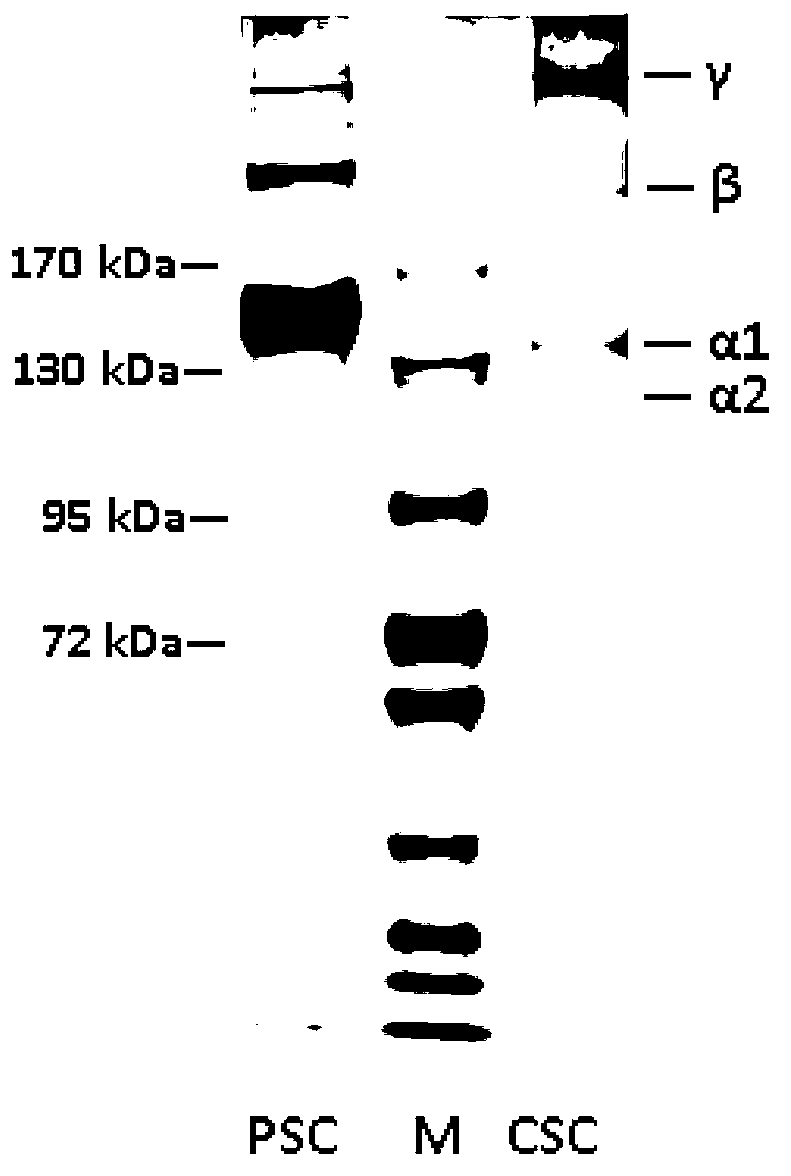Method for extracting and purifying pepsin-soluble collagens of black sea cucumber in East China Sea
A technology of collagen and purification method, which is applied in the field of extraction and purification of enzymatically soluble collagen of Donghai black ginseng, which can solve problems such as pollution and inability to eat directly, and achieve the effect of high-yield extraction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
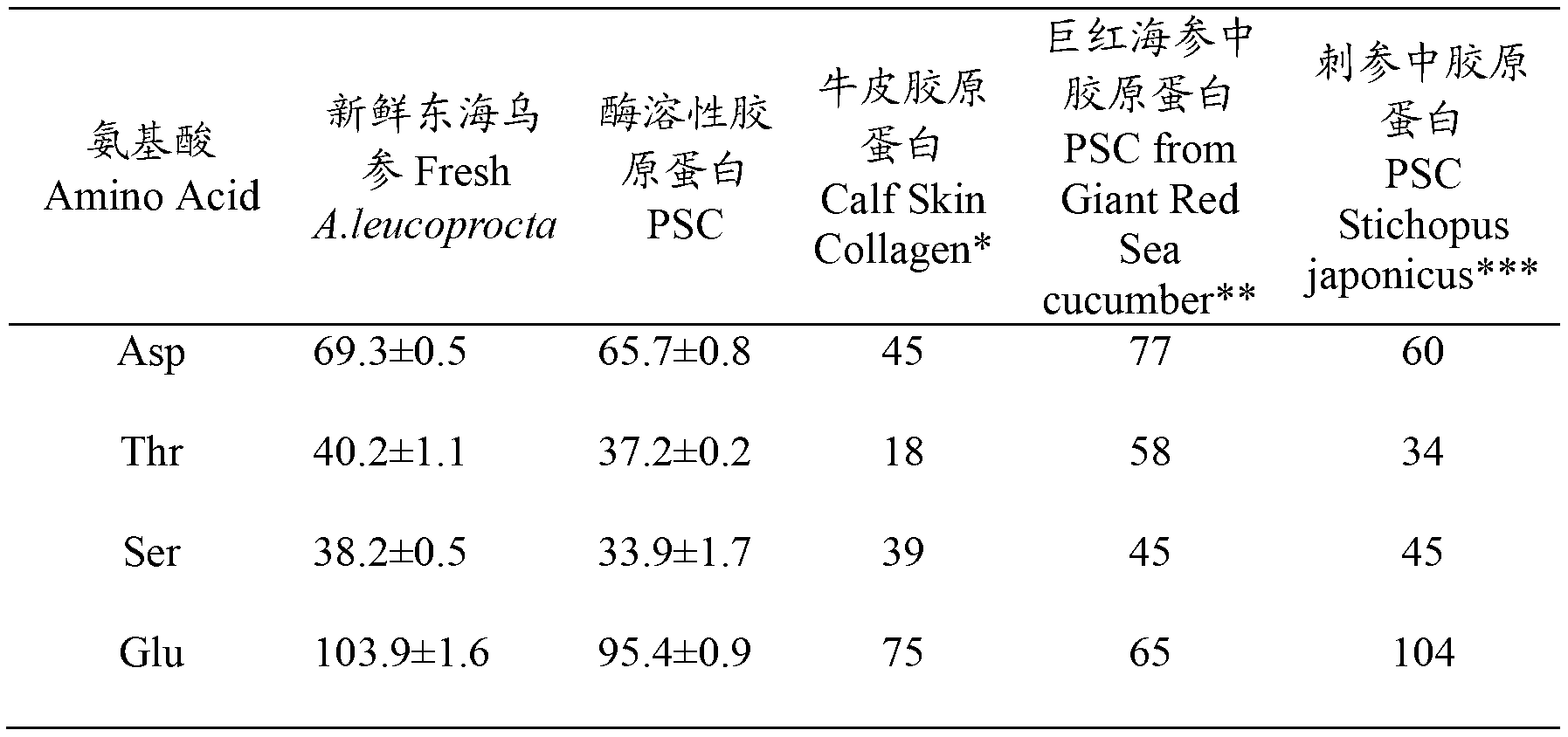
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1. Fresh Donghai black ginseng (commercially purchased, produced in Xiangshan, Zhejiang) samples were washed with tap water at 4°C to remove sediment and internal organs, cut into small pieces of 5mm*5mm, and 200g of block samples were washed with 1000mL0.2M EDTA (pH8 .0) Soak and stir for 5 days, replace the solution every day to remove calcium, iron, manganese, magnesium, lead and other pollution elements and residual impurities.
[0028] 2. After washing with water, add 100g of ice cubes (to reduce the temperature of the solution to below 4°C), homogenize with a stainless steel homogenizer (IKA T25Homogenizer), 18000rpm, 20min, and take the precipitate A after centrifugation.
[0029] 3. Add 0.1M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 20 times volume (solution 20mL / 1g precipitate) to precipitate A, stir for 48 hours to fully dissolve tissue protein, and take precipitate B after centrifugation.
[0030] 4. Add 20 times the volume of 0.1M NaOH to the precipitate B and stir for 48 hour...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 1. Fresh black ginseng samples from the East China Sea were frozen and cut into granules (5mm*5mm in size), washed with ice water and stirred three times to remove impurities such as sediment and viscera, then took 200g block samples and washed them with 2000mL0.2M EDTA (pH8. 0) Soak and stir for 5 days, replace the solution every day to remove calcium, iron, manganese, magnesium, lead and other polluting elements.
[0036] 2. After washing with water, add 200g of ice cubes (to lower the temperature of the solution to below 4°C), use a stainless steel homogenizer (IKA T25Homogenizer) to homogenize at 18000rpm for 20min, and take the precipitate A after centrifugation.
[0037] 3. Add 20 times the volume of 0.1M, pH8.0 Tris-HCl+0.5M NaCl+50mM EDTA+0.2M β-mercaptoethanol to the precipitate A, stir and extract for 72 hours, and take the precipitate B after centrifugation.
[0038] 4. Add 20 times the volume of 0.1M NaOH to the precipitate B and stir for 72 hours. Change th...
Embodiment 3
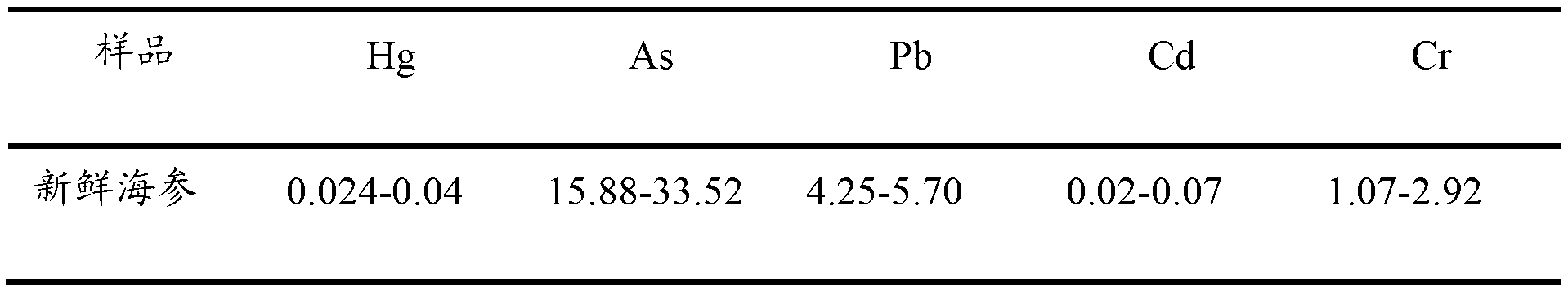
[0043] 1. The tissue water content of fresh black ginseng is 83.61±0.2%, the ash content is 3.9±0.05%, the protein is 13.71±0.1%, and the fat is 0.9±0.05%. The content of heavy metal elements seriously exceeds the standard, as shown in the table below:
[0044]
[0045] It can be seen from the table that the contents of As, Pb and Cr far exceed the standard limit of 0.5mg / Kg.
[0046] 2. The epidermis of fresh Donghai black ginseng is seriously polluted, yellow in color, and partly has a serious rust red color. In 0.2M EDTA with pH 8.0, the solution is changed every day. After soaking for 5 days, the removal rate of Ca, Fe, Mn, Mg, Zn, Sn and other metal elements is above 90%, and the tissue is obviously softened and swollen, and it is easy to homogenize. Add ice water, homogenize at 18000rpm for 20min, centrifuge at 12000G and take precipitate A.
[0047] 3. Precipitate A was dissolved with 20 times the volume of 0.1M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) and stirred for 72 hours. This step...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com