A method for preparing polyamines by direct ammoniation of polyhydroxy compounds
A technology of polyhydroxy compounds and polyamines, applied in the preparation of amino hydroxyl compounds, amino compounds, organic compounds, etc., can solve the problems of high pressure, high cost of raw materials, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve good selectivity and reactivity high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Catalyst A Preparation
[0020] Add 800mL of ethylene glycol, 10g of copper acetate, 50g of powdered ZSM-5 molecular sieve and 50g of deionized water into a 1500mL round-bottomed flask, mechanically stir evenly and raise the temperature to 90°C until the copper acetate is completely dissolved. Add 150mL of NaOH aqueous solution with a mass concentration of 10% to the solution at a high speed. After dripping the lye, stir for 2 hours and slowly heat up to evaporate the water in the system. After cooling down to room temperature, the solid precipitate was filtered out with suction, and washed thoroughly with deionized water, methanol, and acetone to obtain catalyst A for the reaction.
[0021] Amination reaction
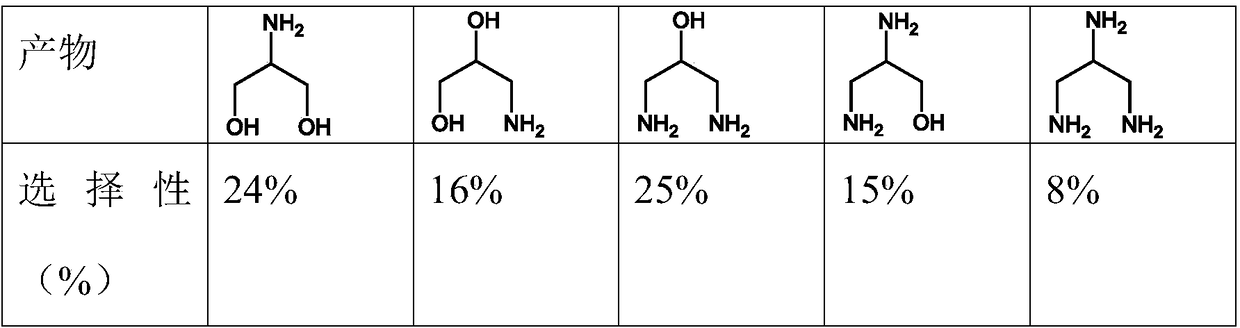
[0022] Add 30g of 1,4-butanediol and 4g of the above-mentioned catalyst A into a 100mL autoclave, replace it with nitrogen and raise the temperature to 250°C, pressurize ammonia gas at a pressure of 6Mpa into the autoclave, and continue to pressurize hydrogen g...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Catalyst B Preparation
[0025] Add 800mL of ethylene glycol, 10g of nickel acetate, 50g of powdered ZSM-5 molecular sieve and 50g of deionized water into a 1500mL round-bottomed flask, mechanically stir evenly and raise the temperature to 90°C until the copper acetate is completely dissolved. Drop 150mL of 10% NaOH aqueous solution into the solution at a high speed. After dropping the lye, stir for 2 hours and slowly raise the temperature to evaporate the water in the system. At room temperature, the solid precipitate was filtered out with suction, and washed thoroughly with deionized water, methanol, and acetone to obtain catalyst B for the reaction.
[0026] Amination reaction
[0027] Add 30g of 1,4-butanediol and 4g of the above-mentioned catalyst B into a 100mL autoclave, replace it with nitrogen and raise the temperature to 250°C, pressurize ammonia gas with a pressure of 6Mpa into the autoclave, and continue to pressurize hydrogen gas with a pressure of 8Mpa ,...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Catalyst C Preparation
[0030] Add 800mL of ethylene glycol, 5g of copper acetate, 5g of nickel acetate, 50g of powdered ZSM-5 molecular sieve and 50g of deionized water into a 1500mL round bottom flask, mechanically stir evenly and heat up to 90°C until the copper acetate is completely dissolved. Drop 150mL of 10% NaOH aqueous solution into the solution at a rate of 1mL / min. After dropping the lye, stir for 2 hours and slowly raise the temperature to evaporate the water in the system. When the temperature of the system rises to 180°C, reflux the ethylene glycol for 8 hours , when it was lowered to room temperature, the solid precipitate was filtered out by suction, and then washed thoroughly with deionized water, methanol and acetone to obtain catalyst C for the reaction.
[0031] Amination reaction
[0032] Add 30g of 1,4-butanediol and 4g of the above-mentioned catalyst C into a 100mL autoclave, replace it with nitrogen and program the temperature to 250°C, pressur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com