Multi-epitope fusion antigen for detecting virus serum antibody of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and kit prepared with multi-epitope fusion antigen
A technology for respiratory syndrome and fusion antigen, applied in biological testing, hybrid peptides, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, complicated and laborious virus purification process, and achieve long response duration, simple purification process, and control The effect of missed detection risk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1 Design of multiple epitope fusion antigen (MEFA) NSP7-N1 and cloning of its coding gene
[0052] 1. Design of multiple epitope fusion antigen NSP7-N1
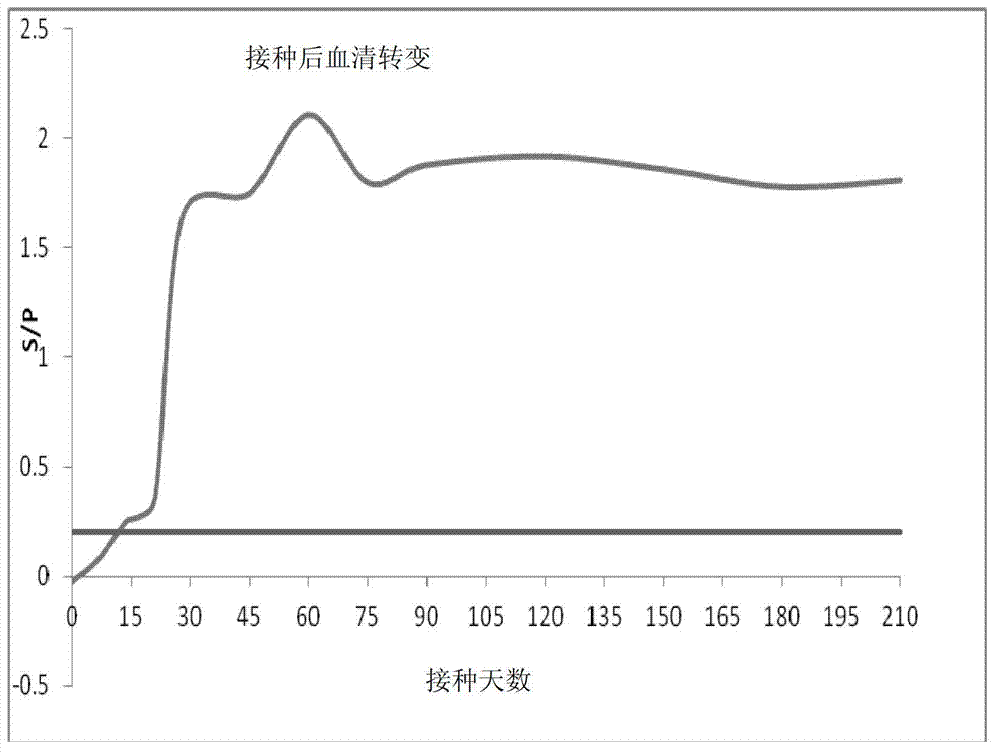
[0053] According to the online database search provided by NCBI, the genome sequence of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (GenBank: JQ663567.1), the amino acid residue sequence of NSP7 (NCBI Reference Sequence: NP 740601.1), and the amino acid residue sequence of nucleocapsid protein N can be obtained (GenBank: AAY53878.1). Wherein NSP7 is encoded by ORF1a nucleotide residues, divided according to the non-structural proteins of European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Lelystad strain, the start and end positions of the Nsp7 amino acid coding sequence are Ser2083-Glu2351. The starting and ending positions of the Nsp7 amino acid sequence of North American porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus VR-2332 strain are Ser2200-Glu2458. The porcine reproductive and res...
Embodiment 2
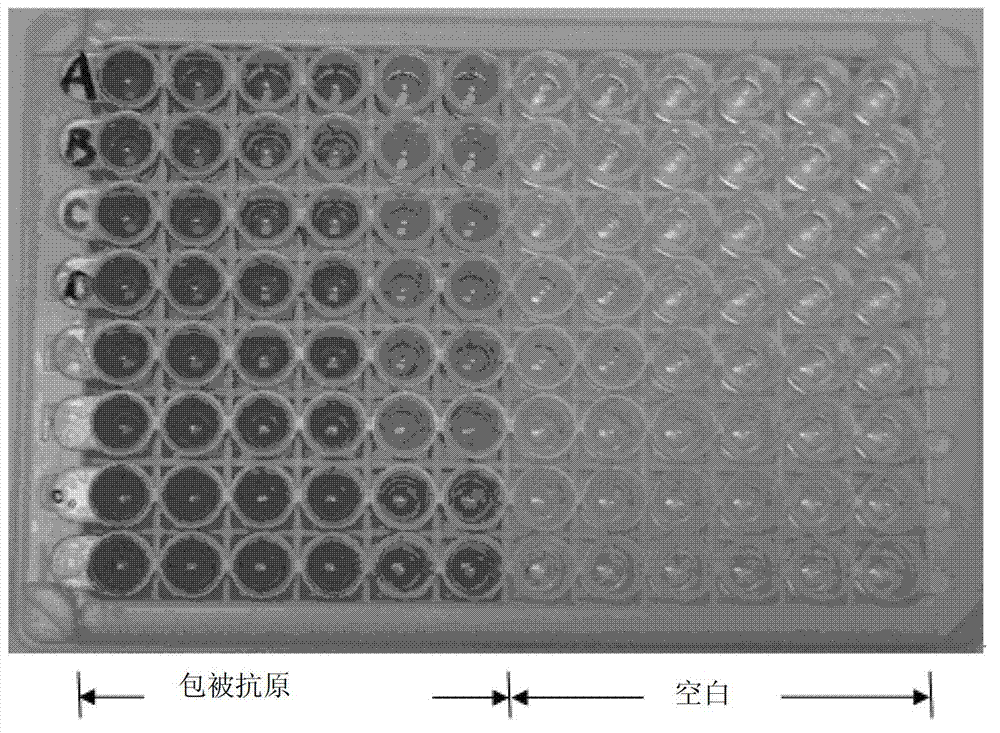
[0057] Transform BL21codon plus (DE3) engineering bacteria by conventional methods (molecular cloning: an experimental manual (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989)), take the recombinant pET42a-NSP7-N1 plasmid to transform BL21codon plus (DE3) bacteria, and spread on the Chloramphenicol-resistant and kanamycin-resistant LB solid medium, cultivated overnight in a 37°C incubator, picked white colonies and inoculated them in LB medium for expanded culture the next day, cultured at 30°C, and the measured bacterial OD value reached 0.6 At ~0.8 hours, IPTG with a final concentration of 0.6mmol / L was added to induce, and the induced bacteria were collected at time points 1, 2, 4, and 6 hours for SDS-PAGE identification. The results showed that the engineered bacteria induced by IPTG had a specific protein band with a molecular weight of about 34kD, which was consistent with the expected molecular weight value of the expression product of pET42a-NSP7-N1, accounting for ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The purification of embodiment 3NSP7-N1 recombinant protein
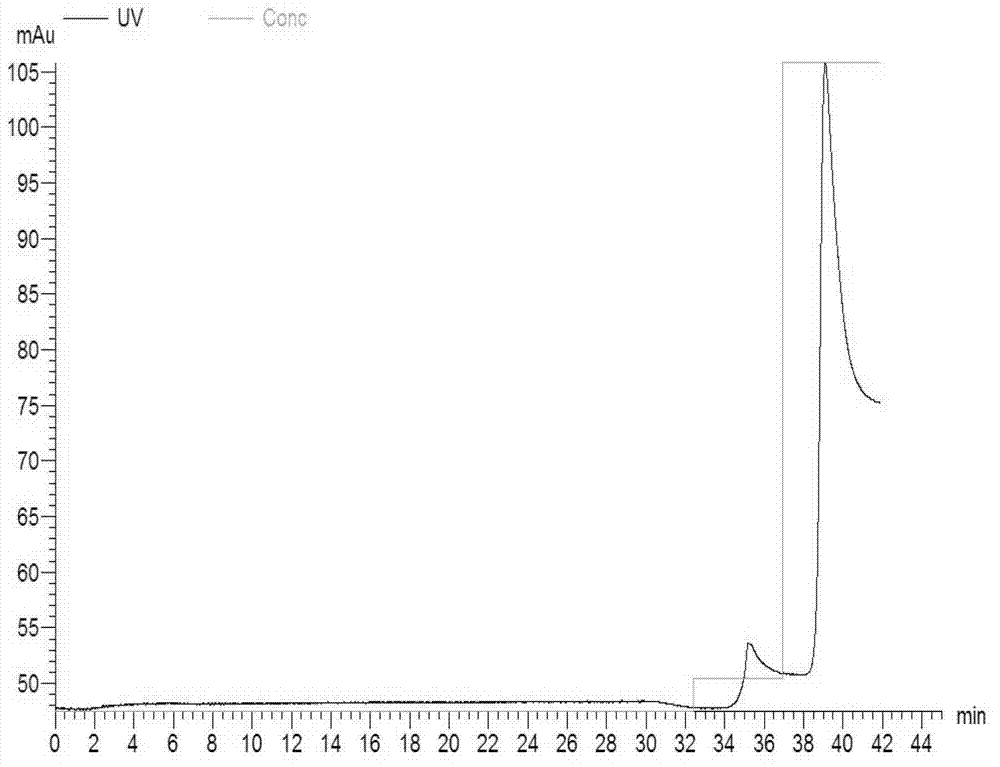
[0059] The engineered bacteria transformed with the pET42a-NSP7-N1 recombinant plasmid were induced and expressed by 0.6mmol / L IPTG, and then purified using GSTrap F.F. After suspension, the bacteria were ultrasonically broken on ice, centrifuged at 4°C at high speed, and the supernatant was filtered and put on the column with Amersham's AKTAprime. , pH8.0) to collect the eluted protein. Dilute the eluted peak containing the target protein with His-binding buffer (20mmol / l, sodium phosphate, 0.5M NaCl, pH7.4) at a volume ratio of 1:9 and then repurify on HisTrap HP, His-binding buffer After equilibration, use His-elution buffer (20mmol / L sodium phosphate, 0.5M NaCl, 0.5M imidazole, pH7.4), first elute with 10% buffer to remove non-specific binding impurities, and then use 100% buffer after equilibration solution to wash off the target protein. A desalting column is used to desalt and remove imidazole, and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com