High-performance permanent-magnet ferrite pre-sintered material prepared based on NdFeB wastes and preparation method thereof
A permanent magnet ferrite, NdFeB technology is applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of waste resources, which can solve the problems of high resource and energy consumption and low economic value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
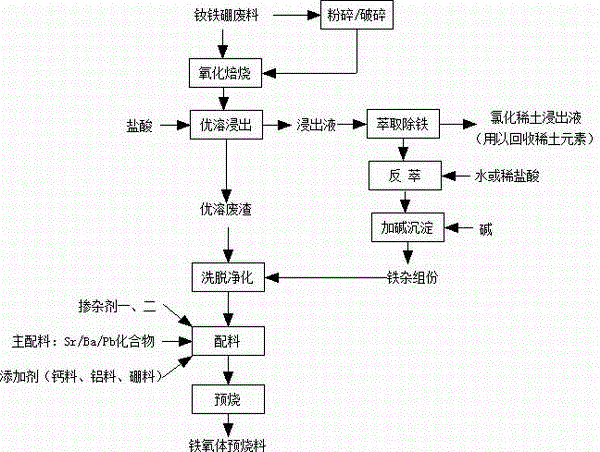
[0072] Take a batch of scraps from the machining process of NdFeB permanent magnet materials and a mixture of grinding powder generated during the grinding process, wherein the weight ratio of scraps and grinding powders is 82:18. After testing, the above-mentioned metal elements in each 100g of NdFeB scrap include: total rare earth elements 32.77g (including Nd 29.57g, Pr 2.13g, Dy 0.65g, Gd 0.42g), Fe element content 60.35g, Co element content 2.11g g. Al element content 0.42g, Zn element content 0.25g (Cu, Nb element content not detected).
[0073] Take 2000Kg of the above-mentioned batch of NdFeB waste materials, grind and pulverize them through a ball mill to an average particle size of less than 100 mesh, and oxidize and roast the pulverized materials in a rotary kiln (calcination temperature 900 ° C, roasting time 1 hour), and then The oxidized and roasted material is leached with 3N hydrochloric acid (leaching temperature is 85°C, and the pH value of the leaching end p...
Embodiment 2
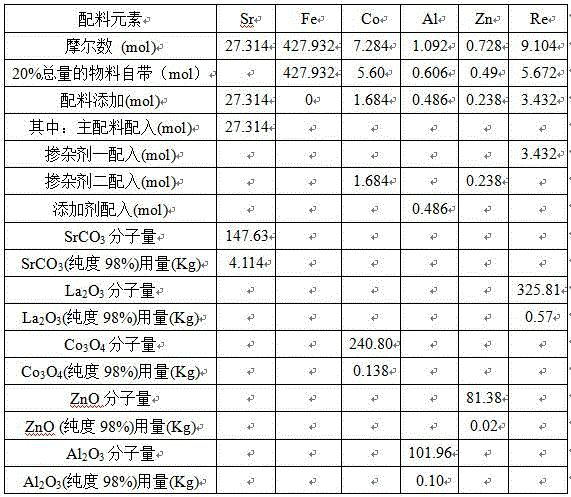
[0094] In addition, 20% of the total amount of the material after elution and purification in Example 1 was used for batching before pre-calcination. Carry out batching according to the batching table of embodiment 1, differ from embodiment 1, do not add CaCO in batching 3 , boric acid.
[0095] According to the same method of embodiment 1, calcined coarse powder is obtained.
[0096] Crystallinity analysis of calcined material:
[0097] Samples were taken for SEM scanning electron microscope analysis, and the generated ferrite grains were analyzed at different resolutions. The analysis showed that the calcined material was fine and uniform in crystallization, and the grain size was between 1 and 2 μm.
[0098] Magnetic performance testing of pre-fired materials:
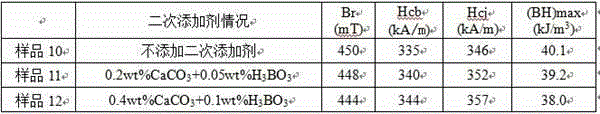
[0099] Take pre-fired coarse powder samples, add different contents of secondary additives, and carry out wet grinding; after wet grinding, the particle size of the powder is 0.8 μm, hang the filter cloth to dry, a...
Embodiment 3
[0106] In addition, 20% of the total amount of the material after elution and purification in Example 1 was used for batching before pre-calcination.
[0107] According to Sr 0.72 Re 0.28 Fe 11.75 co 0.25 al 0.015 Zn 0.015 o 19 Carry out batching, all the other are with embodiment 1.
[0108] On the basis of the ingredients list, add 0.4wt% CaCO relative to the total amount of material 3 (98% purity), 0.1wt% boric acid (98% purity) as an additive.
[0109] The calcined coarse powder was obtained in a similar manner to Example 1, except that the calcined temperature used was 1250°C.
[0110] Crystallinity analysis of calcined material:
[0111] Samples were taken for SEM scanning electron microscope analysis, and the generated ferrite grains were analyzed at different resolutions. The analysis showed that the dry calcined material crystallized finely and uniformly, and the grain size was between 1 and 2 μm.
[0112] Magnetic performance testing of pre-fired materials:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com