Method for detecting golden glucose coccus by using immune optical-fiber evanescent-wave biosensor
A biosensor, glucococcus technology, applied in the field of inspection and quarantine, can solve problems such as the inability to form an evanescent wave conduction environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
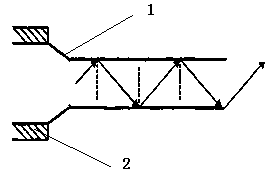
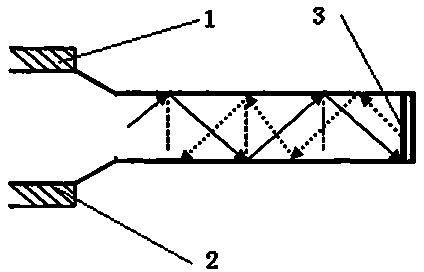
[0017] See figure 1 , 2 , an immune optical fiber evanescent wave biosensor probe, which includes a cladding portion 11 and an adsorption portion 12, the end section of the adsorption portion 12 is provided with a silver reflective layer 13; the silver reflective layer 13 is welded Or the vacuum coating method is used to fit the cross-section of the end of the adsorption part; the adsorption part 12 is tapered.
Embodiment 2
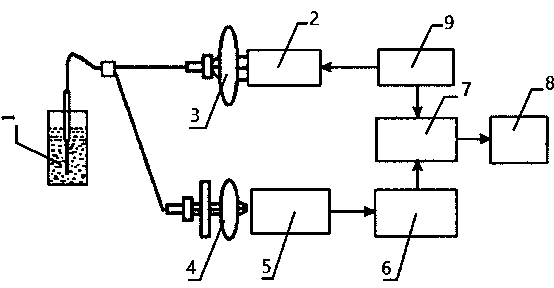
[0019] See Figure 1-3 , an immune optical fiber evanescent wave biosensor, which includes: an optical system, a photoelectric conversion and signal amplification system, and a data acquisition and processing device;
[0020] The optical system includes: a drive circuit 9, a laser 2, a convex lens 3, an optical fiber probe 1, and a filter 4;
[0021] The photoelectric conversion and signal amplification system includes: photomultiplier tube 5 and signal amplifier 6;
[0022] The data acquisition and processing system includes: data acquisition card 7 and laboratory virtual instrument engineering platform (LabVIEW) 8;
[0023] The laser 2 emits laser light through the convex lens 3 to the fiber optic probe, and the fluorescent signal returns; the fluorescent signal is converted and amplified by the photomultiplier tube 5 and the signal amplifier 6; the data acquisition card 7 and the laboratory virtual instrument engineering platform 8 collect, process, and detect signal stren...
Embodiment 3
[0027] 1) Preparation of immuno-optical fiber probe: After peeling the fiber probe, soak it in sodium hydroxide for 10 min, and then soak it in hydrochloric acid for 10 min. After rinsing with deionized water three times, let it dry naturally. The optical fiber was then placed in 10% acetone solution for 1 h, and rinsed with acetone 6 times to remove the residual acetone solution. The surface of the fiber core is activated by reagents such as triaminopropyltriethoxysilane and glutaraldehyde. The treated optical fiber was inserted into the solution of Staphylococcus aureus monoclonal antibody and soaked for 24 hours, and then it was taken out and washed with deionized water to obtain an immune optical fiber probe coated with the captured antigen.
[0028] 2) Detection of Staphylococcus aureus
[0029] Using an immune optical fiber evanescent wave biosensor system described in Example 2, the CdTe-polyclonal antibody conjugate is made into an aqueous solution, the capture a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com