A kind of method for preparing hydrolyzed sugar from lignocellulose raw material
A technology of lignocellulose and hydrolyzed sugar, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the effect of cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation, low concentration of hydrolyzed sugar, and affecting energy consumption of ethanol rectification, so as to omit the process of detoxification and concentration , high sugar concentration, and the effect of reducing the production of inhibitors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
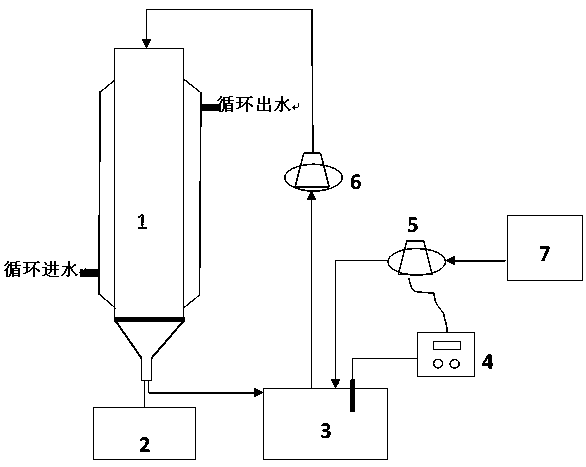
[0033] Using the present invention figure 1 In the process flow shown, the effective volume of the column reactor is 5 L. The lignocellulose raw material is corn stalks with a particle size of 0.15mm. 5 kg of corn stalk particles were packed into the column reactor and compacted, and the pressure of the hydraulic piston was 0.4 MPa. A dilute acid eluent was prepared to elute the lignocellulosic raw material. The dilute acid eluent included 2.5wt% dilute sulfuric acid, 0.5wt% NaCl, 0.01wt% SDS and 0.2wt% ammonium oxalate. The liquid-solid mass ratio is 3.5:1, the liquid phase residence time is 1 h, the elution time is 3.5 h, no circulation, and the eluent is collected into the waste liquid tank. After elution, extrusion dehydration can be carried out, so that the moisture content of corn stalks is 40%, and a part of inhibitors can be squeezed out from the other side. Prepare 6.67 L of 2.5wt% dilute sulfuric acid, start the temperature control device, control the temperature ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Using the same conditions as in Example 1, the difference is that: the dilute acid eluent includes a concentration of 0.5wt% dilute sulfuric acid, 1.0wt% NaCl, 0.05wt% SDS and 0.6wt% ammonium oxalate, washing The removal time is 4.0 h; the second difference is that the temperature of dilute acid hydrolysis is 75°C. After dilute acid hydrolysis, the concentration of glucose in the collector was determined to be 0.47wt%, and the concentration of xylose was 10.4wt%. The yield of xylose in the dilute acid hydrolysis stage was 93.1%, and the yield of glucose was 0.03%. The third difference is: set the pH in the collector to 5.5, and the temperature to 55°C. After enzymolysis, the glucose concentration in the collector was measured to be 18.9wt%, and the xylose concentration was 10.9wt%. The xylose yield was 95.8% and the glucose yield was 92.1% after dilute acid hydrolysis and cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis. The concentrations of inhibitors total phenol, acetic acid, furfu...
Embodiment 3
[0037] The same conditions as in Example 1 were used, except that the dilute acid eluent included 2.0wt% dilute sulfuric acid and 0.5wt% ammonium oxalate, and the elution time was 4.5h. After dilute acid hydrolysis, the concentration of glucose in the collector was determined to be 0.51wt%, and the concentration of xylose was 10.1wt%. The yield of xylose in the dilute acid hydrolysis stage was 92.4%, and the yield of glucose was 0.03%. After enzymolysis, the glucose concentration in the collector was measured to be 19.1wt%, and the xylose concentration was 10.1wt%. The xylose yield was 94.8% and the glucose yield was 92.1% after dilute acid hydrolysis and cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis. The concentrations of inhibitors total phenol, acetic acid, furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural in the hydrolyzate were 0.04 g / L, 3.3 g / L, 0.81 g / L and 0.7 g / L, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com