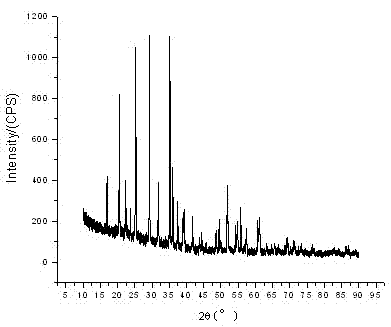
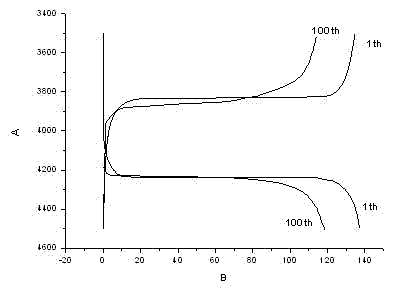
Preparation method for manganese phosphate lithium nanosheet
A technology of lithium manganese phosphate and nanosheets, applied in electrical components, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable lithium ion battery energy density, slow lithium ion diffusion speed, poor conductivity, etc., and achieve high-current charging and discharging performance , easy to scale production, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0020] 1) Measure 25ml of ethylene glycol and 25ml of deionized water and mix to form a uniform solution;
[0021] 2) Take 50ml of water / ethylene glycol mixed solvent, add 0.141g of ascorbic acid into it, fully dissolve to obtain ascorbic acid solution with a concentration of 20mmol / l;
[0022] 3) Take 15 ml of the ascorbic acid solution prepared in step 2), add 2.45 g of manganese acetate tetrahydrate and 0.98 g of phosphoric acid in sequence, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm to obtain an ascorbic acid solution of 0.25 mol / l phosphoric acid and manganese acetate;
[0023] 4) Take 15ml of the ascorbic acid solution prepared in step 2), dissolve 1.02g of lithium acetate in it, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm to obtain a lithium acetate solution;
[0024] 5) In the state of stirring, drop lithium acetate into the ascorbic acid solution of phosphoric acid and manganese acetate through a dropper at a rate of 3ml / min. The volum...
example 2
[0028] 1) Measure 37.5ml of ethylene glycol and 12.5ml of deionized water and mix to form a uniform solution.
[0029] 2) Get the mixed solvent of 50ml water / ethylene glycol, add 0.7g ascorbic acid wherein, fully dissolve, obtain ascorbic acid solution, its concentration is 100mmol / l;
[0030] 3) Take 15 ml of the ascorbic acid solution prepared in step 2), add 2.45 g of manganese acetate tetrahydrate and 0.98 g of phosphoric acid in sequence, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm to obtain an ascorbic acid solution of 0.25 mol / l phosphoric acid and manganese acetate;
[0031] 4) Take 15ml of the ascorbic acid solution prepared in step 2), dissolve 1.02g of lithium acetate in it, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm to obtain a lithium acetate solution;
[0032] 5) In the state of stirring, drop lithium acetate into the ascorbic acid solution of phosphoric acid and manganese acetate through a dropper at a rate of 6ml / min. The volume...
example 3
[0035] 1) Measure 45ml of ethylene glycol and 5ml of deionized water and mix to form a uniform solution.
[0036] 2) Get the mixed solvent of 50ml water / ethylene glycol, add 0.07g ascorbic acid wherein, fully dissolve, obtain ascorbic acid solution, its concentration is 10mmol / l;
[0037] 3) Take 15 ml of the ascorbic acid solution prepared in step 2), add 7.84 g of manganese acetate tetrahydrate and 3.14 g of phosphoric acid in sequence, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm to obtain an ascorbic acid solution of 0.80 mol / l phosphoric acid and manganese acetate;
[0038] 4) Take 15ml of the ascorbic acid solution prepared in step 2), dissolve 3.26g of lithium acetate in it, and stir magnetically for 30 minutes at a speed of 2000 rpm to obtain a lithium acetate solution;
[0039] 5) In the state of stirring, drop lithium acetate into the ascorbic acid solution of phosphoric acid and manganese acetate at a rate of 4ml / min through a dropper, the volume rati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com