Method for preparing biological feed by taking manioc residues as raw materials
A technology of biological feed and cassava residue, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, animal feed, etc., can solve the problems of low cellulose degradation effect, bacterial strain treatment, and low degradation effect, and achieve low price, Increase protein content, high protein yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
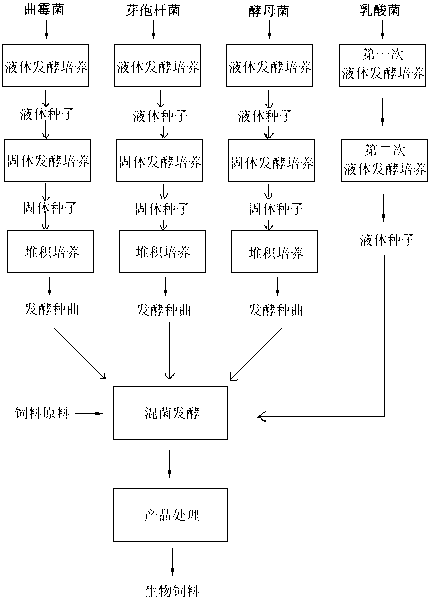
[0039] 1. Preparation of fermentation strains:
[0040] Liquid fermentation media formulations for Aspergillus, Bacillus and Saccharomyces:
[0041] 1 part of soybean peptone, 10 parts of glucose, 0.1 part of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1 part of ammonium nitrate, 0.1 part of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.1 part of magnesium sulfate and 500 parts of water.
[0042] Formula of liquid fermentation medium for lactic acid bacteria:
[0043] 5 parts of glucose, 5 parts of yeast juice, 0.1 part of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1 part of sodium chloride, 1 part of calcium carbonate, 0.1 part of magnesium sulfate and 500 parts of water.
[0044] Put the liquid fermentation medium of Aspergillus, Bacillus, saccharomyces and lactic acid bacteria into No. 1-4 fermentation tanks respectively, sterilize the fermentation tank and the liquid fermentation medium, take 1 part of Aspergillus, 1 part of Bacillus, 1 part of yeast and 1 part of lactic acid bacteria were respecti...
Embodiment 2
[0057] 1. Preparation of fermentation strains:
[0058] Liquid fermentation media formulations for Aspergillus, Bacillus and Saccharomyces:
[0059] 5 parts of soybean peptone, 30 parts of glucose, 2 parts of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 2 parts of ammonium nitrate, 0.5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.6 parts of magnesium sulfate and 1500 parts of water.
[0060] Formula of liquid fermentation medium for lactic acid bacteria:
[0061] 15 parts of glucose, 15 parts of yeast juice, 1 part of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.5 parts of sodium chloride, 5 parts of calcium carbonate, 0.5 parts of magnesium sulfate and 1500 parts of water.
[0062] Put the liquid fermentation medium of Aspergillus, Bacillus, saccharomyces and lactic acid bacteria into No. 1-4 fermentation tanks respectively, sterilize the fermentation tank and the liquid fermentation medium, take 8 parts of Aspergillus, 5 parts of Bacillus, 5 parts of yeast and 5 parts of lactic acid bacteria wer...
Embodiment 3
[0074] 1. Preparation of fermentation strains:
[0075] Liquid fermentation media formulations for Aspergillus, Bacillus and Saccharomyces:
[0076] 3 parts of soybean peptone, 20 parts of glucose, 1 part of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 1 part of ammonium nitrate, 0.3 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.4 parts of magnesium sulfate and 1000 parts of water.
[0077] Formula of liquid fermentation medium for lactic acid bacteria:
[0078] 10 parts of glucose, 10 parts of yeast juice, 0.5 parts of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3 parts of sodium chloride, 3 parts of calcium carbonate, 0.3 parts of magnesium sulfate and 1000 parts of water.
[0079] Put the liquid fermentation medium of Aspergillus, Bacillus, saccharomyces and lactic acid bacteria into No. 1-4 fermentation tanks respectively, sterilize the fermentation tank and the liquid fermentation medium, and mix 4 parts of Aspergillus, 2 parts of Bacillus, 2 parts of yeast and 2 parts of lactic acid bacteria ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com