Preparation method of graphene/bacterial cellulose composite material
A technology of bacterial cellulose and composite materials, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problem of uncontrollable distribution of graphene sheet aggregation components, achieve good adsorption, simple preparation process, and inhibit agglomeration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] First, use pure water, glucose, peptone, citric acid, disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and yeast powder to prepare a bacterial cellulose fermentation culture solution. The pH of the culture solution is 5.0, and the bacterial cellulose fermentation culture solution is placed in In a sterilizing pot, sterilize at 120°C and 0.1MPa for 30 minutes; then, insert the activated Acetobacter xylinum species into the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose culture solution, and cultivate it on a shaking table for 12 hours; the mass volume concentration is 0.2mg / ml of graphene dispersion, ultrasonically dispersed for 1 hour, and sterilized by ultraviolet light three times, each time for 15 minutes; In the bacterial cellulose culture solution of bacterial strain; Shake the above-mentioned mixed liquid shaker for 12 hours to make the mixed liquid uniform; put the incubator at 28° C. for static cultivation for 1 week, and obtain the graphene / bacterial cellulose...
Embodiment 2
[0037] The difference between the preparation process of this embodiment 2 and the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is that, wherein, the graphene dispersion is added to the bacteria-carrying In the bacterial cellulose culture solution of species; shake the above-mentioned mixed liquid shaker for 12 hours to make the mixed liquid uniform.
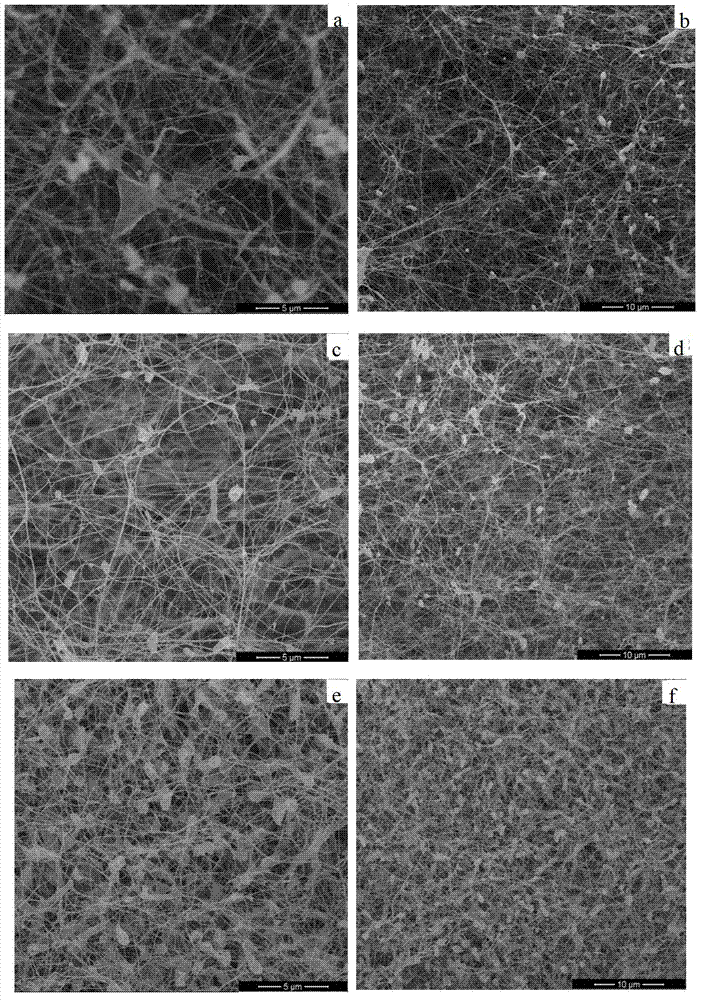
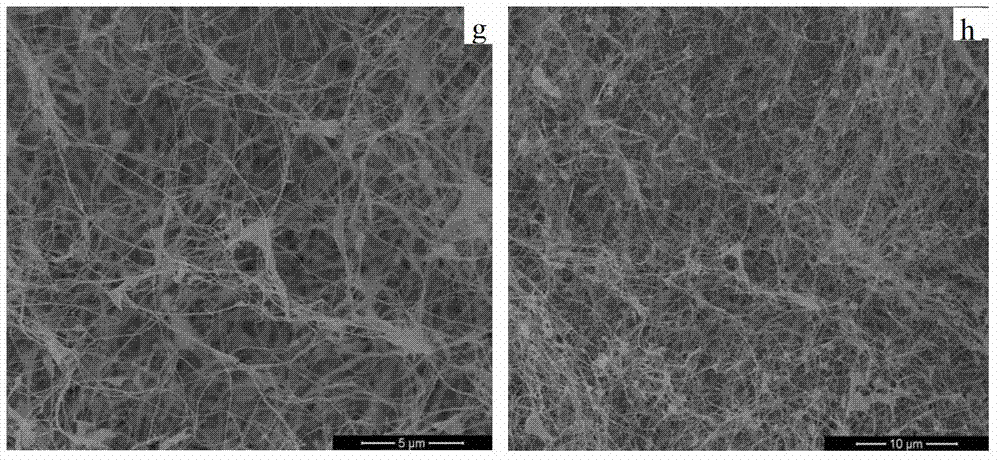
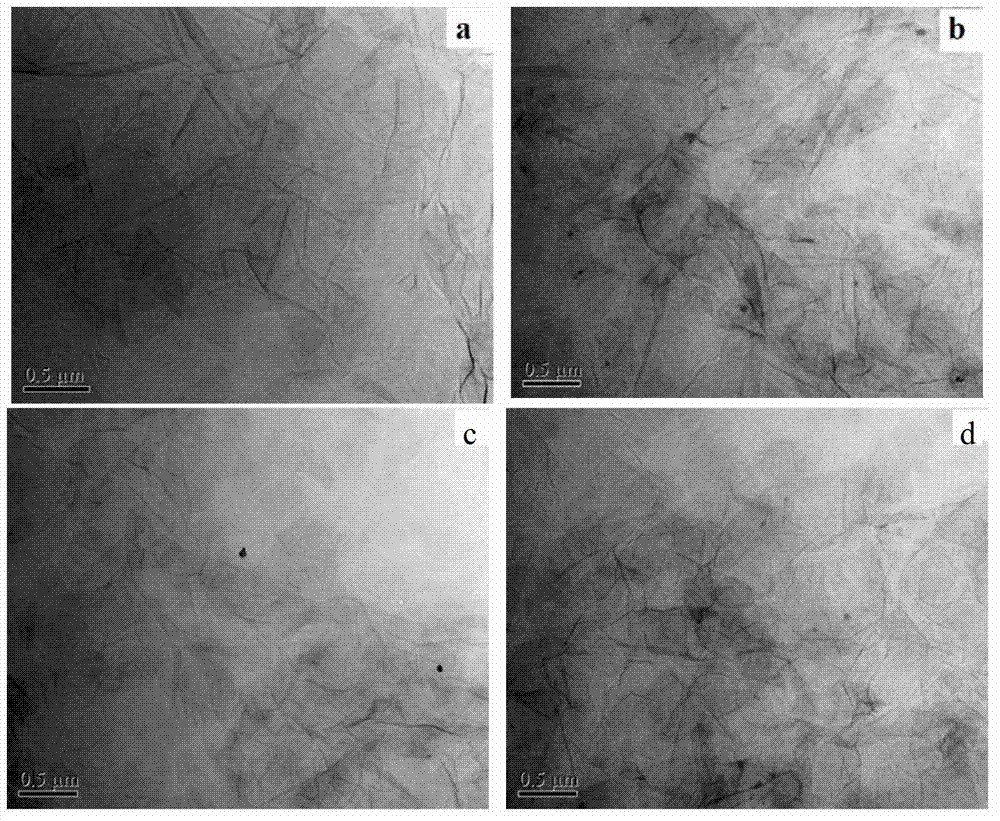
[0038] figure 1 (c) and figure 1 (d) are respectively the SEM photos of the graphene / bacterial cellulose composite material of Example 2; figure 2 (b) is a TEM photo of the graphene / bacterial cellulose composite material of Example 2; FIG. 3(b) is a Raman spectrum test curve of the graphene / bacterial cellulose composite material of Example 2.
Embodiment 3
[0040]The only difference between the present embodiment 3 and the preparation process of the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is that the activated Acetobacter xylinum species is inserted into the above-mentioned bacterial cellulose culture solution, and cultured on a shaking table for 24 hours; the mass volume concentration is 0.2 mg / ml graphene dispersion, ultrasonically dispersed for 2 hours; shake the mixed liquid on a shaker for 24 hours to make the mixed liquid uniform; put it in an incubator at 28°C for static culture for 2 weeks.
[0041] figure 1 (e) and figure 1 (f) SEM photos of the graphene / bacterial cellulose composite material of Example 3; figure 2 (c) is the TEM photo of the graphene / bacterial cellulose composite material of Example 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com