Sample preparation method and detection method for water-soluble heavy metal elements in solid waste
A detection method and solid waste technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of high technical requirements, high reagent consumption, and long cycle of using cost inspection conditions, and achieve low requirements for analytical equipment performance and experimental conditions, and the lower limit of quantitative determination The effect of low cost and low measurement cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] The preparation method of the water-soluble heavy metal element sample in the solid waste of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0025] a. Add water-soluble heavy metal element extractant pure water to the solid waste to be tested; according to the solid-liquid ratio, the solid waste to be tested: pure water=1:2~2.5g / mL;
[0026] b. Add a neutral oxidizing atmosphere protective agent, and continuously oscillate and extract on an oscillator for 4-6 hours;
[0027] c, filter, take the filtrate, remove the insoluble solids in the solution, add an oxidizing strong acid solution to the filtrate, supplement and add a neutral oxidizing atmosphere protective agent, to obtain a mixed solution;
[0028] d. Put the mixed solution on a low-temperature electric heating plate or a hot water bath, let it evaporate and concentrate in a sub-boiling state, cool to room temperature, dilute it with water, and set the volume in a small-volume container to obtain water-sol...
Embodiment 1
[0054] 1. Preparation of sample solution for titanium chloride extraction tailings
[0055] Weigh 50g of titanium chloride extraction tailings sample (Sample No. 1) into a conical flask, add 100g (or mL) of water and 5mL of hydrogen peroxide, place on a shaker and continuously vibrate for extraction for 4 hours; filter and discard the solution Medium-insoluble solid, the filtrate is collected in a wide-mouth container, add 5mL concentrated nitric acid and 3mL hydrogen peroxide respectively, place it in a hot water bath and keep it in a sub-boiling heating state at 80°C, continue to evaporate and concentrate the solution to about 3mL, and cool to room temperature Afterwards, dilute with water to a constant volume in a 5mL colorimetric tube and mix well.
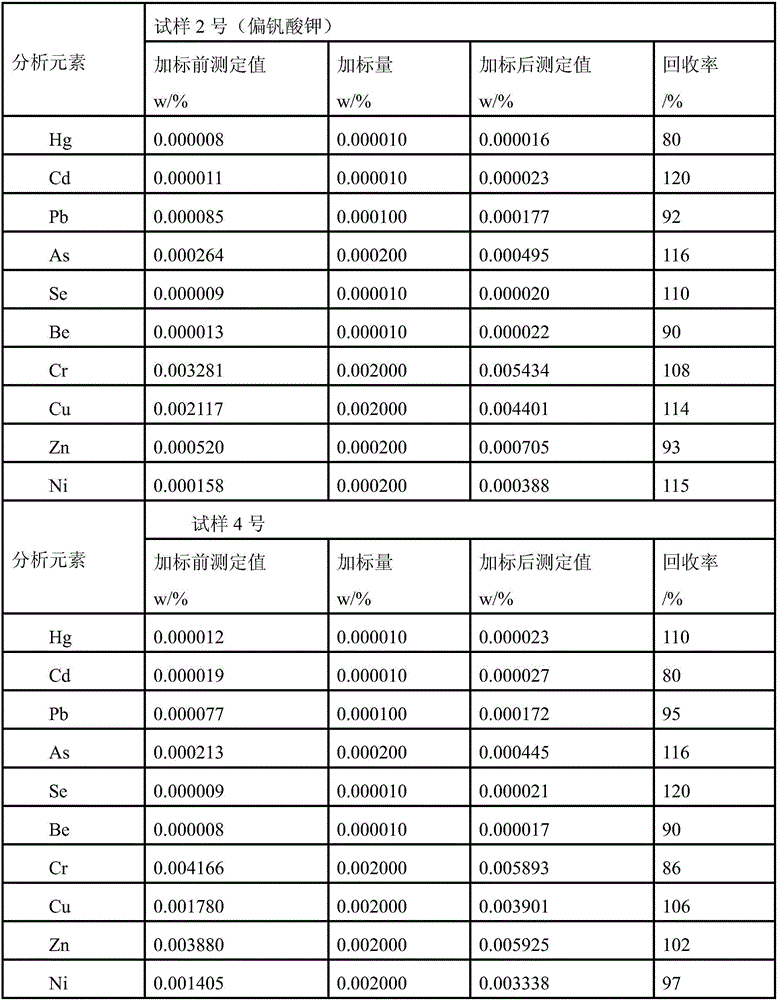
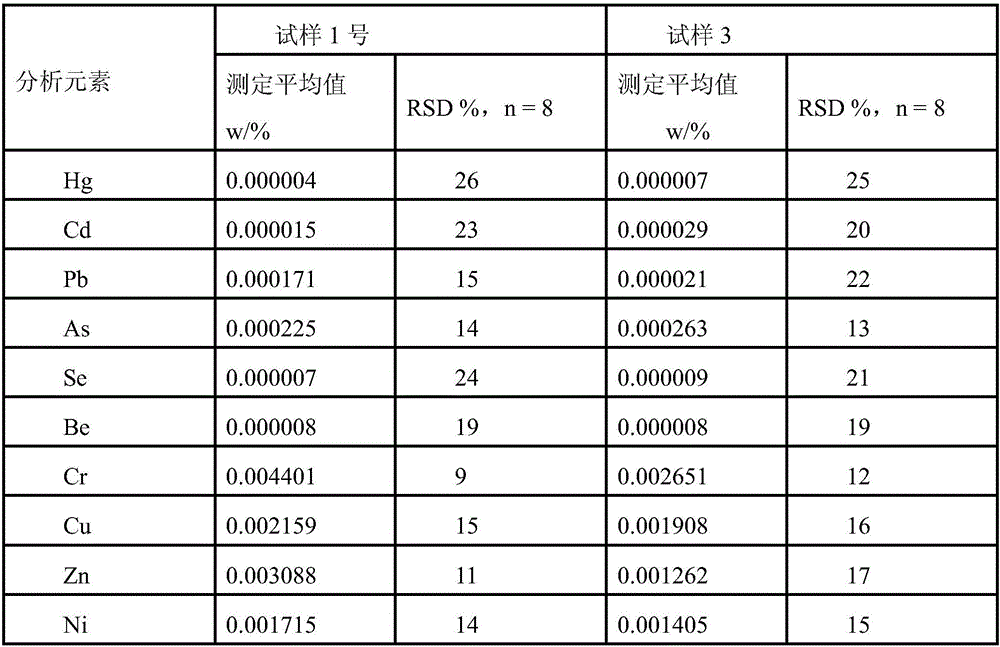
[0056] 2. Use ICP-OES to determine the content of heavy metal elements in the sample solution of titanium chloride extraction tailings
[0057] Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) as a dete...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Weigh 100g of titanium chloride extraction tailings sample (Sample No. 2), add 250g (or mL) of water and 10mL of hydrogen peroxide, shake and extract for 6 hours; add 10mL of concentrated nitric acid and 6mL of hydrogen peroxide to the filtrate collected by filtration , sub-boiling evaporation to concentrate the solution to about 5mL, after cooling, dilute with water to volume and mix in a 10mL colorimetric tube.
[0062] In addition, the sample solution of the titanium chloride extraction tailings was prepared according to the same method as that of Example 1, and the content of heavy metal elements contained in the solution was determined by ICP-OES.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com