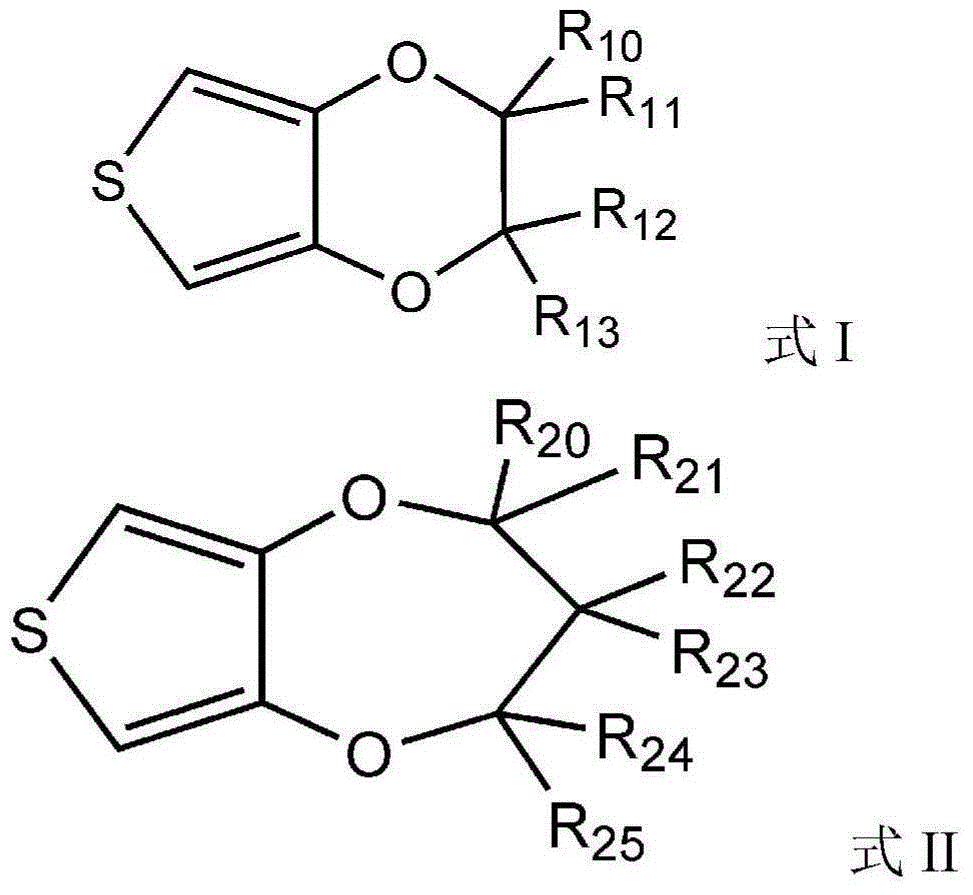
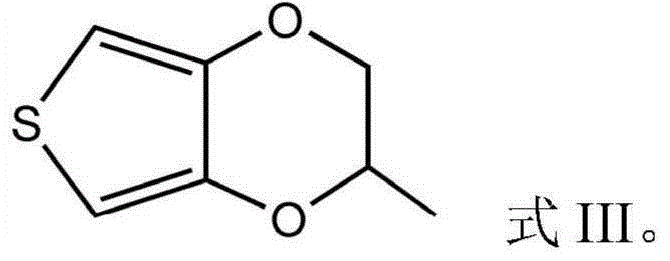
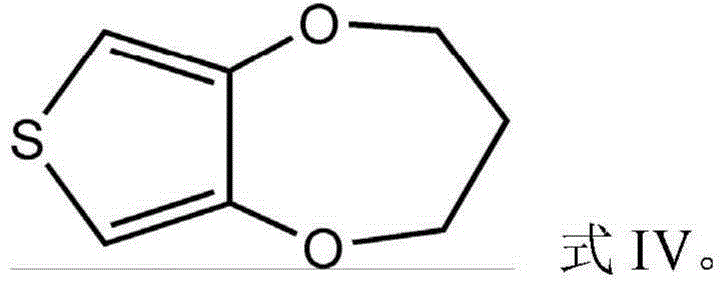
Electrolyte additive and application thereof
An electrolyte additive and additive technology, which is applied in the field of lithium-ion batteries, can solve the problems of battery rate and cycle performance attenuation, lithium ion migration and diffusion kinetics, and interface impedance increase, etc., to improve rate performance and cycle stability. And safety performance, the effect of suppressing side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Positive plate P1 # preparation of
[0064] The positive electrode active material lithium cobaltate (molecular formula LiCoO 2 ), conductive agent (the mass percentage of carbon nanotube CNT in the conductive agent is 6%, and the mass percentage of conductive carbon black is 94%), binder polyvinylidene fluoride (abbreviated as PVDF, binder The mass percentage of polyvinylidene fluoride is 7%) is uniformly dispersed in the solvent N-methylpyrrolidone (abbreviated as NMP) to prepare positive electrode slurry. The solid content in the positive electrode slurry is 77wt%, and the solid component contains 98.26wt% lithium cobalt oxide, 0.9% PVDF and 0.84wt% conductive agent. Coat the positive electrode slurry evenly on the positive electrode current collector aluminum foil with a thickness of 12 μm, and the coating amount on one side is 0.0215 g / cm 2 . After drying at 85°C, cold press, edge trimming, cutting, and slitting were carried out, and then dried under vacuu...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Electrolyte L2 # preparation of
[0075] with electrolyte L1 # The preparation method is the same, the difference is that the mass percentage of the additive 2-methyl-2,3-dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxane is changed from 1% to 0.1%, the resulting electrolyte is denoted as L2 # .
[0076] Lithium-ion secondary battery C2 # preparation of
[0077] With lithium-ion secondary battery C1 # The preparation method is the same, the difference is that the electrolyte is changed to L2 # , the resulting lithium-ion secondary battery is denoted as C2 # .
Embodiment 3
[0079] Electrolyte L3 # preparation of
[0080] with electrolyte L1 # The preparation method is the same, the difference is that the mass percentage of the additive 2-methyl-2,3-dihydrothieno[3,4-b][1,4]dioxane is changed from 1% to 3%, the resulting electrolyte is denoted as L3 # .
[0081] Lithium-ion secondary battery C3 # preparation of
[0082] With lithium-ion secondary battery C1 # The preparation method is the same, the difference is that the electrolyte is changed to L3 # , the resulting lithium-ion secondary battery is denoted as C3 # .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com