A bioactive hard tissue engineering scaffold material and preparation method thereof
A bioactive scaffold material technology, applied in the field of hard tissue engineering scaffold materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of not being able to repair bone defects in weight-bearing parts, destroying the natural three-dimensional structure, and being expensive, and achieving good biocompatibility and degradation Sexuality, good application prospects, and high biological safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
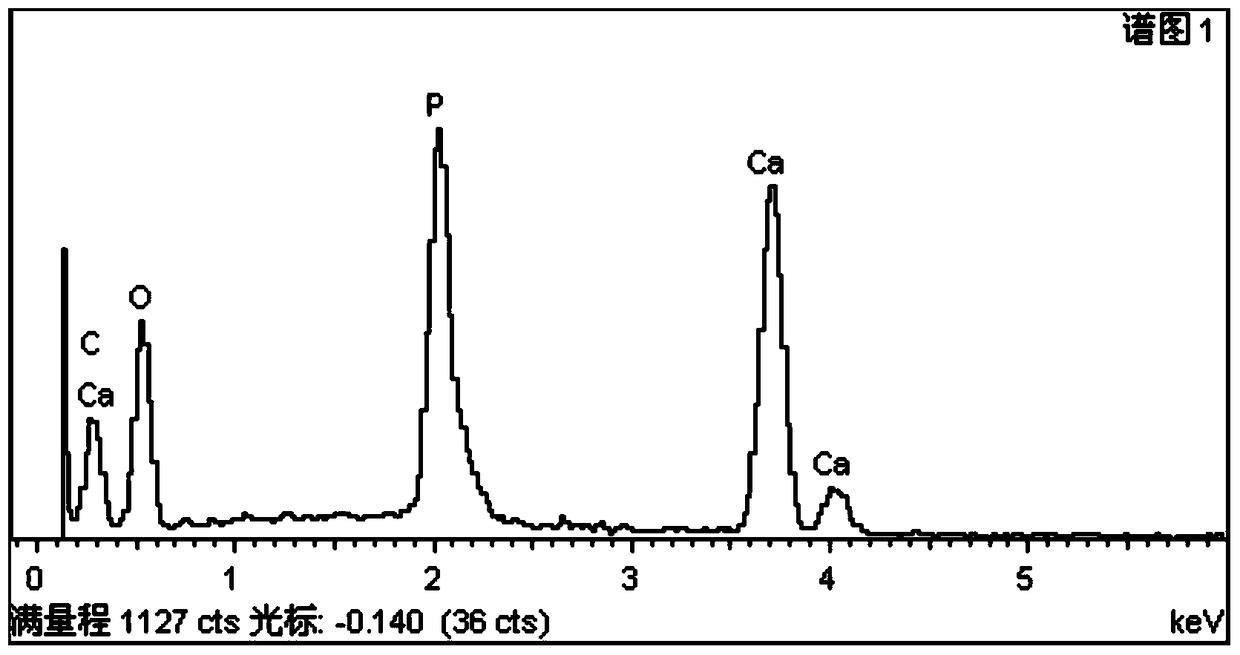
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The preparation of embodiment 1 support material
[0037] Preparation of porcine small intestinal submucosa: the fresh porcine small intestinal submucosa was disinfected with peracetic acid or alcohol, after disinfection, the porcine small intestinal submucosa was sequentially immersed in sodium hydroxide and EDTA, and then washed repeatedly with deionized water to obtain the ECM material.
[0038] Soak the prepared ECM material in Tris buffer solution with pH = 8.8, put it in a shaker at 37°C to make it fully swell for 12 hours, take it out and rinse it with deionized water for 3 times, each time for 10 minutes; then dry it with filter paper The surface moisture was quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen for 2 hours, and vacuum freeze-dried at -80°C for 8 hours to obtain a fully expanded collagen scaffold. The collagen scaffold: a) Soak in 25ml 0.2M CaCl 2 solution, and shake it at a speed of 120 rpm in a shaker at 20°C for 1 hour, take it out and wash it with deionized wa...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The preparation of embodiment 2 support material
[0041] Preparation of bovine pericardium matrix: fresh bovine pericardium was sterilized with peracetic acid or alcohol, after disinfection, the bovine pericardium was immersed in sodium hydroxide and EDTA in sequence, and then washed with deionized water repeatedly. Get the ECM material.
[0042] Soak the prepared ECM material in Tris buffer solution with pH=8.8 (preparation method is to add 121.1g Tris to 800ml purified water, add concentrated HCL to adjust the pH value to 8.8, continue to add water to 1 liter), shake at 37°C Let it fully swell in the bed for 24 hours, take it out and wash it with deionized water for 3 times, 10 minutes each time; then dry the surface moisture with filter paper, put it into liquid nitrogen and freeze it for 2 hours, and vacuum freeze-dry it at -80°C for 8 hours , to obtain fully expanded collagen scaffolds. The collagen scaffold: a) soaked in 25ml 0.1M CaCl 2 solution, and shake it...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The preparation of embodiment 3 support material
[0044] Preparation of bovine leather matrix: fresh bovine leather is sterilized with peracetic acid or alcohol, after disinfection, the bovine leather is immersed in petroleum ether and sodium hydroxide in sequence, and then washed with deionized water repeatedly. Get the ECM material.
[0045] Soak the prepared ECM material in PBS buffer solution with pH = 8.8, place it in a shaker at 37°C to fully swell for 36 hours, take it out and wash it with normal saline 10 times, 10 minutes each time; then dry the surface moisture with filter paper , placed in -40°C for rapid freezing for 12 hours, and vacuum freeze-dried at -80°C for 8 hours to obtain fully expanded collagen scaffolds. The collagen scaffold: a) Soak in 25ml 0.3M CaCl 2 solution, and shake it at a speed of 120 rpm for 4 hours in a shaker at 25°C, take it out and wash it with normal saline for 5 times, each time for 5 minutes; b) soak it in 25ml of 0.5M (NH 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com