Bacterial strain and method for preparing glucosyl group apigenin by glycosylation in nonaqueous phase
A glucosyl apigenin, non-aqueous phase technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria and other directions, can solve problems such as high cost, cumbersome steps, etc., and achieves low cost, simple separation, and glycosylation. product single effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Screening and identification of organic solvent-resistant natural strains of glycosylated apigenin by biological method
[0036] Using sucrose as the carbon source for the growth of organic solvent-resistant bacteria, adding 10% to 25% (V / V) organic solvents such as methyl sulfoxide and dimethylformamide as the screening pressure, screening and separating from chemically polluted soil samples Obtaining resistance to organic solvents for extremophiles. The formulation of the screening medium was: sucrose 5 g / L, yeast extract 2.5 g / L, corn steep liquor 3 mL / L, KH 2 PO 4 2.0 g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.0 g / L, initial pH 7.0.
[0037] Inoculate the screened microorganisms resistant to organic solvents into sieve medium, and culture them at 30° C. and 180 rpm for 12 to 24 hours to obtain fermentation broth or bacterial cell suspension. Configure reaction solution: dimethyl sulfoxide 5% (V / V), apigenin 0.05 g / L, sucrose or maltose or lactose 10 g / L, 50 mM pH 6.5 b...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Fermentation of Staphylococcus saprophyticus CQ16 CCTCC M2012099 and Preparation of Resting Cells
[0041] Staphylococcus saprophyticus CQ16 CCTCC M2012099 was inoculated into the seed medium: yeast extract 5.0 g / L, peptone 10.0 g / L, NaCl 10.0 g / L, pH 7.0, cultured at 30°C, 180 rpm for 12 hours.
[0042] Expansion medium, fermentation medium, its components and contents are: sucrose 15g / L, yeast powder 10 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 0.8 g / L, CaCl 2 0.5g / L. The pH was adjusted to 8.0 with NaOH. The seed solution was inoculated into the expansion medium and fermentation medium at 0.5% (V / V), and cultivated at 30°C and 180 rpm for 12 hours.
[0043] After centrifuging at 8000-10000 rpm for 15 minutes, the bacterial cells were collected and washed 1-2 times with normal saline to obtain resting cells of Staphylococcus saprophyticus CQ16.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Resting cells of Staphylococcus saprophyticus CQ16 CCTCC M2012099 were obtained according to Example 2.
[0046] Configure reaction solution with dimethyl sulfoxide, apigenin, sucrose, phosphate buffer, the ratio of organic solvent dimethyl sulfoxide in the reaction solution is 15% (V / V), apigenin 0.2 g / L, the mole of phosphate buffer The concentration is 150 mmol / L, the pH of phosphate buffer is 8.3, and the ratio of sucrose to apigenin is 150:1 (w / w).
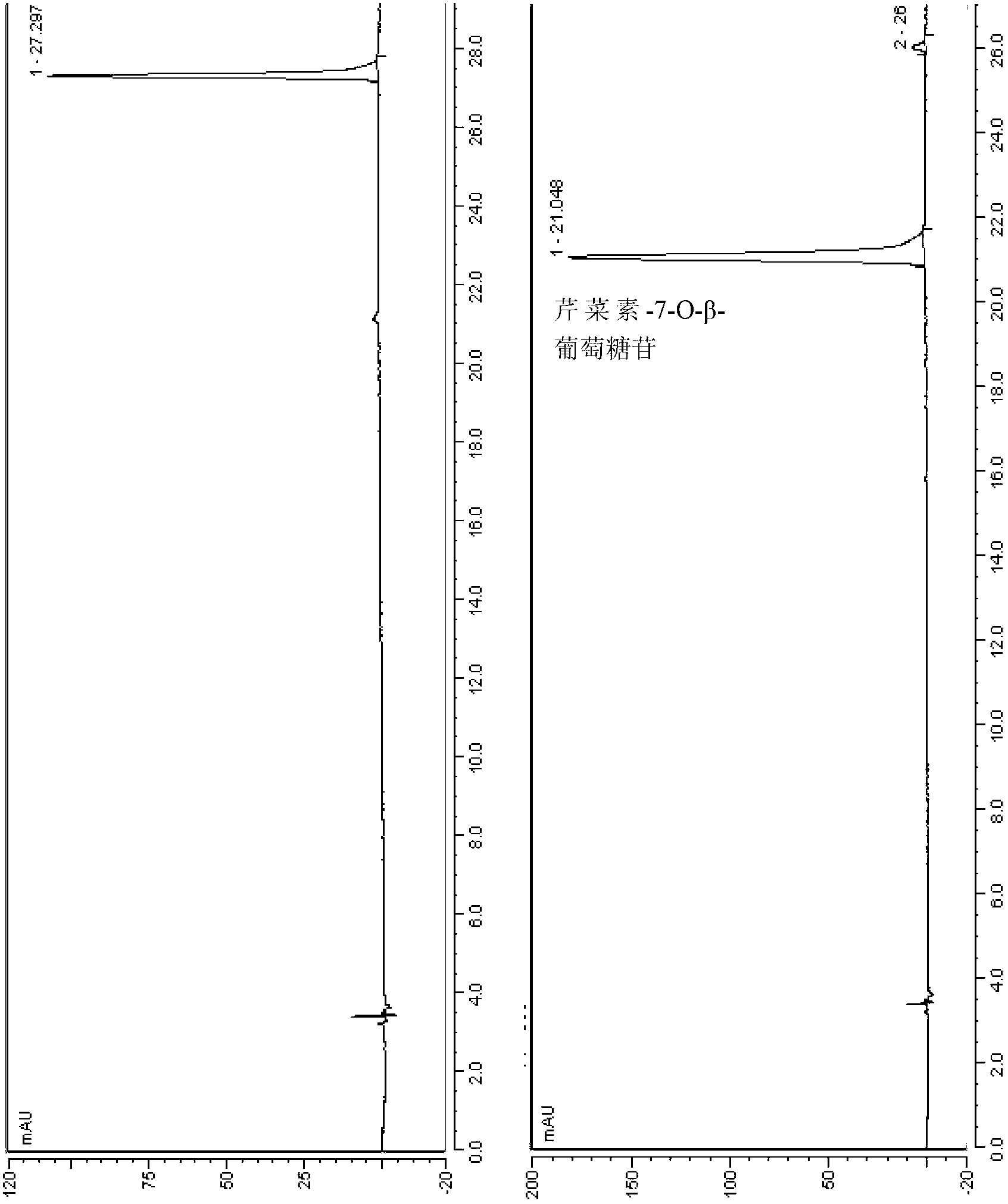
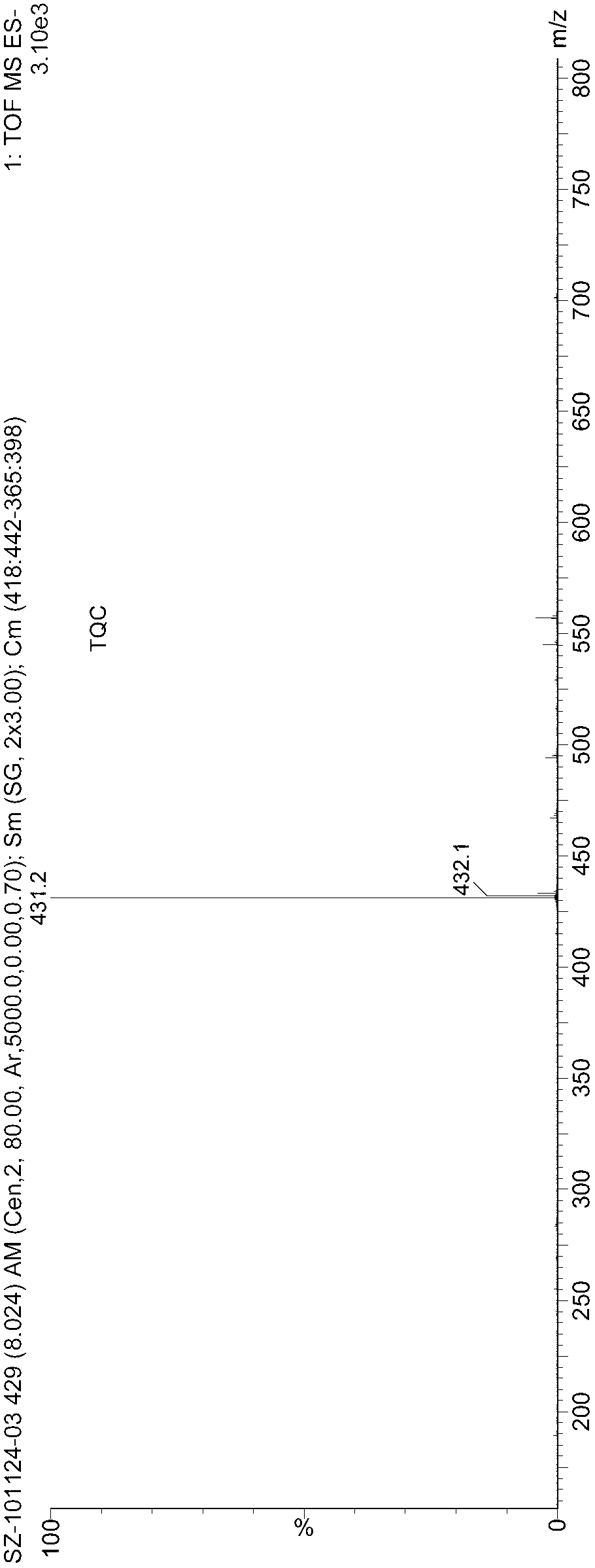
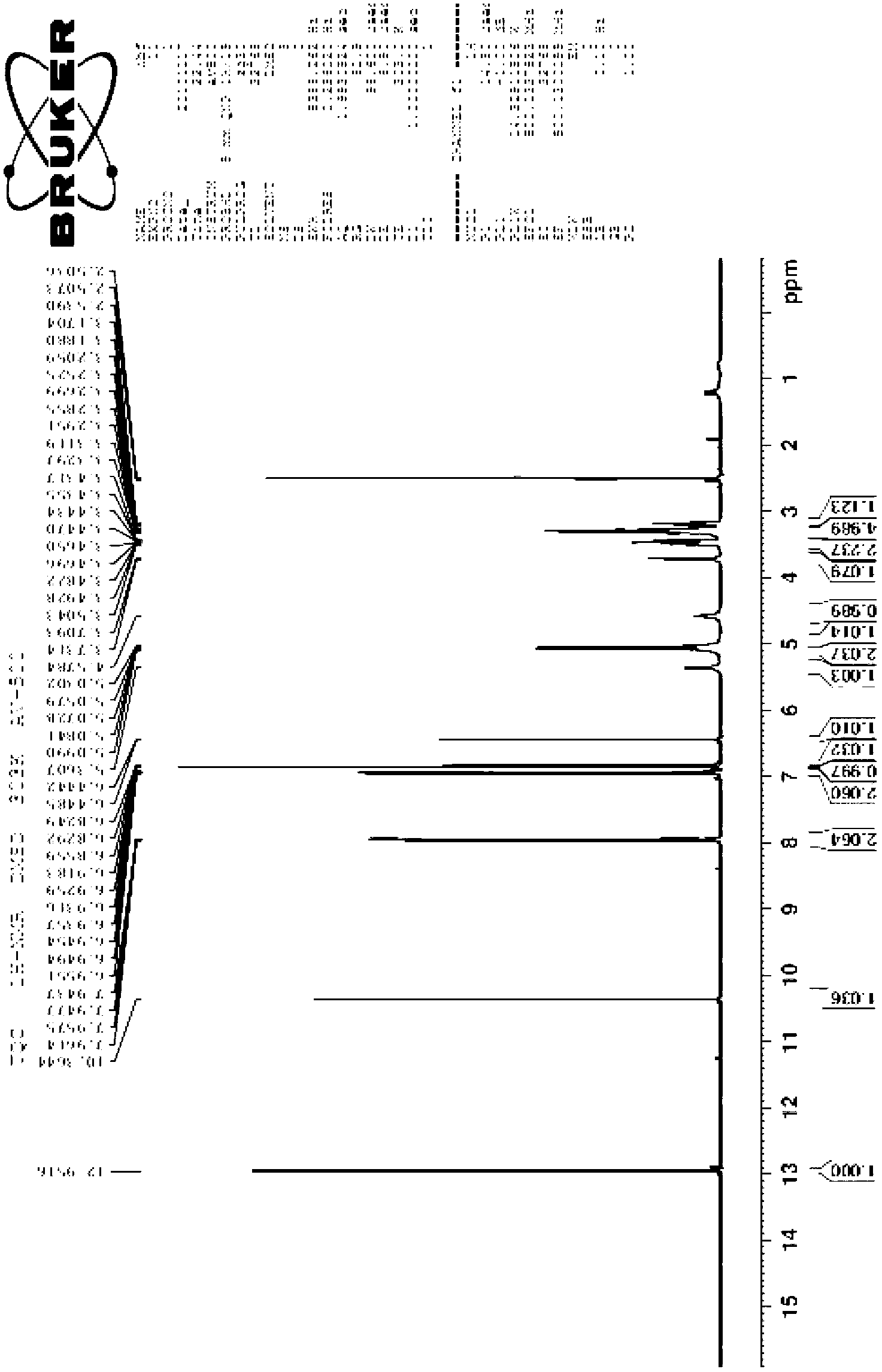
[0047] Disperse the bacteria obtained above in the reaction solution, add to the reactor, wet the cells at 1% (W / V), at 30 ℃, 180 rpm, react for 36 hours, then centrifuge at 8000-10000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain the reaction solution The supernatant was analyzed by HPLC.
[0048] Take an appropriate amount of AB-8 macroporous adsorption resin, wet-pack the column (chromatographic column 40×600mm), pretreat the resin with 5% (V / V) hydrochloric acid, 2% sodium hydroxide solution, and wash with distilled water until ne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com