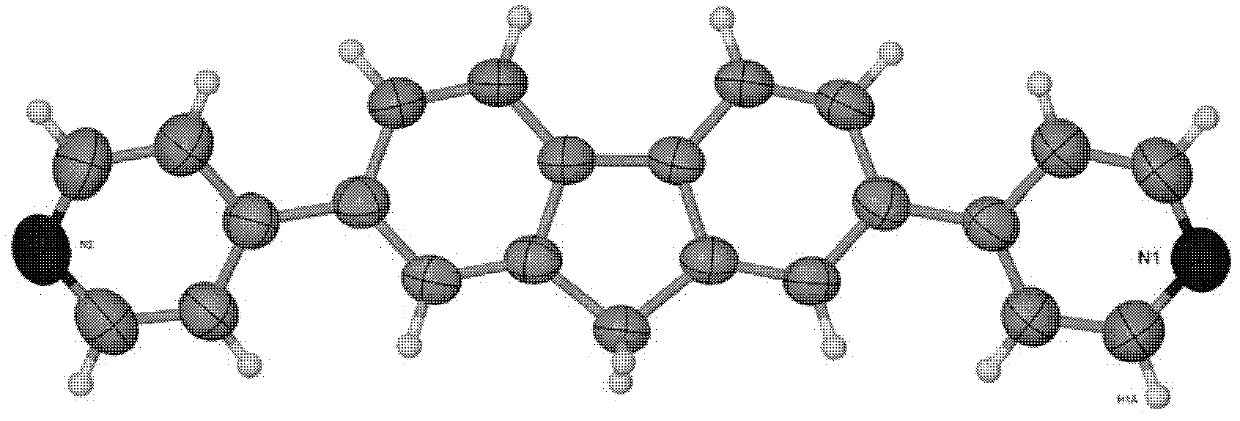
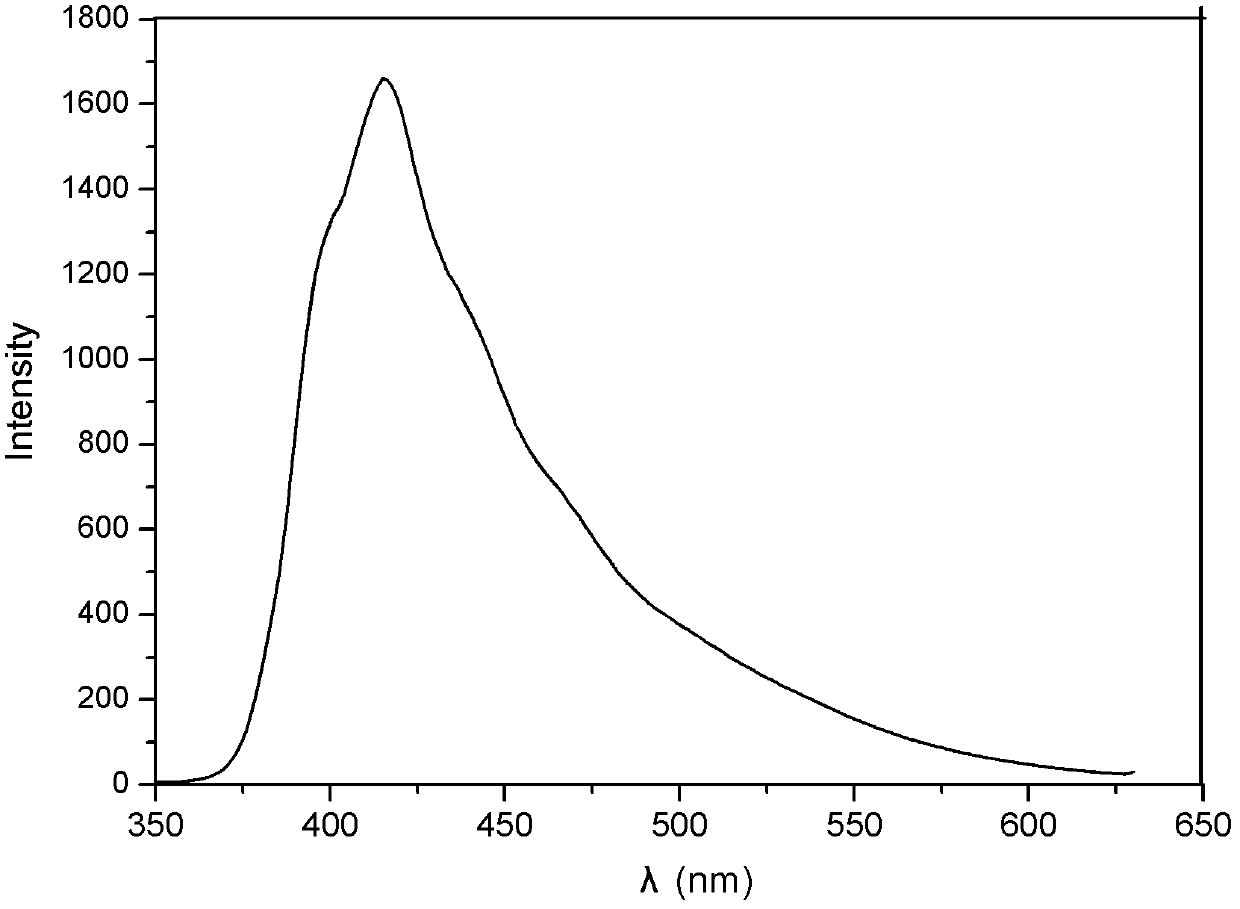
Fluorine pyridine fluorescent material and preparation method thereof
A fluorescent material, a technology of fluorenepyridine, applied in the field of fluorescent materials, can solve the problems of cumbersome synthesis steps, expensive preparation, harsh preparation conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of simple synthesis steps, high luminous efficiency, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Get 2,7-dibromofluorene (2.0g 6.2mmol), 4-pyridine boronic acid (2.3g 18.6mmol), tetrakis triphenylphosphine palladium (0.21g0.186mmol), sodium carbonate (5.9g 55.8mmol) mixed in 150ml In the reaction device, the reaction device was evacuated and flushed with nitrogen three times, then a mixture of 50 ml of deoxygenated ethylene glycol dimethyl ether and 25 ml of water was added, and the reaction was carried out at 70° C. for 2 days under the protection of nitrogen. After the reaction was completed, it was extracted with dichloromethane, and the organic phases were combined and dried over magnesium sulfate to remove water. Use a rotary evaporator to remove dichloromethane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether to obtain a solid powder, then use petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 1:2 (volume ratio) eluent to separate through the column to obtain an organic compound of fluorenpyridine.
Embodiment 2
[0020] Get 2,7-dibromofluorene (2.0g 6.2mmol), 4-pyridine boronic acid (3.4g 27.9mmol), tetrakis triphenylphosphine palladium (0.21g0.186mmol), sodium carbonate (9g 83.6mmol) mixed in 150ml In the reaction device, the reaction device was vacuumed and flushed with nitrogen three times, then a mixture of 60 ml of deoxygenated ethylene glycol dimethyl ether and 30 ml of water was added, and the reaction was carried out at 80° C. for 3 days under the protection of nitrogen. After the reaction was completed, it was extracted with dichloromethane, and the organic phases were combined and dried over magnesium sulfate to remove water. Use a rotary evaporator to remove dichloromethane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether to obtain a solid powder, then use petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 1:2 (volume ratio) eluent to separate through the column to obtain an organic compound of fluorenpyridine.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Get 2,7-dibromofluorene (4.0g 12.4mmol), 4-pyridineboronic acid (4.6g 37.2mmol), tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium (0.42g0.372mmol), sodium carbonate (11.8g 111.6mmol) mixed in 250ml In a three-necked flask, the reaction device was evacuated and flushed with nitrogen three times, then a mixture of 100 ml of deoxygenated ethylene glycol dimethyl ether and 50 ml of water was added, and the reaction was carried out at 95° C. for 3 days under the protection of nitrogen. After the reaction was completed, it was extracted with dichloromethane, and the organic phases were combined and dried over magnesium sulfate to remove water. Use a rotary evaporator to remove dichloromethane and ethylene glycol dimethyl ether to obtain a solid powder, then use petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 1:2 (volume ratio) eluent to separate through the column to obtain an organic compound of fluorenpyridine.
[0023] The substances participating in the reaction in the above examples are all chemic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com