Cholesterol derivatives, chelates, recombinant high-density lipoproteins and uses thereof
A technology of high-density lipoprotein and cholesterol derivatives, applied in steroids, organic chemistry, nuclear magnetic resonance/magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents, etc., to reduce the dosage and enhance the effect of magnetic resonance imaging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
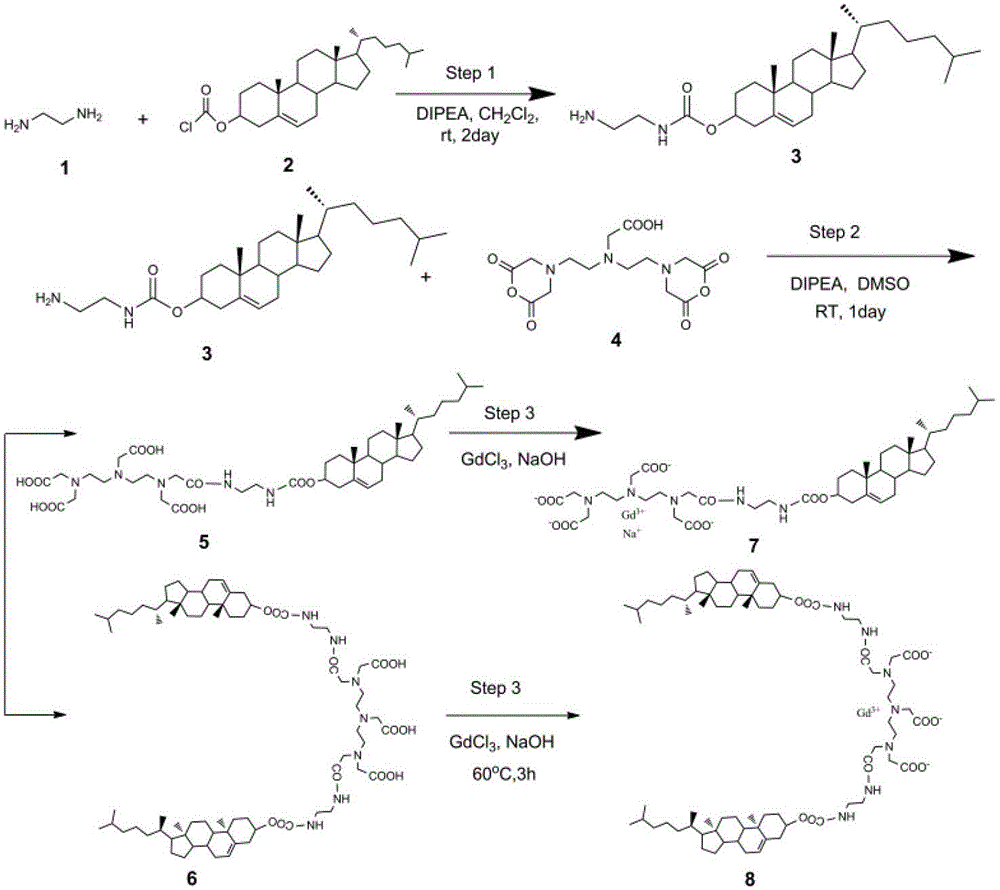
[0050] Embodiment 1, the preparation of cholesterol derivative and chelate thereof
[0051] 1.1. Preparation of Cholesterol Derivatives
[0052] 1.1.1. Preparation of Cholesterol Derivatives I
[0053] Such as figure 1 As indicated, dissolve 500mmol of ethylenediamine in 100ml of anhydrous dichloromethane and add it to a dried 100ml three-necked flask, and at the same time add 10mmol of N,N-diisopropylethylamine, and stir to mix. Dissolve 5 mmol of cholesterol chloroformate in 20 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane, and slowly add it dropwise to the solution of ethylenediamine under an ice-water bath for half an hour, and the temperature of the reaction system rises to room temperature. Nitrogen was passed into the three-necked flask, and the reaction system was sealed and stirred at room temperature for 2 days. After the reaction, the reaction solvent was added to a 250ml eggplant-shaped flask, and the methylene chloride was removed using a vacuum pump to a minimum volume. I...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Embodiment 2, preparation of contrast agent
[0082] The gadolinium chelate Gd-DTPA-chol of the monocholesterol derivative in cholesterol derivatives Ⅰ was assembled into high-density lipoprotein using sodium cholate surfactant method to obtain recombinant high-density lipoprotein Gd-chol-HDL (used as contrast agent). The molar ratio of each component of high-density lipoprotein is: Gd-DTPA-chol: DMPC: sodium cholate=1:1:2 (mol / mol); Described high-density lipoprotein and chelate are mixed, at room temperature After incubation, sodium cholate was removed by dialysis to obtain recombinant high-density lipoprotein. Specifically: weigh Gd-DTPA-chol (5 mg, 5 μmol), DMPC (3.4 mg, 5 μmol), dissolve them in a mixed solvent of chloroform / methanol (3 / 1, v / v), dry the chloroform with nitrogen, and vacuum Remove the residual solvent in a drying oven, add 4.30 mg of sodium cholate, dissolve it with 1 ml of TBS buffer, and sonicate for 30 minutes to dissolve it. According to ap...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Embodiment 3, particle size and longitudinal relaxation efficiency measurement
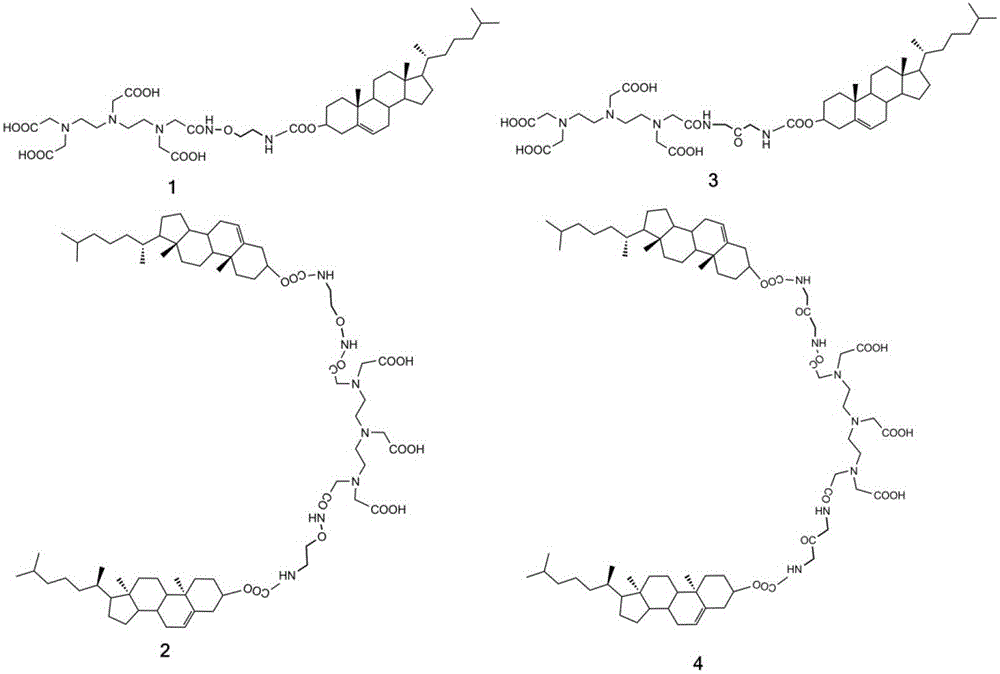
[0093] The formulation of recombinant HDL can affect its properties. According to the method in Example 2, the gadolinium chelate Gd-DTPA-(chol) of the double cholesterol derivative in the cholesterol derivative II 2 To produce recombinant high-density lipoprotein, different lipid formulations were used to measure the particle size and longitudinal relaxation efficiency of recombinant high-density lipoprotein after production. Particle size was determined using dynamic light scattering and results are shown as particle size under intensity results. Table 2 below shows that when the molar ratio of DMPC: chelate increases, the particle size of the recombinant HDL increases proportionally, but the longitudinal relaxation efficiency decreases inversely.
[0094] Table 2
[0095]
[0096] In summary, the present invention connects cholesterol to the nitrogen-containing multi-carboxylate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com