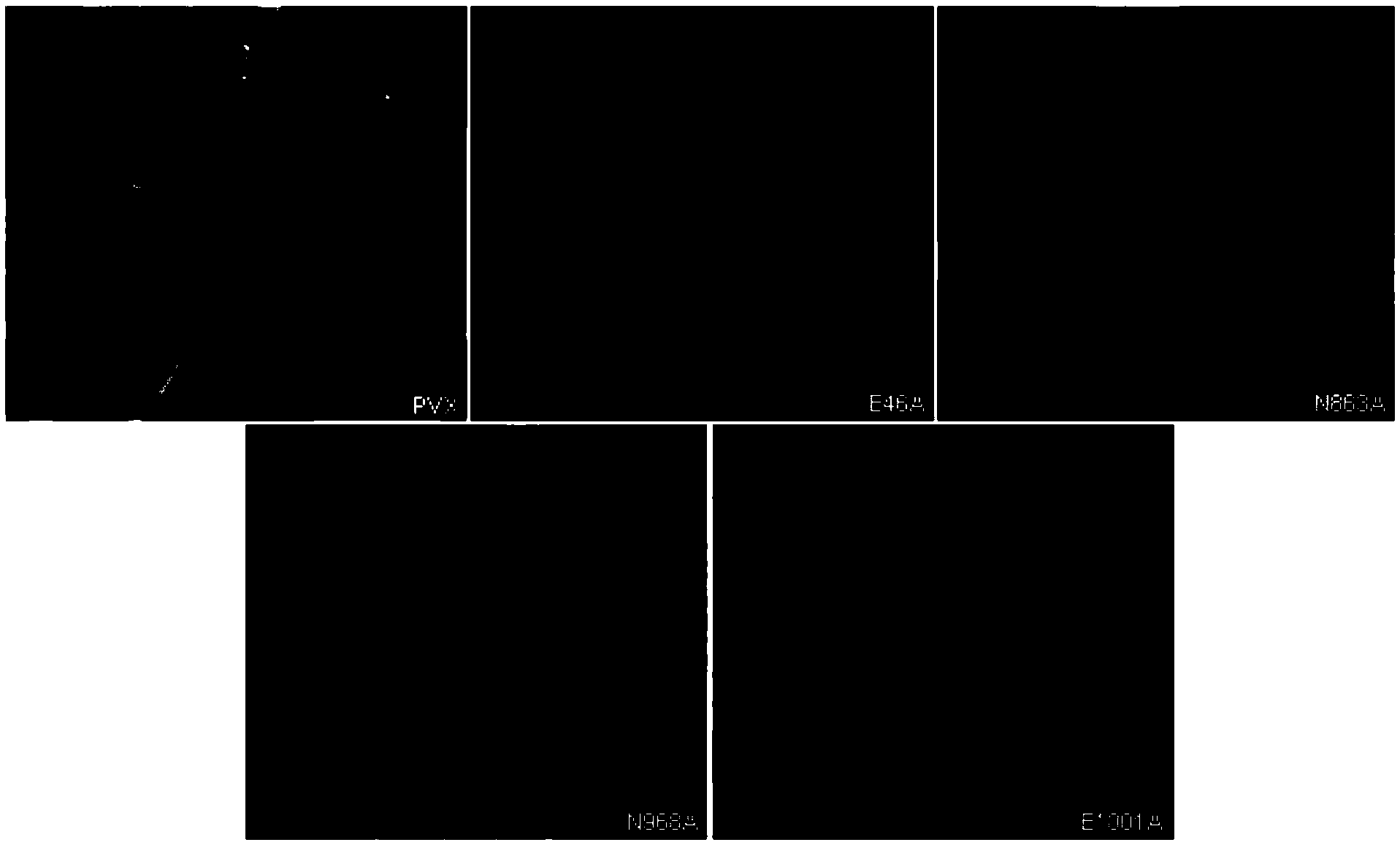Screening of potato virus X (PVX) low virulent strains and application in cross protection
A technology of attenuated strains and potatoes, applied in the field of plant virus genetic engineering, can solve the problems of little research and loss of PVX attenuated strains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Site-directed mutation
[0023] Using Potato X virus invasive clone pCaPVX100 as a template, four sites were mutated by PCR, and the polymerase used was Phusion high-fidelity polymerase (Finnzymes).
[0024] The PCR reaction system is as follows:
[0025]
[0026] After the reaction is over, add 0.5μL of DpnI (20U / μL) to the PCR product, treat it at 37°C for 2h, add 125μL of absolute ethanol and 5μL of 3mol / L sodium acetate (pH=5.2) to mix, and precipitate at -20°C overnight. Centrifuge at 13000r / min for 10min, discard the supernatant, wash the pellet with 1mL of 75% ethanol and place it at room temperature to dry naturally, add 10μL of ddH 2 O water was re-dissolved and transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α. The mutant plasmid was verified by sequencing.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2: Virus inoculation
[0028] Transform pCaPVX100 or mutant plasmid into Agrobacterium GV3101. After colony PCR verification, a single spot was inoculated into liquid LB medium containing kanamycin (50μg / mL), rifamycin (50μg / mL), and tetracycline (50μg / mL). Add 500μL of bacterial solution to 5mL of LB medium containing 10mmol / L 2-(N-morpholine)-ethanesulfonic acid (MES), 20μmol / L acetosyringone (AS) and the above three antibiotics, and shake at 28°C Cultivate to the logarithmic growth phase. Collect the bacteria by centrifugation and resuspend in 10mmol / L MgCl 2 , 10mmol / L MES, 150μmol / LAS, adjust the concentration to OD 600 It is about 0.5, and let stand at room temperature for 3 hours. Take a 5mL disposable syringe, remove the needle to suck the Agrobacterium liquid, and infiltrate it from the back of the leaf of Ben's tobacco (5-6 weeks old or 4-6 true leaves). Each plant is infiltrated with 2 leaves. The infiltrated plants were cultured in a light incubator...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: Symptom observation and virus concentration detection
[0030] Observe the symptoms of inoculated plants, and use Western blot to detect virus accumulation. On the 6th day after inoculation, pCaPVX100 caused obvious mosaic and shrinkage symptoms on the leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana system, while the replica enzyme RdRp had E at position 46, N at position 863, and N at position 968. The four mutants where N and E at position 1001 were mutated to A respectively showed almost no symptoms on Ben's smoke ( figure 1 ). 15 days after inoculation, pCaPVX100 caused severe mosaic on Ben's tobacco, and the four mutants still showed no symptoms. The inventors named these attenuated mutants as E46A, N863A, N968A, E1001A (wherein, the nucleotide sequence of E1001A RdRp is shown in Seq ID No. 9, and the amino acid sequence is shown in Seq ID No. 10). Western blot analysis showed that the wild-type virus (WT) pCaPVX100 accumulated to a very high concentration in Ben's smok...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com