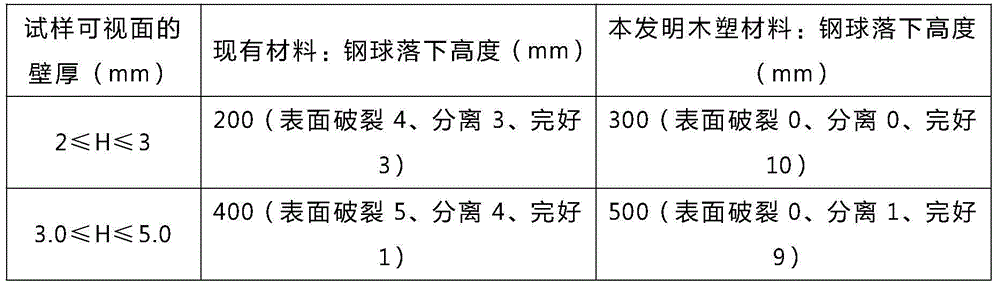
Wood-plastic material for manufacturing furniture board and preparation method thereof
A technology for wood-plastic materials and furniture boards, applied in the field of wood-plastic materials and their processing, can solve the problems that the comprehensive performance cannot meet the standards, the physical performance indicators do not meet the national standards, and cannot be directly applied to outdoor doors and windows, etc. The effect of improving overall performance and reducing the rate of dimensional change
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] The weight composition of wood-plastic material component described in this example is as follows:
[0017] 52% PVC; 10% plant fiber; 3.0% processing aid MBS;
[0018] 0.5% zinc stearate; 0.5% calcium stearate; 1.0% dibasic lead phosphite;
[0019] 1.0% paraffin; 1.0% stearic acid; 4% dimethyl ester copolymer ACR401;
[0020] 15% chlorinated polyethylene CPE 135A; 1% talc; 1% chitin;
[0021] 3.0% chitosan; 13% ground calcium carbonate.
[0022] The wood-plastic material preparation method of the above-mentioned components is as follows:
[0023] Turn on the mixer (model: JW-500X1000), the main engine runs at a low speed of 300rpm; add plant fiber, resin, light calcium carbonate, talcum powder from the discharge port and stir, continue to stir, the stirring speed is 800rpm, heat to temperature rise to 80°C,
[0024] Then add the rest of the ingredients, and when the mixing temperature of the material reaches 115 degrees, the high-speed operation is changed to the l...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The weight composition of wood-plastic material component described in this example is as follows:
[0027] 60% PP; 15% plant fiber; 2.0% processing aid MBS;
[0028] 0.3% zinc stearate; 0.3% calcium stearate; 0.6% dibasic lead phosphite;
[0029] 0.5% paraffin; 0.5% stearic acid; 2% dimethyl ester copolymer ACR401;
[0030] 10% CPE chlorinated polyethylene 135A; 1% talc; 1% chitin;
[0031] 1.8% chitosan; 5% ground calcium carbonate.
[0032] The wood-plastic material preparation method of the above-mentioned components is as follows:
[0033] Turn on the mixer (model: JW-500X1000), in the state of stirring at a speed of 200rpm, add plant fiber, resin, light calcium carbonate, talcum powder from the discharge port and stir, continue stirring, the stirring speed is 1100rpm, Heating until the temperature rises to 80°C;
[0034] Add the remaining components, cover the discharge port, continue to stir, the stirring speed is 800rpm, and continue to heat until the mater...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The weight composition of wood-plastic material component described in this example is as follows:
[0037] 75% PE; 9% plant fiber; 1.0% processing aid MBS;
[0038] 0.1% zinc stearate; 0.1% calcium stearate; 0.2% dibasic lead phosphite;
[0039] 0.2% paraffin; 0.2% stearic acid; 1% dimethyl ester copolymer ACR401;
[0040] 4% chlorinated polyethylene CPE 135A; 0.5% talc; 1% chitin;
[0041] 1.0% chitosan; 6.7% ground calcium carbonate.
[0042] The wood-plastic material preparation method of the above-mentioned components is as follows:
[0043] Turn on the mixer (model: JW-500X1000), in the state of stirring at a speed of 500rpm, add plant fiber, resin, light calcium carbonate, talcum powder from the discharge port and stir, continue stirring, the stirring speed is 1100rpm, Heating until the temperature rises to 80°C;
[0044] Add the remaining components, cover the discharge port, continue to stir, the stirring speed is 900rpm, and continue to heat until the mi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Areal density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com