Chitosan non-woven fabric and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of chitosan and non-woven fabrics, applied in non-woven fabrics, textiles, papermaking, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of pure chitosan electrospinning difficulties, achieve good structural stability, expand the scope of application, The effect of improving spinnability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
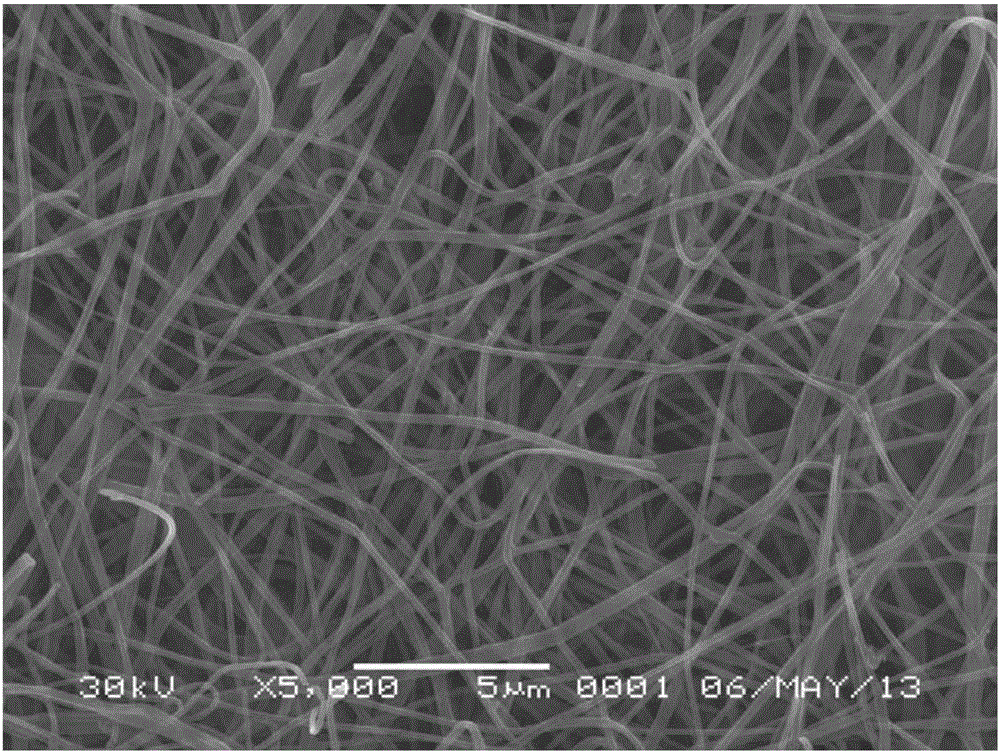
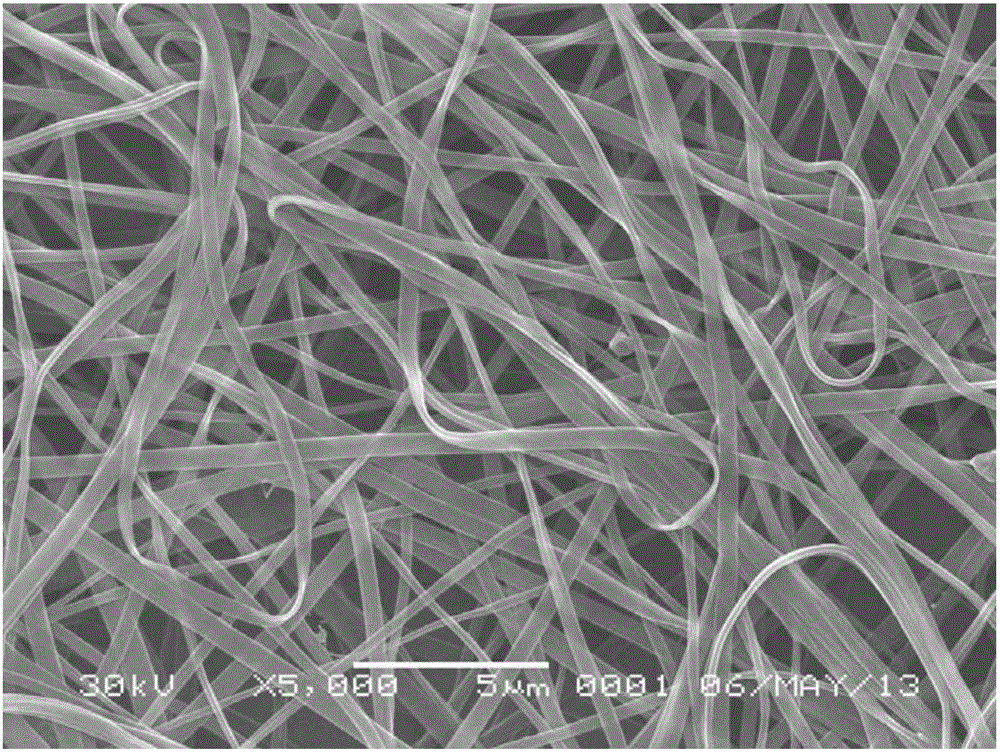
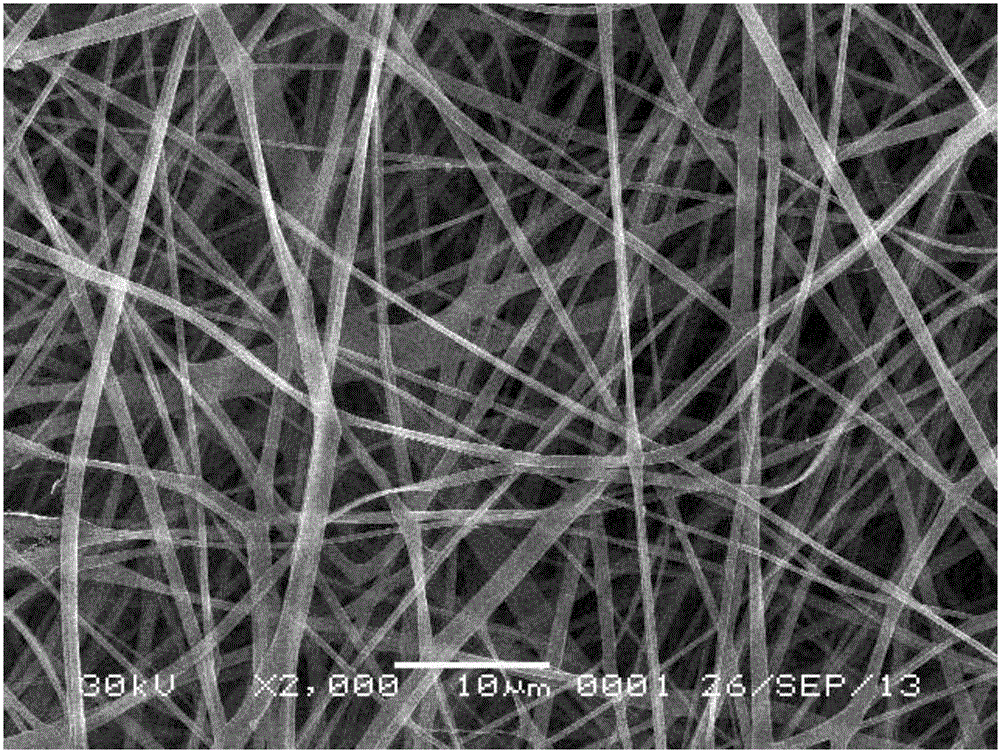
[0031] Take 0.35 g of chitosan with a molecular weight of 200,000, and 0.35 g of polymethacrylic acid with a molecular weight of 80,000, dissolve them in 7.0 g of 65 wt.% acetic acid aqueous solution at 60°C, and then add 1.0 g of N,N-Di Methylformamide solvent, after stirring and dissolving, then add 0.035g salicylic acid to dissolve, stir and dissolve, inject the spinning solution into a 20mL syringe with an inner diameter of 1.2mm flat needle, fix the syringe on the micro-injection pump, A metal receiving screen was placed at a distance of 15 cm from the needle; the needle was connected to a 25 kV high-voltage DC power supply, and a flow rate of 2.0 mL / h was set for electrospinning. After 20 h, the receiving screen collected chitosan ultrafine particles with a diameter of about 187 nm. The fine fibers were then treated in an oven at 180 °C for 2 h to obtain chitosan nonwoven fabrics.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Take 0.35g of chitosan with molecular weight of 200,000, 0.35g of 20,000 polymethacrylic acid, dissolve in 7.0g, 65 wt.% aqueous acetic acid solution at 60°C, then add 1.0g of dimethyl sulfoxide, stir After dissolving, add 0.035 g of salicylic acid to dissolve, and stir to dissolve. Inject the spinning solution into a 20 mL syringe with a flat needle with an inner diameter of 1.2 mm, fix the syringe on a microsyringe pump, and place a metal receiving screen 15 cm away from the needle. Connect the needle to a 25 kV high-voltage DC power supply, set a flow rate of 2.0 mL / h for electrospinning, and collect chitosan microfibers with a diameter of about 457 nm on the receiving screen after 20 h; then place them in an oven at 160 °C After treatment for 2 h, chitosan non-woven fabrics were obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Embodiment 3, the influence of different cross-linking time on sustained-release performance.
[0035] The preparation method is the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the crosslinking time is changed, and crosslinking is carried out at 180° C. for 1, 2, and 6 hours to study its influence on the salicylic acid slow-release performance of the chitosan nonwoven fabric. The test results are as follows: Figure 5 shown. The sustained-release performance experiment is as follows: 20 mg chitosan non-woven fabric was placed in 100 mL PBS solution (pH=7.4), oscillated at a constant temperature of 20 ° C, and the absorption peak of the solution at a wavelength of 295 nm was detected by ultraviolet spectroscopy (salicylic acid UV characteristic absorption peak) changes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com