Boric sludge comprehensive utilization method for preparing nanometer magnesia and nanocrystalline iron oxide
A nano-iron oxide and nano-magnesium oxide technology, applied in the nano field, can solve the problems of complex process, high energy consumption, large pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing added value, saving energy, and reducing exhaust emissions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
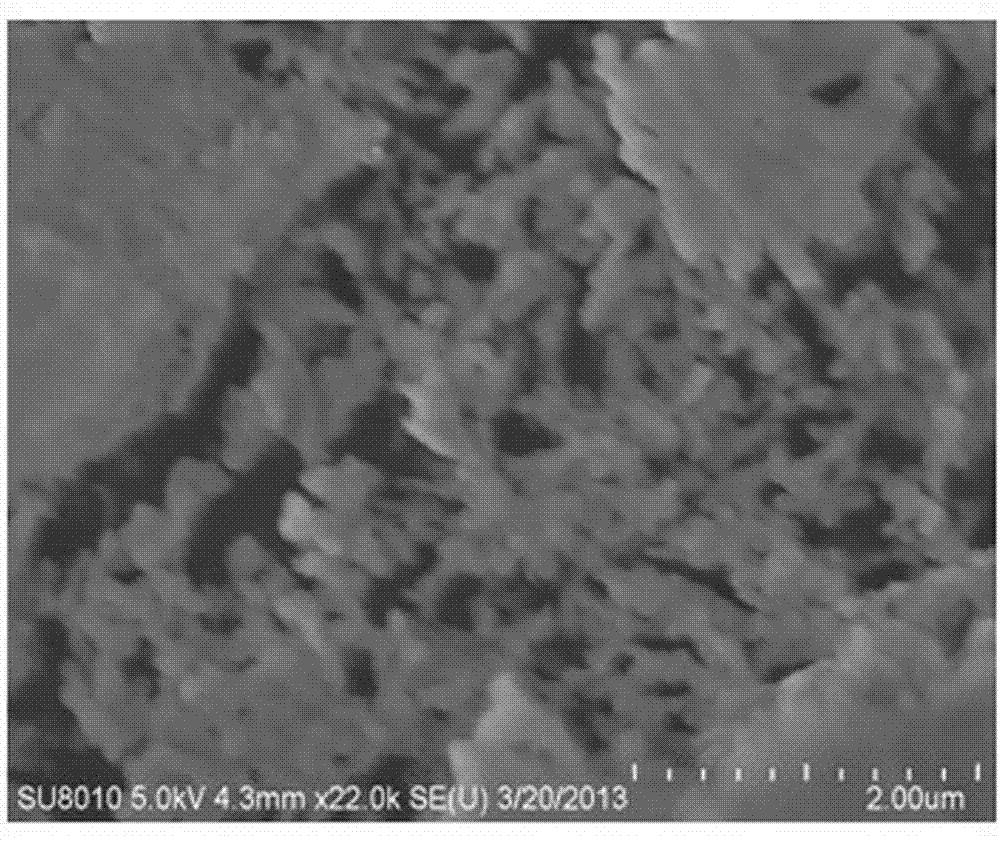
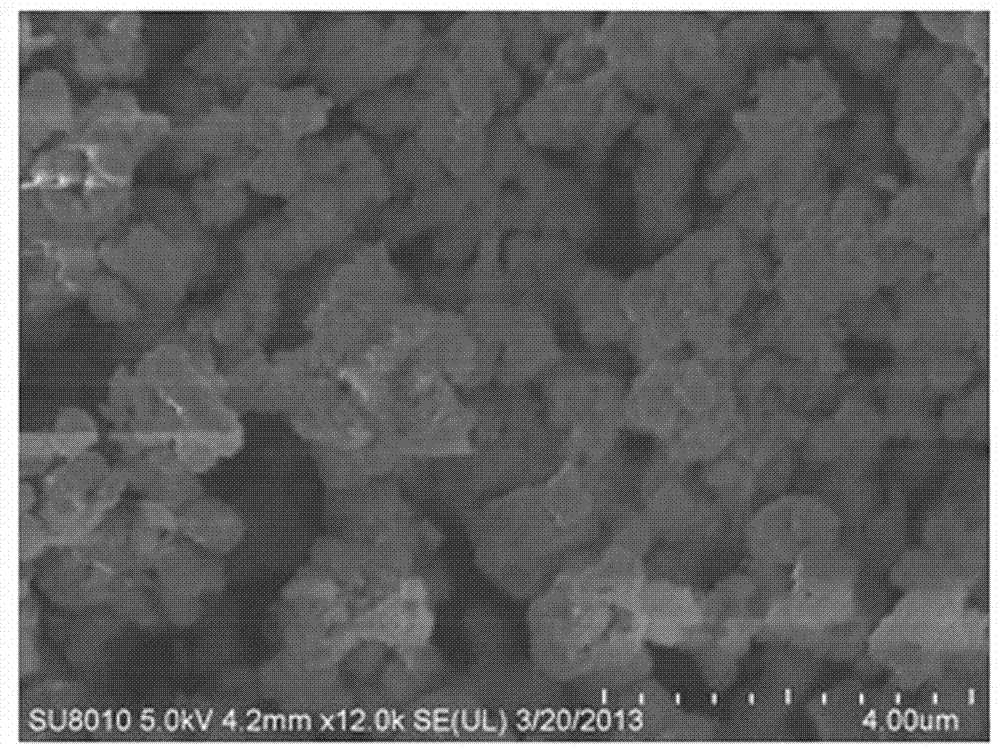
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
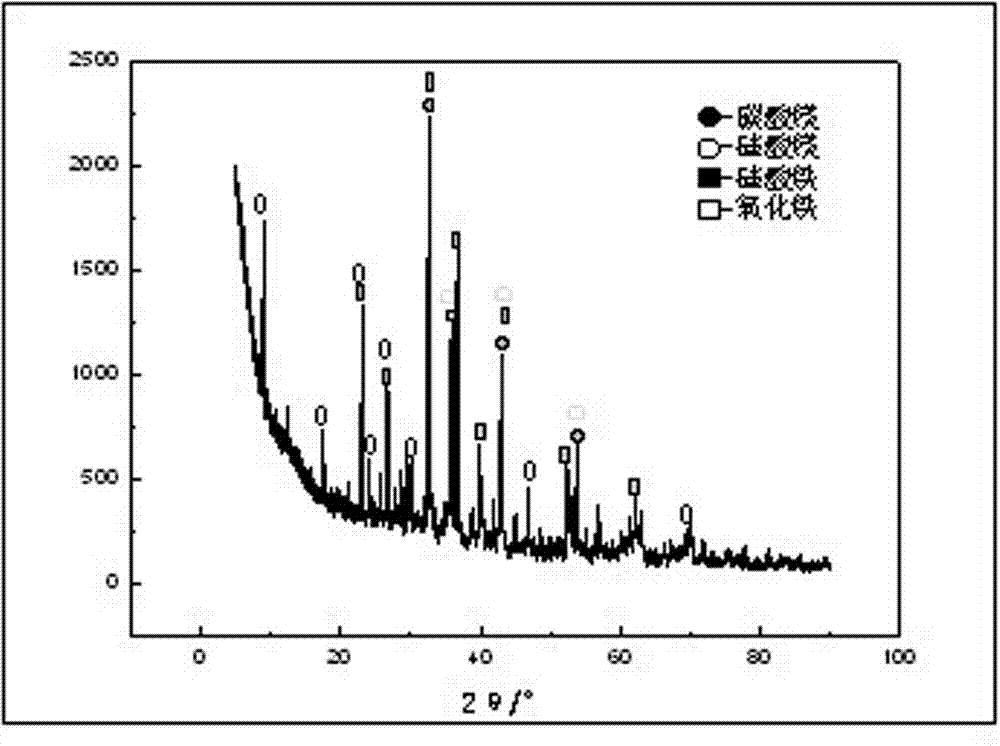
[0029] The XRD of boron mud used is attached figure 1 As shown, it is mainly composed of magnesium carbonate, magnesium silicate, iron silicate, iron oxide and other phases, and its chemical composition is shown in Table 1.
[0030] Table 1 Chemical composition of boron mud / mass%
[0031] composition B 2 o 3 MgO CaO SiO 2 Fe 2 o 3 Al 2 o 3 content 2.5 35 5 18 25 2
[0032] (1) Carry out low-temperature pressure leaching of boron mud in hydrochloric acid system, and then filter and separate to obtain magnesium chloride, ferric chloride leaching solution and borosilicate-rich slag. The low-temperature pressure leaching conditions are: the solid-to-liquid ratio of boron mud to hydrochloric acid is 1kg: 5L, the leaching temperature is 120°C, the concentration of hydrochloric acid is 8mol / L, the leaching time is 30min, and the leaching rates of magnesium and iron are 95.5% and 95.2% respectively;
[0033] (2) Add MgO or Fe to the m...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Boron mud used is with embodiment 1.
[0039] (1) Carry out low-temperature pressure leaching of boron mud in hydrochloric acid system, and then filter and separate to obtain magnesium chloride, ferric chloride leachate and borosilicate-rich slag. The low-temperature pressure leaching conditions are: the solid-to-liquid ratio of boron mud to hydrochloric acid is 1kg: 10L, the leaching temperature is 100℃, the concentration of hydrochloric acid is 5mol / L, the leaching time is 90min, and the leaching rates of magnesium and iron are 96.5% and 95.5% respectively;
[0040] (2) Add MgO or Fe to the magnesium chloride and ferric chloride leaching solution obtained in step (1) 2 o 3 Adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 3.2. In order to effectively precipitate and separate iron, add H during the precipitation process. 2 o 2 Oxidize the ferrous ions in the leach solution to ferric ions, precipitate the iron ions in the form of ferric hydroxide, and then filter and s...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Boron mud used is with embodiment 1.
[0046] (1) Carry out low-temperature pressure leaching of boron mud in hydrochloric acid system, and then filter and separate to obtain magnesium chloride, ferric chloride leachate and borosilicate-rich slag. The low-temperature pressure leaching conditions are: the solid-to-liquid ratio of boron mud to hydrochloric acid is 1kg: 15L, the leaching temperature is 80°C, the concentration of hydrochloric acid is 3mol / L, the leaching time is 60min, and the leaching rates of magnesium and iron are 97.5% and 96.2% respectively;
[0047] (2) Add MgO or Fe to the magnesium chloride and ferric chloride leaching solution obtained in step (1) 2 o 3 Adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 3.5. In order to effectively precipitate and separate iron, add H during the precipitation process. 2 o 2 Oxidize the ferrous ions in the leach solution to ferric ions, precipitate the iron ions in the form of ferric hydroxide, and then filter and s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com