Process for producing in-situ modified nano-magnesium hydroxide by taking phosphate tailings as raw materials
A nano-magnesium hydroxide and in-situ modification technology, which is applied in the field of waste resource utilization and functional nanomaterials, can solve the problems of environmental damage and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, simple process and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
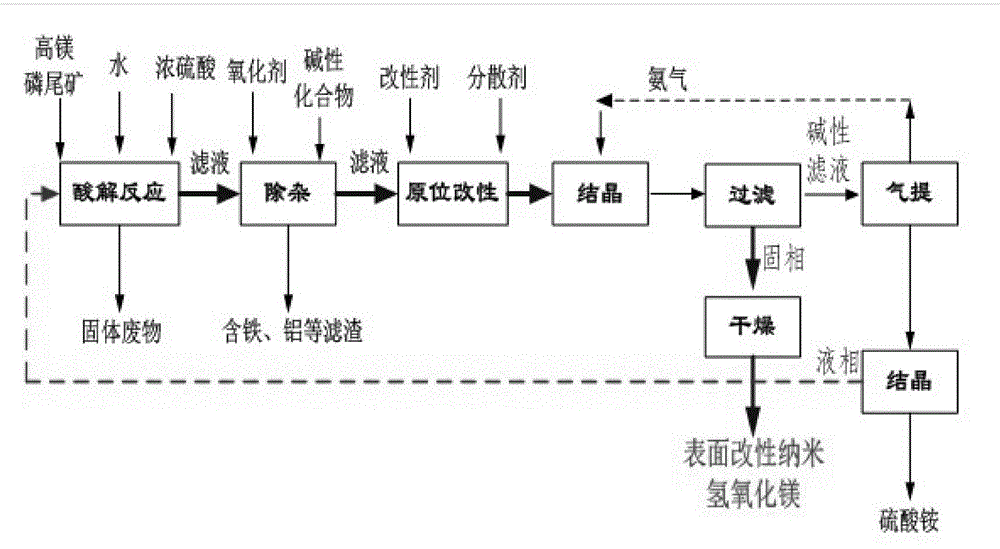
[0044] Put 52 kg of phosphorus tailings obtained from flotation into the acidolysis reactor, add 470 liters of water and stir to mix evenly. After reaching the preset temperature of 25°C, slowly add 29 liters of 98wt% sulfuric acid to react. After reacting for 2 hours, filter and wash For solid-liquid separation; add 0.347 liters of H 2 o 2 Oxidation, use ammonia water to control the pH of the filtrate to 6.7, and obtain a refined magnesium sulfate solution after removing impurities; add the silane coupling agent KH-570 and the dispersant polyethylene glycol to the refined magnesium sulfate solution, and fully stir for 2.5 hours; move into the crystallization In the reactor, the temperature of the solution is controlled at 25°C, and ammonia gas is slowly introduced for 1.5 hours. After the reaction, the final pH value is 10.7, aged at a constant temperature of 30°C for 20 minutes, filtered, washed, and dried to obtain in-situ modified nano-hydroxide Magnesium products.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Put 104 kg of phosphorus tailings obtained from flotation into the acidolysis reactor, add 470 liters of water and stir to mix evenly. After reaching the preset temperature of 35°C, slowly add 29 liters of 98wt% sulfuric acid to react. After reacting for 2 hours, filter and wash Carry out solid-liquid separation; add 0.694 liters of H 2 o 2 Oxidation, use ammonia water to control the pH of the filtrate to 6.5, remove impurities to obtain a refined magnesium sulfate solution; add the silane coupling agent KH-560 and dispersant sodium polyphosphate to the refined magnesium sulfate solution, and fully stir for 3 hours; move into the crystallization In the reactor, the temperature of the solution is controlled at 35°C, and ammonia gas is slowly introduced for 2 hours. After the reaction, the final pH value is 11, aged at a constant temperature of 45°C for 30 minutes, filtered, washed, and dried to obtain in-situ modified nano-hydroxide Magnesium products.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Put 36.5 kg of phosphorous tailings obtained from flotation into the acidolysis reactor, add 440 liters of water and stir and mix evenly. After reaching the preset temperature of 45°C, slowly add 60 liters of 98wt% sulfuric acid to react. After reacting for 3 hours, filter and wash Carry out solid-liquid separation; add 0.243 liters of H 2 o 2 Oxidation, use ammonia water to control the pH of the filtrate to 6.5, and remove impurities to obtain a refined magnesium sulfate solution; add the silane coupling agent KH-550 and the dispersant polyethylene glycol to the refined magnesium sulfate solution, and fully stir for 2.5 hours; move into the crystallization In the reactor, the temperature of the solution is controlled at 55°C, and ammonia gas is slowly introduced for 2 hours. After the reaction, the final pH value is 10.5, aged at a constant temperature of 50°C for 40 minutes, filtered, washed, and dried to obtain in-situ modified nano-hydroxide Magnesium products.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com