Preparation method and application of in-situ carbon-compounded prussian blue type compound thin film
A Prussian blue, in-situ composite technology, applied in the field of energy material preparation and electrochemistry, can solve the problems of high internal vacancy and water content, poor electronic conductivity of materials, insufficient contact, etc., to increase the integrity of the crystal structure and reduce the vacancy. and the effect of improving water content and electrode conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The preparation method of the Prussian blue compound thin film of in-situ composite carbon comprises the following steps:
[0025] 1) Ultrasonic dispersion of carbon materials in NaCl solution;
[0026] 2) Weigh the transition metal cyano complex, reducing agent and inorganic acid in proportion and add them to the above solution;
[0027] 3) Electrolysis of water for 3 to 5 minutes to clean the surface of the ITO conductive substrate;
[0028] 4) Under the constant voltage condition of -2.0-2.0V relative to the standard Ag / AgCl electrode, a Prussian blue compound film with in-situ composite carbon was formed on the ITO conductive substrate.
[0029] The mole fraction ratio of the transition metal cyano complex, inorganic acid, reducing agent and carbon material is 1:(0.1-30):(0.1-10):(0.1-20).
[0030] The carbon material is selected from at least one of Ketjen black, acetylene black, carbon black, Super P, graphene, carbon nanotubes, mesophase microspheres or pyrolyt...
Embodiment 1
[0041] In this example, an in-situ composite carbon Prussian blue thin film positive electrode material was prepared by an electrochemical deposition method. The molar ratio of each substance required for the reaction is Na 4 Fe(CN) 6 : HCl: Ketjen Black: Sodium Borohydride = 1:5:1:0.2. The specific steps are:
[0042] 1) Ultrasonic dispersion of Ketjen black in 1.0M NaCl solution;
[0043] 2) Weigh Na in proportion 4 Fe(CN) 6 , HCl and sodium borohydride were added to the above solution;
[0044] 3) Electrolysis of water for 3 to 5 minutes to clean the surface of the ITO conductive substrate;
[0045] 4) Under the constant voltage condition of -0.5V relative to the standard Ag / AgCl electrode, a Prussian blue film of in-situ composite carbon was formed on the ITO substrate, and finally the film was peeled off the substrate with a microknife for future use.
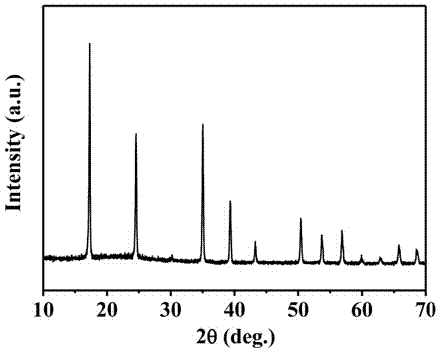
[0046] Analyze the crystal structure of product with powder X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku D / Max-2550pc, CuK ray), ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The preparation method of this example is the same as that of Example 1, but the carbon material is acetylene black, and the reducing agent is sodium citrate. The molar ratio of each substance required for the reaction is Na 4 Fe(CN) 6 : HCl: acetylene black: sodium citrate=1:10:2:0.5. The specific steps are:
[0052] 1) Ultrasonic dispersion of acetylene black in 1.0M NaCl solution;
[0053] 2) Weigh Na in proportion 4 Fe(CN) 6 , HCl and sodium citrate were added to the above solution;
[0054] 3) Electrolysis of water for 3 to 5 minutes to clean the surface of the ITO conductive substrate;
[0055] 4) Under the constant voltage condition of -1.0V relative to the standard Ag / AgCl electrode, a Prussian blue film of in-situ composite carbon was generated on the ITO substrate, and finally the film was peeled off the substrate with a microknife for future use.
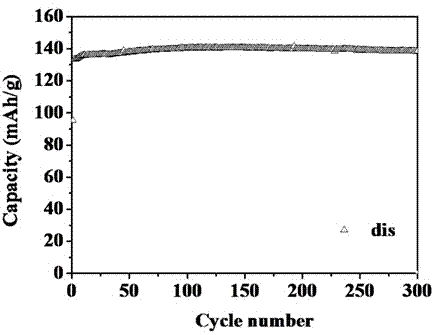
[0056] The assembly process and testing method of the button cell are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com