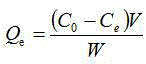Artemisinin molecular imprinting film, preparation method and applications thereof
A molecular imprinting, artemisinin technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, semi-permeable membrane separation, etc., to achieve the effects of good thermal stability, fast adsorption kinetic properties, and not easy to damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
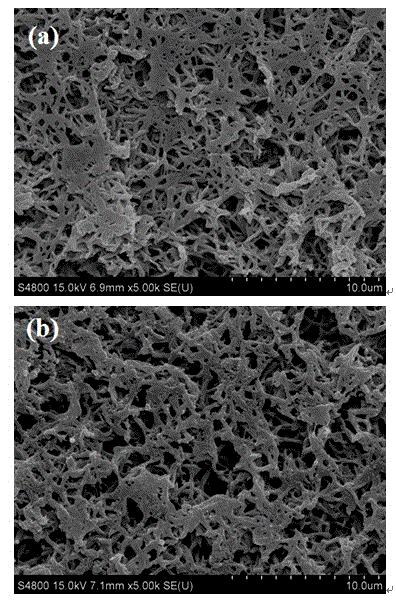
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] (1) Activation of the surface of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane
[0043] A piece of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane was placed in 100 mL of methanol, and after standing at room temperature for 60 min, it was fully washed with deionized water, and dried in a vacuum oven at 45 °C to constant weight.
[0044] (2) Preparation of catalytic system
[0045] 0.1 mmol cuprous bromide (CuBr 2 ), 0.2 mmol 2,2-bipyridine (2,2'-Bipyridine) and 0.2 g n-hexadecane were dissolved in a round bottom flask containing 5 mL ethanol, 60 o C oil bath heating for 3 h. After heating, cool quickly in an ice-water bath and set aside.
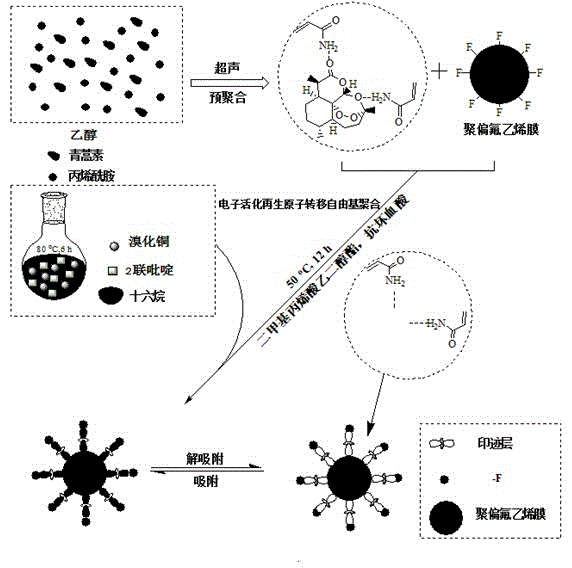
[0046] (3) Preparation of artemisinin molecularly imprinted composite membrane
[0047] Dissolve 1 mmol of artemisinin and 4 mmol of acrylamide in 100 mL of ethanol, sonicate it to fully dissolve it, then leave the system at room temperature for 24 h to form a stable template-monomer complex , and then adding 20 mmol ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) t...
Embodiment 2
[0061] (1) Activation of the surface of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane
[0062] A piece of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane was placed in 100 mL of methanol, and after standing at room temperature for 60 min, it was fully washed with deionized water, and dried in a vacuum oven at 45 °C to constant weight.
[0063] (2) Preparation of catalytic system
[0064] 0.1 mmol cuprous bromide (CuBr 2 ), 0.15 mmol 2,2-bipyridine (2,2'-Bipyridine) and 0.2 g n-hexadecane were dissolved in a round bottom flask containing 5 mL ethanol, 60 o C oil bath heating for 3 h. After heating, cool quickly in an ice-water bath and set aside.
[0065] (3) Preparation of artemisinin molecularly imprinted composite membrane
[0066] Dissolve 1 mmol of artemisinin and 6 mmol of acrylamide in 100 mL of ethanol, sonicate it to fully dissolve, and then leave the system at room temperature for 24 h to form a stable template-monomer complex , and then adding 20 mmol ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA)...
Embodiment 3
[0080] (1) Activation of the surface of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane
[0081] A piece of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane was placed in 100 mL of methanol, and after standing at room temperature for 60 min, it was fully washed with deionized water, and dried in a vacuum oven at 45 °C to constant weight.
[0082] (2) Preparation of catalytic system
[0083] 0.1 mmol cuprous bromide (CuBr 2), 0.1 mmol 2,2-bipyridine (2,2'-Bipyridine) and 0.2 g n-hexadecane were dissolved in a round bottom flask containing 4 mL of ethanol, 60 o C oil bath heating for 3 h. After heating, cool quickly in an ice-water bath and set aside.
[0084] (3) Preparation of artemisinin molecularly imprinted composite membrane
[0085] Dissolve 1 mmol of artemisinin and 8 mmol of acrylamide in 100 mL of ethanol, sonicate it to fully dissolve, and then leave the system at room temperature for 24 h to form a stable template-monomer complex , and then adding 20 mmol ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Saturated adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com