Decellularized matrix-source tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of tissue engineering scaffold and acellular matrix, which is applied in the field of tissue engineering scaffold derived from acellular matrix and its preparation, can solve the problems of poor mechanical strength, single structure, poor biocompatibility, etc., and achieve good mechanical properties, good Effects of biocompatibility and low immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
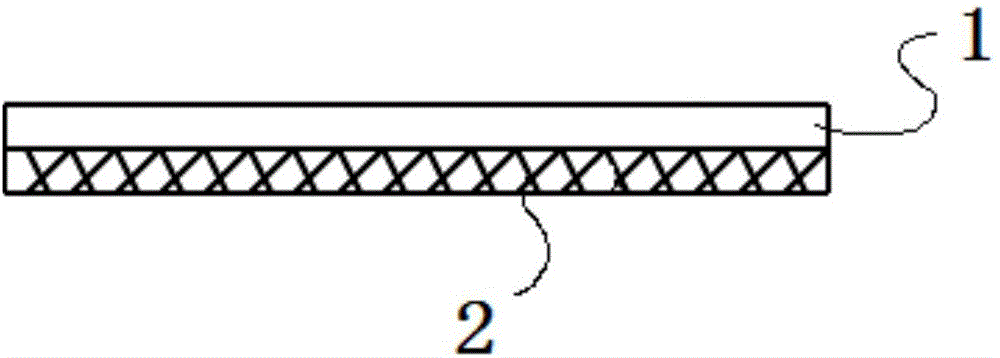
[0060] An acellular matrix-derived tissue engineering scaffold, such as figure 1 As shown, the biofilm substrate 1 obtained after pretreatment, degreasing, decellularization, cross-linking and fixing, removing antigens and other steps of the animal film material is adhered to the surface of the biofilm substrate 1 by animal tendon tissue Collagen loose layer 2 obtained by drying collagen obtained through pretreatment, degreasing, decellularization, cross-linking fixation, antigen removal, and collagen extraction and purification. Wherein, the biofilm substrate 1 has a rough surface and a smooth surface, and the loose collagen layer adheres to the rough surface.
Embodiment 2
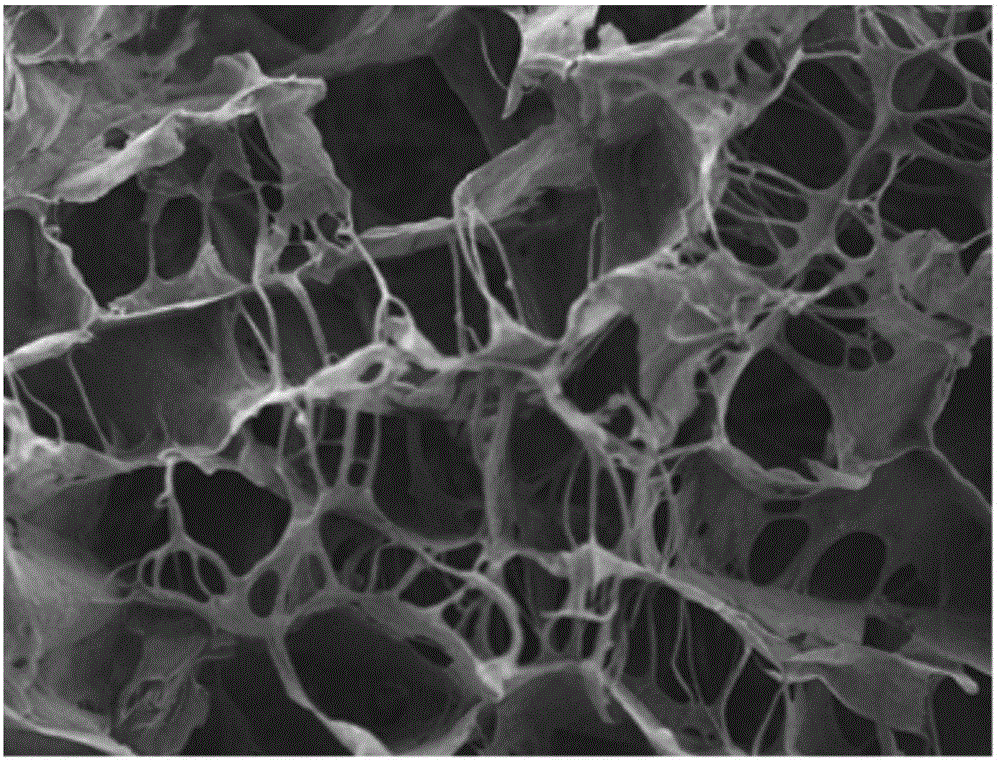
[0062] A cartilage scaffold derived from an acellular matrix, a biofilm substrate 1 obtained after pretreatment, degreasing, decellularization, cross-linking and fixing, and removing antigens from an animal membrane material, on the surface of the biofilm substrate 1 The surface is adhered to the collagen loose layer 2 obtained by drying the collagen obtained from the animal tendon tissue through the steps of pretreatment, degreasing, decellularization, cross-linking and fixing, removing antigens, and collagen extraction and purification. Wherein the collagen loose layer has pores, the porosity is 65-86%, and the pore diameter is 50-500 μm. The collagen loose layer is fixed on the rough surface of the biofilm substrate through physical adsorption. Alternatively, the loose layer of collagen is bonded and fixed on the rough surface of the biofilm substrate through bioprotein glue. Preferably, the thickness of the loose collagen layer is 0.1-2.9 mm. The cartilage scaffold mater...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The preparation method of a kind of acellular matrix source tissue engineering scaffold of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0065] (1) Pretreatment: Take fresh animal pericardium and tendon tissues of equal quality, wash them, soak them in a broad-spectrum high-efficiency disinfectant solution of bromogeramine for 15 hours, and remove adipose tissue, fibers and villi;
[0066] (2) Degreasing: use acetone solution with a mass concentration of 3.0% to extract animal pericardium and tendon tissue to remove fat and fat-soluble impurities. The extraction time is 24 hours. The quality of acetone solution and animal pericardium and tendon tissue The ratio is 10:1;
[0067] (3) Decellularization: using Triton-100 with a mass concentration of 0.1% in combination with pepsin at a mass concentration of 0.1% (the stated concentration is the final concentration), ultrasonic digestion of animal pericardium and Tendon tissue for 48 hours to completely remove cel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com