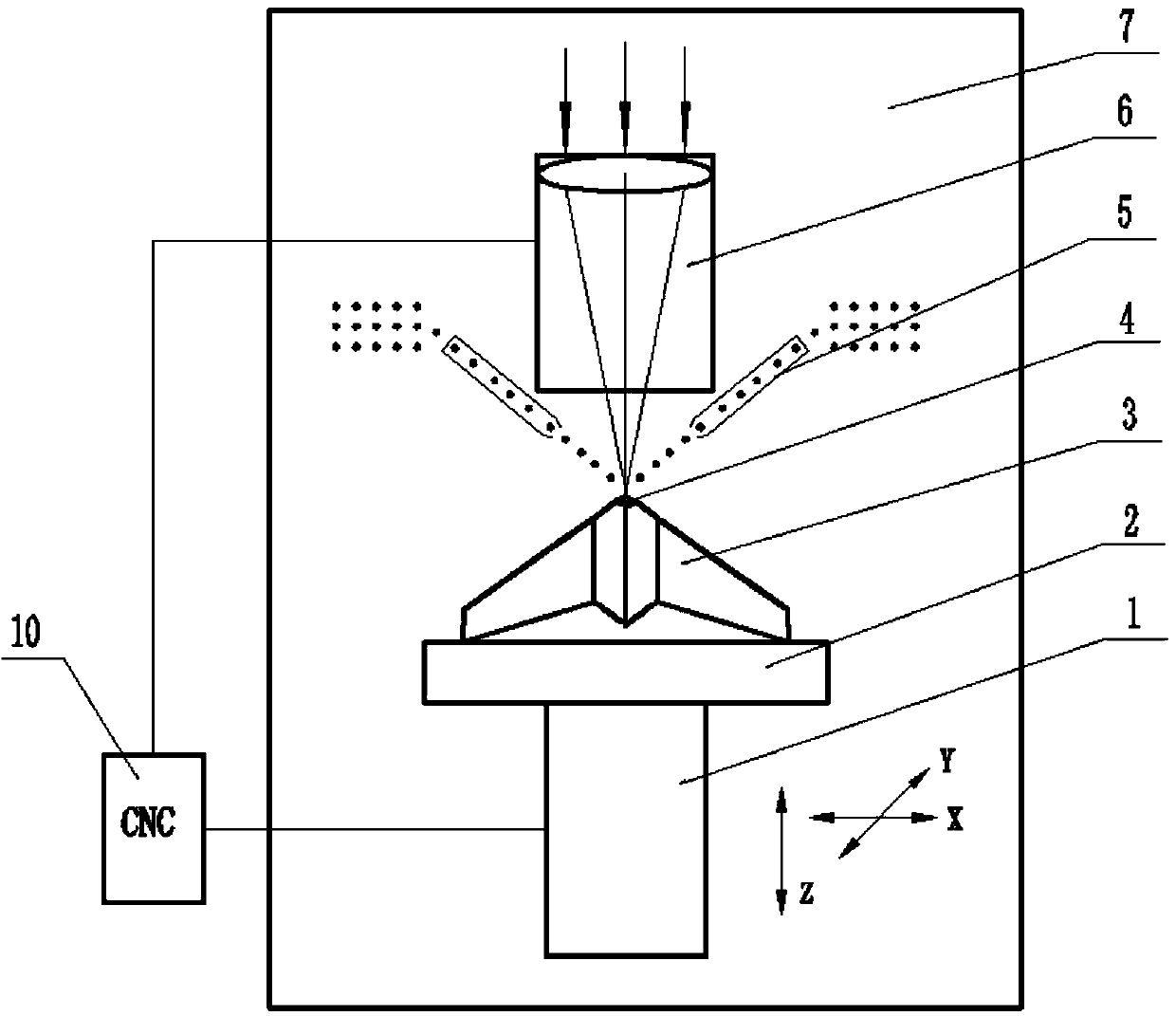
Titanium alloy thin-wall blade laser-cladding low-stress local orientation cooling restoration method
A technology of laser cladding and directional cooling, which is applied in the field of laser cladding low-stress local directional cooling repair of titanium alloy thin-walled blades. Overheating, over-burning, loss of burn-through strength, and little effect, etc., to achieve uniform microstructure, improve the quality of repair molding, and reduce the effect of the affected area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] 1) Mix iron powder with a particle size of 50-100 μm and water glass evenly according to a mass ratio of 3:1 to obtain an iron powder mixture;
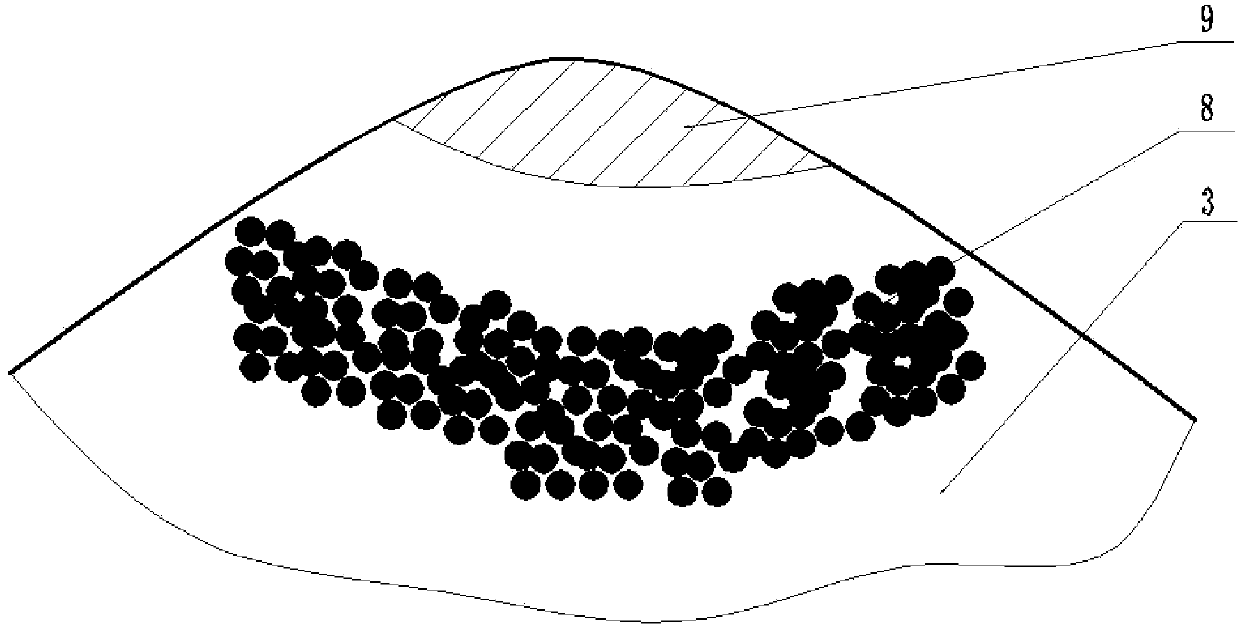
[0039] 2) Paste the iron powder mixture on the damaged titanium alloy thin-walled blade, wherein the diameter of the defect repair point is ≤10mm, and the iron powder mixture is pasted at a distance of 3mm from the defect repair point of the titanium alloy thin-walled blade, in a circular distribution, and the defect repair point The ratio of the area to the paste area of the iron powder mixture is 1:1;
[0040] 3) Put the titanium alloy thin-walled blade pasted with the iron powder mixture into a glove box filled with inert gas, and use a powder feeder to transport the titanium alloy powder for repair to the titanium alloy thin-walled blade at a speed of 30g / min. At the defect repair point, a laser with a power of 2000W is used to emit a laser with a spot diameter smaller than or equal to the diameter of the defect repair po...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1) According to the mass ratio of 5:1, the iron powder with a particle size of 150-200 μm and the paraffin-based binder are uniformly mixed to obtain an iron powder mixture;
[0044] 2) Paste the iron powder mixture on the damaged titanium alloy thin-walled blade, wherein the diameter of the defect repair point is ≤10mm, and the iron powder mixture is pasted at a distance of 8mm from the defect repair point of the titanium alloy thin-walled blade, in a circular distribution, and the defect repair point The ratio of the area to the paste area of the iron powder mixture is 1:2;
[0045] 3) Put the titanium alloy thin-walled blade pasted with the iron powder mixture into a glove box filled with inert gas, and use a powder feeder to transport the titanium alloy powder for repair to the titanium alloy thin-walled blade at a speed of 120g / min. At the defect repair point, a laser with a power of 2000W is used to emit a laser with a spot diameter smaller than or equal to the ...
Embodiment 3
[0048] 1) According to the mass ratio of 4:1, the iron powder with a particle size of 100-150 μm and the polymer binder are uniformly mixed to obtain an iron powder mixture;
[0049] 2) Paste the iron powder mixture on the damaged titanium alloy thin-walled blade, wherein the diameter of the defect repair point is ≤10mm, and the iron powder mixture is pasted at a distance of 5mm from the defect repair point of the titanium alloy thin-walled blade, in a circular distribution, and the defect repair point The ratio of the area to the sticking area of the iron powder mixture is 1:1.5;
[0050] 3) Put the titanium alloy thin-walled blade pasted with the iron powder mixture into a glove box filled with inert gas, and use a powder feeder to transport the titanium alloy powder for repair to the titanium alloy thin-walled blade at a speed of 80g / min. On the defect repair point, a laser with a power of 2000W is used to emit a laser with a spot diameter smaller than or equal to the dia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com