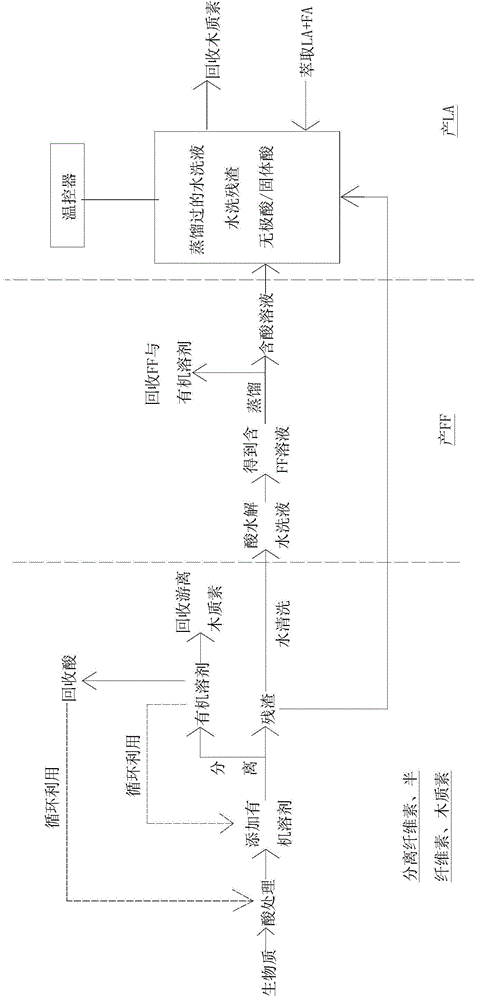
A method for preparing furfural after fractional treatment of biomass and preparing levulinic acid by rapid temperature change method
A technology of grading treatment and levulinic acid, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of carboxylate, etc. The effect of less by-products, less side reactions, and less water consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The method process of this embodiment is as figure 1 shown.
[0021] 10g of corn cobs were treated with 80mL of analytically pure phosphoric acid at 50°C for 60min with stirring and impregnation, added 300mL of pre-cooled acetone, stirred thoroughly, placed in a centrifuge, and centrifuged at 4000rpm for 20min to separate the supernatant. Wash the residue after centrifugation with 300mL distilled water and filter. The residue obtained after filtration was used for later use, and the washing solution was hydrolyzed in an autoclave at 120° C. for 2 hours. After the reaction, the hydrolyzate was taken out and distilled. After cooling, it was detected by liquid chromatography that the yield of FF was 63%. The distilled hydrolyzate, from which FF and traces of organic solvents were removed, totaled about 280 mL and contained a small amount of acid. The distilled washing liquid and washing residue are mixed, placed in a high-pressure tubular reactor, and then Amberlyst-70 ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The method process of this embodiment is as figure 1 shown.
[0026] Mix 10g of bagasse and 80mL of pre-cooled concentrated hydrochloric acid to form a uniform suspension, then slowly add 20mL of pre-cooled concentrated sulfuric acid in the fume hood several times, seal it and place it on a magnetic stirrer, and stir slowly for 60min. Add 300 mL of pre-cooled dioxane, stir slowly for about 30 min, then place in a centrifuge, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 min, and separate the supernatant. Wash again with 200 mL of pre-cooled dioxane, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 10 min, and separate the supernatant. The two supernatants can be mixed. Wash the centrifuged residue with 300 mL of distilled water and filter. The residue obtained after filtration was used for later use, and the washing solution was hydrolyzed in an autoclave at 110° C. for 1 hour. After the reaction, the hydrolyzate was taken out and distilled. After cooling, it was detected by liquid chromatography that t...
Embodiment 3
[0028] The method process of this embodiment is as figure 1 shown.
[0029] 10g of corn stalks were soaked with 80mL of trifluoroacetic acid at 50°C for 45min, then added 200mL of pre-cooled isopropanol, stirred thoroughly and then placed in a centrifuge for 1h, then centrifuged at 4000rpm for 20min to separate the supernatant. Wash the residue after centrifugation with 300mL distilled water and filter. The residue obtained after filtration was used for later use, and the washing solution was hydrolyzed in an autoclave at 120° C. for 80 minutes. After the reaction, the hydrolyzate was taken out and distilled. After cooling, it was detected by liquid chromatography that the yield of FF was 61%. After distillation of the hydrolyzate, FF and traces of organic solvent were removed, leaving a small amount of acid. The distilled washing solution and the washing residue are mixed, placed in a high-pressure tubular reactor, and then HZSM-5 (0.7wt%) is added, and the pH of the react...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com