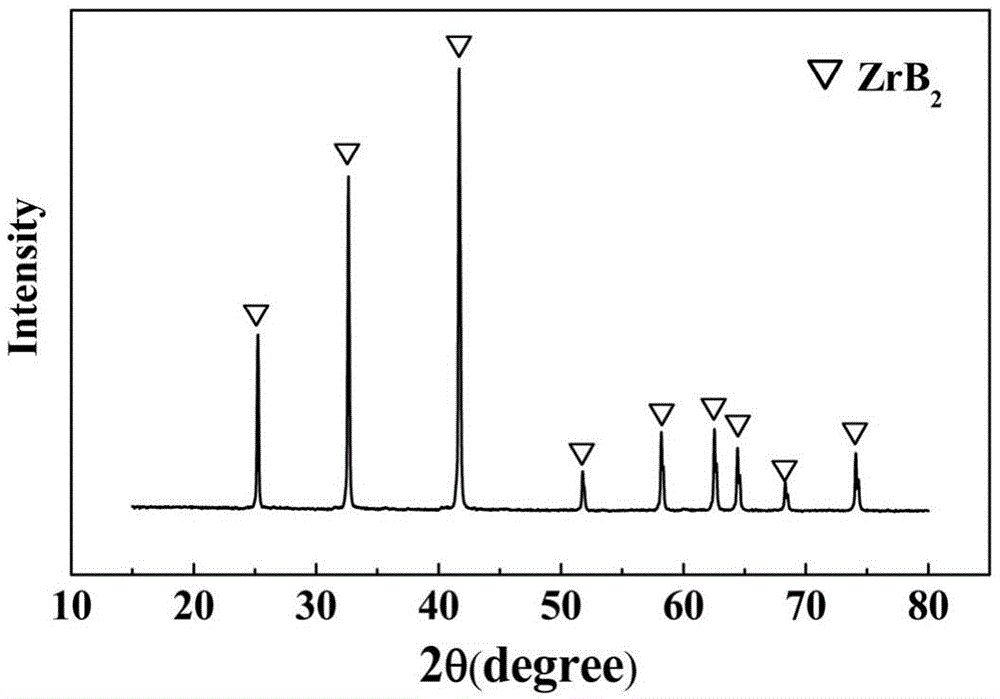
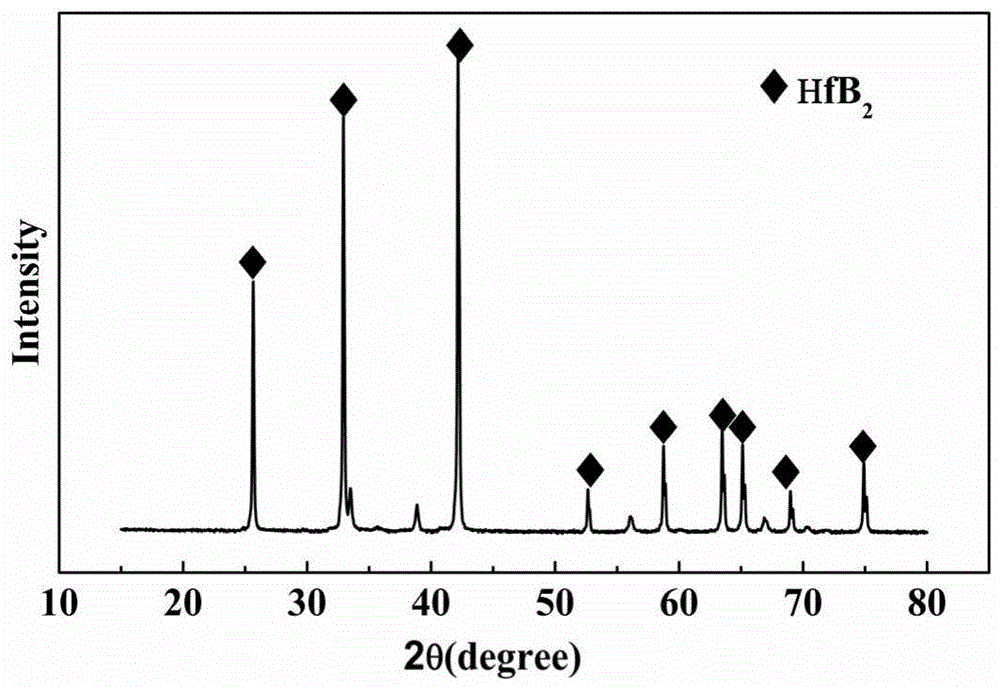
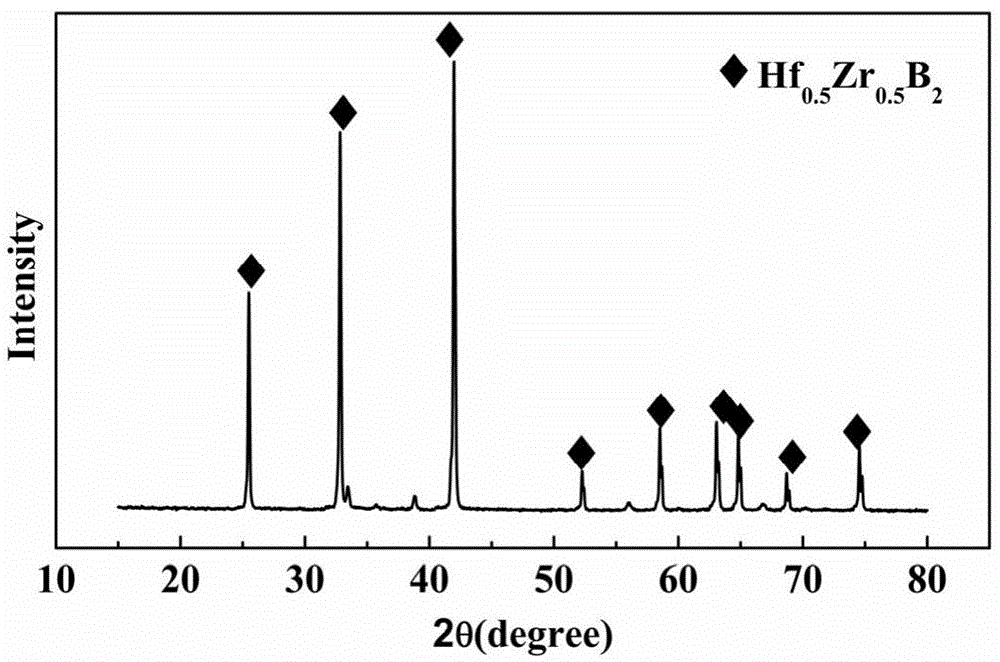
Preparation method and application of boride ceramic precursor
A technology of ceramic precursors and borides, applied in the field of ultra-high temperature ceramics, can solve the problems of low product purity, high preparation temperature, humidity sensitivity, etc., and achieve the effect of high purity, low preparation temperature and easy composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] a) ZrOCl with a molar ratio of 1:0:15:400 2 ·8H 2 O, malic acid, glycerol and solvent distilled water are added in the beaker, placed on a magnetic heating stirrer, stirred until each reactant is dissolved, after cooling, add boric acid with a Zr molar ratio of 8:1 into the beaker, and heat to Stir at 80°C for 20 minutes to dissolve the boric acid, and obtain ZrB after cooling 2 Ceramic precursors;
[0041] b) ZrB 2 The ceramic precursor was heated at 200°C for 5 hours to obtain a crosslinked precursor;
[0042] c) Put the crosslinked precursor into an alumina crucible, put it into a high-temperature pyrolysis furnace, raise the temperature to 1600°C at 7°C / min under an argon atmosphere, then vacuumize it, and keep it under vacuum for 0.5h to obtain ZrB 2 ceramics.
Embodiment 2
[0044] a) ZrO(NO 3 ) 2 ·xH 2 O. Add malic acid, glycerol and solvent distilled water into the beaker, place it on a magnetic heating stirrer, heat to about 40°C and stir until the reactants are completely dissolved. After cooling, add boric acid with a molar ratio of 2:1 to Zr In a beaker, heat to 60°C and stir for 80 minutes to dissolve the boric acid, and get ZrB after cooling 2 Ceramic precursors;
[0045] b) ZrB 2 The ceramic precursor was heated at 120°C for 20 hours to obtain a crosslinked precursor;
[0046] c) Put the cross-linked precursor into an alumina crucible, put it into a high-temperature cracking furnace, raise the temperature to 1200°C at 7°C / min under an argon atmosphere, and then vacuumize it, and keep it under vacuum for 4h to obtain ZrB 2 ceramics.
Embodiment 3
[0048] a) HfCl with a molar ratio of 1:1:8:800 4 , tartaric acid, ethylene glycol and solvent distilled water into the beaker, placed on a magnetic heating stirrer, heated to about 40 ℃ and stirred until the reactants are completely dissolved, after cooling, add boric acid with a molar ratio of 6:1 to Zr into the beaker , heated to 70°C and stirred for 40 minutes to dissolve boric acid, and HfB was obtained after cooling 2 Ceramic precursors;
[0049] b) HfB 2 The ceramic precursor was heated at 160°C for 8 hours to obtain a crosslinked precursor;
[0050] c) Put the cross-linked precursor into an alumina crucible, put it into a high-temperature cracking furnace, raise the temperature to 1500°C at 7°C / min under an argon atmosphere, and keep it warm for 3h to obtain HfB 2 ceramics.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com