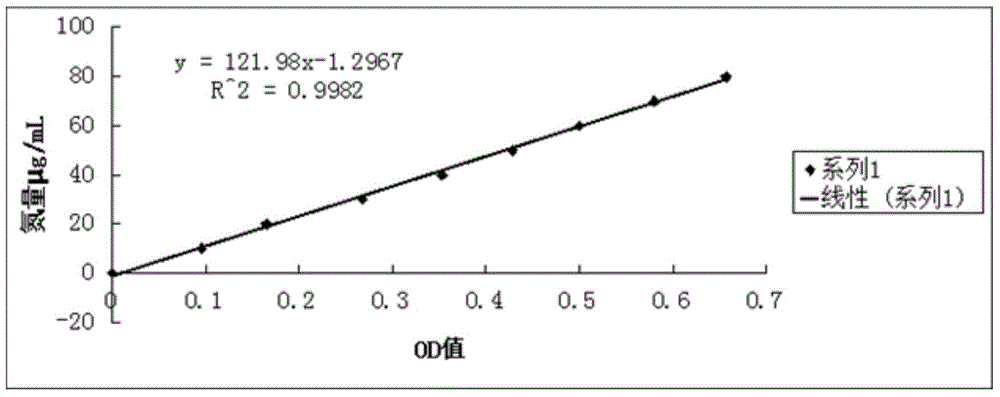
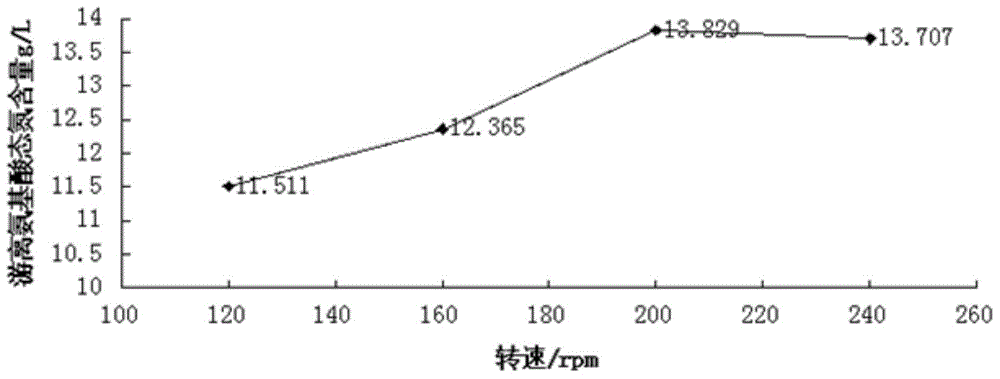
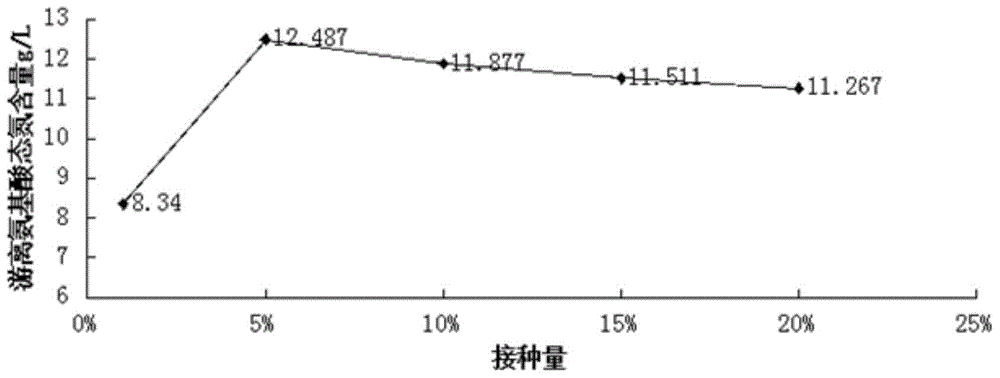
Method for fermenting aquatic product leftovers by mixed culture bacteria
A technology of aquatic product leftovers and mixed strains, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of single strains and limitations, and achieve the effects of stable quality, increased added value, and good market development prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1. Prepare culture medium
[0034] Strain Activation Medium: Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium, Qingdao Hi-Tech Industrial Park Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0035] Seed medium: Potato liquid medium (peel and chop 200g potatoes, boil them to obtain potato juice, add 20g glucose or sucrose, add water to 1000mL).
[0036] Fermentation medium: 10% (w / v) minced low-value aquatic products, 90% distilled water.
[0037] 2 Experimental methods
[0038] 2.1 Culture method
[0039] Plate activation culture: culture at 28°C for 3 days.
[0040] Seed culture: put 50mL of seed medium into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, use an inoculation loop to take one ring each of the strain a acidovorans, b pseudomonas, c aspergillus niger, and strain d yeast, and insert them into the sterilized The seed medium was sealed with a parafilm, and cultured on a shaker at 28°C and 120 rpm until the logarithmic phase of the strain was taken out.
[0041] Fermentation culture: put 50 mL of fermentati...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The difference from Example 1 is that the seed culture step: put 50 mL of seed medium in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, use an inoculation loop to take one ring each of strain a and strain b, two rings each of strain c and strain d, and insert The sterilized seed medium was sealed with a parafilm, and cultured on a shaker at 30° C. and 203 rpm until the logarithmic phase of the strain was taken out; the seed medium was potato liquid medium.
[0098] Strain a: Candida tropicalis,
[0099] Strain b: Cryptococcus laurentii,
[0100] Strain c: Bacillus subtilis,
[0101] Strain d: Bacillus cereus.
Embodiment 3
[0103] The difference from Example 1 is that the seed culture step: 50 mL of seed culture medium is loaded into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, one ring of strain a, one ring of bacterial strain b and one ring of bacterial strain c, and two rings of bacterial strain d are taken with an inoculation loop, and the sterile The seed culture medium of the bacteria was sealed with a parafilm, and cultured on a shaker at 30° C. and 203 rpm until the logarithmic phase of the bacteria was taken out; the seed culture medium was potato liquid culture medium.
[0104] Strain a: Candida tropicalis,
[0105] Strain b: Cryptococcus laurentii,
[0106] Strain c: Bacillus subtilis,
[0107] Strain d: Bacillus cereus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com